Not all allergic reactions happen the same way. Some allergy symptoms occur immediately after exposure to an allergen, while others take hours or days to occur. Scientists think that the biological events leading up to immediate allergic reactions are different from those that result in delayed allergic reactions.
Q. What are the stages of an allergic reaction?
These antibodies travel to cells that release histamine and other chemical mediators, which cause allergy symptoms to occur. The human body carries out an allergic cascade in three stages: sensitization, “early-phase,” and “late-phase.”
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the stages of an allergic reaction?
- Q. What is considered a mild allergic reaction?
- Q. What is a Level 4 allergy?
- Q. What is a Class 1 allergy?
- Q. How can I lower my blood allergy levels?
- Q. What should I drink for an allergic reaction?
- Q. Is coffee good for allergy?
- Q. How long does it take for allergic reaction to clear up?
- Q. Is Benadryl good for an allergic reaction?
- Q. How long does a allergic reaction last?
- Q. Can you suddenly become allergic to something?
- Q. What does an allergic reaction look like on skin?
- Q. How long does an food allergic reaction last?
- Q. How do you flush allergens out of your system?
- Q. How long does an allergic reaction last from medication?
- Q. What should you eat when you have an allergic reaction?
- Q. Does drinking water help allergic reaction?
- Q. What happens in your body when you have an allergic reaction?
- Q. How can I lower my histamine levels quickly?
- Q. Is apple cider vinegar an antihistamine?
- Q. What food is a natural antihistamine?
- Q. Are Bananas high in histamine?
- Q. Is ginger an antihistamine?
- Q. Does coffee have histamine?
- Q. Does exercise lower histamine levels?
- Q. What foods should I avoid with histamine intolerance?
- Q. Does chocolate have histamine?
Q. What is considered a mild allergic reaction?
Allergy symptoms are classified as mild, moderate or severe: Mild reactions include local symptoms (affecting a specific area of your body) such as a rash or hives, itchiness, watery/red eyes, hay fever and runny nose. Mild reactions do not spread to other parts of your body.
Q. What is a Level 4 allergy?
Class 4: Very high level of allergen specific IgE. Clinical diagnosis of allergies depends on the amount of allergen-specific IgE found and physical symptoms when exposed to that specific allergen. It is easier to predict that allergy does not exist if no allergen-specific IgE is found.
Q. What is a Class 1 allergy?
Traditional or class 1 food allergens, such as egg, are heat-, enzyme-, and low pH-resistant water-soluble glycoproteins ranging in size from 10 to 70 kD. Class 1 food allergens induce allergic sensitization via the gastrointestinal tract and are responsible for systemic reactions (traditional or class 1 FA)13).
Q. How can I lower my blood allergy levels?
Other studies have found that green tea lowers blood levels of the IgE antibody, a compound that’s a prime player in the body’s allergic and inflammatory response….Here are five allergy-fighting foods that may help to ease your seasonal allergies:
- Kale.
- Strawberries.
- Turmeric.
- Broccoli.
- Green tea.
Q. What should I drink for an allergic reaction?
Sip a Cup of Green Tea. “Tea, especially green tea, with or without caffeine, is very good for people with allergies,” says Murray Grossan, MD, an ear, nose, and throat doctor in Los Angeles. Tea contains natural antihistamines, he says, which makes it a great addition to your diet to reduce allergy symptoms.
Q. Is coffee good for allergy?
Coffee won’t relieve your allergies, but it might take the edge off some of your worst symptoms. Caffeine is similar to theophylline, a prescription drug used to control asthma; of course, the latter is more effective, but you still may feel a bit less stuffy after a strong cup of coffee.
Q. How long does it take for allergic reaction to clear up?
They may take a few hours to a few days to disappear. If the exposure to the allergen continues, such as during a spring pollen season, allergic reactions may last for longer periods such as a few weeks to months. Even with adequate treatment, some allergic reactions may take two to four weeks to go away.
Q. Is Benadryl good for an allergic reaction?
Just because Benadryl is the oldest antihistamine doesn’t make it the best one to use when you have an allergic reaction. In fact, I rarely recommend using Benadryl for allergic reactions. Today, there are better choices when you have an allergic reaction such as Claritin, Allegra, Zyrtec, and Sublingual Allergy Drops.
Q. How long does a allergic reaction last?
You usually don’t get a reaction right away. It can take anywhere from a few hours to 10 days. Typically, it takes from 12 hours to 3 days. Even with treatment, symptoms can last 2 to 4 weeks.
