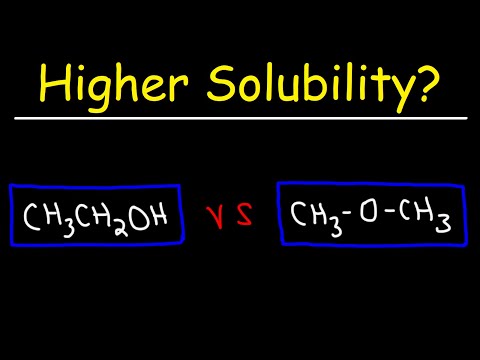
Q. Are alkanes soluble in ether?
Alkanes (both alkanes and cycloalkanes) are virtually insoluble in water, but dissolve in organic solvents. However, liquid alkanes are good solvents for many other non-ionic organic compounds.
Q. Why are ethers more soluble in water than alkanes?
Solubility of Alcohols and Ethers in Water are more soluble in water than alkanes because the oxygen atom can hydrogen bond with water. with 1-4 C atoms are soluble, but not with 5 or more C atoms.
Table of Contents
- Q. Are alkanes soluble in ether?
- Q. Why are ethers more soluble in water than alkanes?
- Q. Why do alkanes dissolve in organic solvents?
- Q. What is the reason for the solubility of alkanes in water?
- Q. Are all alkanes soluble in water?
- Q. Why are lower ethers soluble in water?
- Q. Is water soluble in chloroform?
- Q. Is chloroform heavier than water?
- Q. Is chloroform used in anesthesia?
- Q. What type of ether is used in anesthesia?
- Q. Is ether safer than chloroform?
- Q. Is ether still used?
- Q. How quickly does Ether work?
- Q. Who is ether in the Bible?
- Q. What is ether come from?
- Q. What does Ether mean spiritually?
- Q. What is ether in the 5 elements?
- Q. What chakra is ether?
- Q. How are 5 elements controlled in the body?
- Q. What is another word for ether?
- Q. Is space a natural element?
- Q. Why are alkanes and alkenes insoluble in water?
- Q. Are ethers soluble in water?
- Q. Are alkanes flammable?
- Q. Do all alkanes burn?
- Q. What are the most flammable alkanes?
- Q. What are the first 4 alkanes?
- Q. Are alkanes toxic?
- Q. Why are alkanes toxic?
- Q. Are alkenes dangerous?
- Q. Why are hydrocarbons bad for humans?
- Q. What is the most toxic hydrocarbon?
- Q. Are hydrocarbons toxic to inhale?
- Q. How do hydrocarbons affect the human body?
- Q. What is the world’s deadliest poison?
- Q. How can we prevent hydrocarbons?
- Q. Are hydrocarbons found in the human body?
- Q. What is the function of a hydrocarbon?
- Q. What is the simplest hydrocarbon?
- Q. Which hydrocarbon is most flammable?
- Q. What are 5 common hydrocarbons?
- Q. Where is the fractionating column the hottest coldest?
- Q. What are the main sources of hydrocarbons?
Q. Why do alkanes dissolve in organic solvents?
Solubility. Alkanes (both normal and cycloalkanes) are virtually insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents. In the case of the alkanes, these are the Van der Waals dispersion forces. breaking of the intermolecular forces in the water so that the substance can fit between the water molecules.
Q. What is the reason for the solubility of alkanes in water?
Alkanes are not soluble in water, which is highly polar. The two substances do not meet the criterion of solubility, namely, that “like dissolves like.” Water molecules are too strongly attracted to one another by hydrogen bonds to allow nonpolar alkanes to slip between them and dissolve.
Q. Are all alkanes soluble in water?
No alkanes are not soluble in water. Water is a polar solvent and has hydrogen bonding. For any compound to be soluble in water , it should be polar or have hydrogen bonding in it.
Q. Why are lower ethers soluble in water?
Answer: Water is polar in nature while Ether is non-polar. Ethers are very slightly soluble in water at around 6.8g/100g. This is due to the presence of oxygen in ethers which interact with hydrogen in water to produce H-bonding to make it slightly soluble.
Q. Is water soluble in chloroform?
Chloroform
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Solubility in water | 10.62 g/L (0 °C) 8.09 g/L (20 °C) 7.32 g/L (60 °C) |
| Solubility | Soluble in benzene Miscible in diethyl ether, oils, ligroin, alcohol, CCl4, CS2 |
| Solubility in acetone | ≥ 100 g/L (19 °C) |
| Solubility in dimethyl sulfoxide | ≥ 100 g/L (19 °C) |
Q. Is chloroform heavier than water?
chloroform (CHCl3), also called trichloromethane, nonflammable, clear, colourless liquid that is denser than water and has a pleasant etherlike odour.
Q. Is chloroform used in anesthesia?
Chloroform and halothane are potent anaesthetic agents which are also chemically related. Halothane was introduced into clinical anaesthesia in 1956 at a time when anaesthesia had been fully developed. Chloroform was first used in 1847 by James Young Simpson when anaesthesia was in its infancy.
Q. What type of ether is used in anesthesia?
1 Diethyl ether. Diethyl ether (Figure 1) is a potent anesthetic whose actions are accompanied by analgesic and muscle relaxant activity. It has a long induction period and is highly flammable and explosive.
Q. Is ether safer than chloroform?
Ether has a high incidence of PONV. Chloroform (trichloromethane) is a sweet smelling volatile anesthetics that can be used for inhalational induction. While initially developed as an alternative to ether, chloroform was abandoned due to its association with hepatotoxicity and fatal cardiac arrhythmias.
Q. Is ether still used?
Usage of ether and chloroform later declined after the development of safer, more effective inhalation anesthetics, and they are no longer used in surgery today.
Q. How quickly does Ether work?
In concentrations of 3–5% in air, an anesthetic effect can slowly be achieved in 15–20 minutes of breathing approximately 15–20 ml of ether, depending on body weight and physical condition.
Q. Who is ether in the Bible?
Ether consists of fifteen chapters. The title refers to Ether, a Jaredite prophet who lived at the end of the time period covered by the book, believed to be circa 2600 or 2100 BC through 600 BC or later, at least 1500 but possibly as long as 2500 years.
Q. What is ether come from?
Chemistry, Pharmacology. a colorless, highly volatile, flammable liquid, C4H10O, having an aromatic odor and sweet, burning taste, derived from ethyl alcohol by the action of sulfuric acid: used as a solvent and, formerly, as an inhalant anesthetic.
Q. What does Ether mean spiritually?
Ether Element (Akasa) Ether is the synergy of all the elements. Ether is space, stillness, that which contains and holds. Ether is the element that connect us to spirit, intuition, other realms and planes.
Q. What is ether in the 5 elements?
The element ether, called “akasha” in Sanskrit is the first of the five great elements (pancha mahabhutus). It comes first because it is the most subtle of the elements. Often referred to as “space,” it is the essence of emptiness. It is the space the other elements fill.
Q. What chakra is ether?
throat
Q. How are 5 elements controlled in the body?
The controls for the various elements in our body lie at the fingertips — the little, ring, middle and index fingers representing earth, water, ether and air respectively while the thumb represents fire.
Q. What is another word for ether?
What is another word for ether?
| diethyl ether | ethoxyethane |
|---|---|
| ethyl ether | ethyl oxide |
Q. Is space a natural element?
Everything in nature is made up of five basic elements: earth, water, fire, air, and space.
Q. Why are alkanes and alkenes insoluble in water?
Alkenes are lighter than water and are insoluble in water due to their non-polar characteristics. Alkenes are only soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Q. Are ethers soluble in water?
Ethers can form hydrogen bonds to water, since the oxygen atom is attracted to the partially-positive hydrogens in water molecules, making them more soluble in water than alkanes.
Q. Are alkanes flammable?
Alkanes: Physical Properties In general, alkanes show a relatively low reactivity. Lower alkanes in particular are highly flammable and form explosive mixtures (methane, benzene) with air (oxygen). Solubility of alkanes in water is very low.
Q. Do all alkanes burn?
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with central carbon atom attached to four other atoms (or groups). However, these alkanes burn very rapidly. The combination of alkanes with oxygen generating heat is known as combustion.
Q. What are the most flammable alkanes?
Methane through Butane are very flammable gases at standard temperature and pressure (STP). Pentane is an extremely flammable liquid boiling at 36 °C and boiling points and melting points steadily increase from there; octadecane is the first alkane which is solid at room temperature.
Q. What are the first 4 alkanes?
The first four alkanes are methane, ethane, propane, and butane with the Lewis symbols shown below.
Q. Are alkanes toxic?
Cycloalkanes are more toxic than alkanes or branched alkanes [878]. In humans, high concentrations of inhaled alkanes can result in anesthetic effects or narcosis [878]. Alkanes are CNS depressants [855]. However, high molecular weight alkanes are considered virtually non toxic [878].
Q. Why are alkanes toxic?
Explanation: As the human body contains a large amount of water, and because hydrophobicity increases with chain length, higher alkanes are increasingly incompatible with water. Therefore when ingested they tend to preferentially be stored in the fat cells in our bodies.
Q. Are alkenes dangerous?
In addition to environmental intoxication, acrolein, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) and certain other type-2 alkene derivatives are highly toxic by-products of membrane lipid peroxidation associated with cellular oxidative stress.
Q. Why are hydrocarbons bad for humans?
Some hydrocarbons can cause other effects, including coma, seizures, irregular heart rhythms or damage to the kidneys or liver. Examples of products that contain dangerous hydrocarbons include some solvents used in paints and dry cleaning and household cleaning chemicals.
Q. What is the most toxic hydrocarbon?
Aromatic – contain a benzene ring (most toxic) and are used in solvents and glues but also in paint and paint remover. Aliphatic – petroleum distillates found in polishes, lamp oils, and lighter fluid.
Q. Are hydrocarbons toxic to inhale?
Serious toxicity and death can be associated with hydrocarbon exposure through inhalation, ingestion, or aspiration. Pulmonary toxicity is most common, however cardiovascular, nervous, and gastrointestinal systems can all be affected.
Q. How do hydrocarbons affect the human body?
Swallowing or inhaling hydrocarbons can cause lung irritation, with coughing, choking, shortness of breath, and neurologic problems. Sniffing or breathing fumes can cause irregular heartbeats, rapid heart rate, or sudden death, particularly after exertion or stress.
Q. What is the world’s deadliest poison?
Botulinum toxin Scientists differ about the relative toxicities of substances, but they seem to agree that botulinum toxin, produced by anaerobic bacteria, is the most toxic substance known. Its LD50 is tiny – at most 1 nanogram per kilogram can kill a human.
Q. How can we prevent hydrocarbons?
The remediation of hydrocarbon polluted wastewater can be achieved by three methods, which are phytoremediation, bioremediation and chemical remediation. Phytoremediation entails the use of plants to reduce the volume, mobility and toxicity of contaminants in soil and water.
Q. Are hydrocarbons found in the human body?
Aromatic Hydrocarbons are present in the nucleic acids of the human body such as the DNA and amino acids.
Q. What is the function of a hydrocarbon?
Hydrocarbons are the principal constituents of petroleum and natural gas. They serve as fuels and lubricants as well as raw materials for the production of plastics, fibres, rubbers, solvents, explosives, and industrial chemicals.
Q. What is the simplest hydrocarbon?
Methane
Q. Which hydrocarbon is most flammable?
The longest hydrocarbons have very high boiling points. They leave the column as a hot liquid called bitumen. Shorter hydrocarbon molecules have weaker intermolecular forces and lower boiling points. They are highly volatile and therefore extremely flammable.
Q. What are 5 common hydrocarbons?
Common hydrocarbons:
- Methane(CH4)
- Ethane(C2H6)
- Propane(C3H8)
- Butane(C4H10)
- Pentane(C5H12)
- Hexane(C6H14)
Q. Where is the fractionating column the hottest coldest?
Fractional distillation This uses a fractionating column that is hotter at the bottom, and cooler at the top. The different liquids are collected from different parts of the column. In the laboratory a glass fractionating column is used.
Q. What are the main sources of hydrocarbons?
A hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon found in crude oil, natural gas, and coal. Hydrocarbons are highly combustible and the main energy source of the world. Its uses consist of gasoline, jet fuel, propane, kerosene, and diesel, to name just a few.