Q. Can you suddenly become allergic to something?
When allergies typically develop But it’s possible to develop an allergy at any point in your life. You may even become allergic to something that you had no allergy to before. It isn’t clear why some allergies develop in adulthood, especially by one’s 20s or 30s.
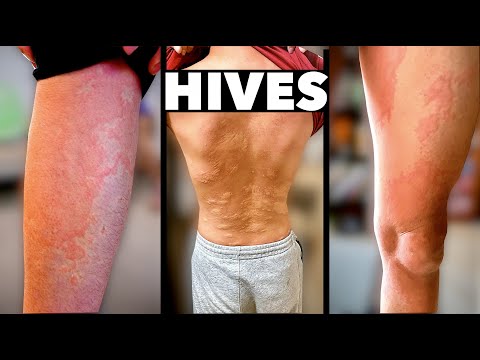
Q. What does an allergic reaction look like on skin?
There are several different types of skin allergy reactions that allergists treat. Hives (also known as urticaria) are raised itchy bumps. Typically hives appear reddish, and will “blanch” (or turn white) in the center when pressed. Contact dermatitis is typically caused by exposure to an allergen or irritant.
Q. How long does an food allergic reaction last?
Overall, the rash should subside within a day or two. According to FARE, it’s possible to have a second wave of food allergy symptoms, which may occur up to four hours after the initial reaction, though this is rare.
Q. How do you flush allergens out of your system?
“While your body is purging the allergen food from it is system, the best thing you can do is drink plenty of fluids,” Zeitlin says. Water is always a good idea, but you can also sip on low calorie sports drinks to replenish the electrolytes you’re likely losing, Zeitlin says.
Q. How long does an allergic reaction last from medication?
In a drug reaction, a medication triggers the release of histamine. Hives may also develop as a result of an allergic reaction to food, an insect bite, or even hot and cold temperatures. A breakout of hives may be acute and last for fewer than six weeks, or it may be chronic and last for six weeks or more.
Q. What should you eat when you have an allergic reaction?
6 Foods That May Help Curb Your Allergies
- Onions, peppers, berries, and parsley all have quercetin.
- Kiwi is a fuzzy fruit rich in vitamin C.
- Pineapple has an enzyme called bromelain.
- Tuna, salmon, and mackerel have Omega-3 fatty acids.
Q. Does drinking water help allergic reaction?
Once your body is dehydrated, the histamine production increases, which causes the body to have the same trigger symptoms as seasonal allergies. Drinking plenty of water will help prevent the higher histamine production and alleviate the allergy symptoms.
Q. What happens in your body when you have an allergic reaction?
When you have allergies, your immune system makes antibodies that identify a particular allergen as harmful, even though it isn’t. When you come into contact with the allergen, your immune system’s reaction can inflame your skin, sinuses, airways or digestive system.
Q. How can I lower my histamine levels quickly?
Some foods low in histamine include:
- fresh meat and freshly caught fish.
- non-citrus fruits.
- eggs.
- gluten-free grains, such as quinoa and rice.
- dairy substitutes, such as coconut milk and almond milk.
- fresh vegetables except tomatoes, avocados, spinach, and eggplant.
- cooking oils, such as olive oil.
Q. Is apple cider vinegar an antihistamine?
Most people with seasonal allergies use medications, such as antihistamines, which prevent compounds called histamines from attaching to cells and causing allergy symptoms. But apple cider vinegar doesn’t really have any antihistamine properties, Dr. Wolbert says.
Q. What food is a natural antihistamine?
People with allergies may find relief by using natural plant extracts and foods that act as antihistamines….Quercetin is naturally present in many foods and herbs, including:
- apples.
- berries.
- black tea.
- broccoli.
- buckwheat tea.
- grapes.
- Ginkgo biloba.
- green tea.
Q. Are Bananas high in histamine?
Some high-histamine foodsinclude aged or preserved meats such as smoked or cured meat, aged cheeses, fermented foods, and alcohol. Cocoa, certain nuts, avocado, banana, shellfish, tomatoes, citrus fruits, legumes, and strawberries are other foods high in naturally-occurring histamines.
Q. Is ginger an antihistamine?
1. Ginger is a histamine blocker or antihistamine but is also great for the immune system.
Q. Does coffee have histamine?
Coffee is high in histamine which can set off what looks like an allergic reaction but it doesn’t occur through the typical allergy mechanism. Instead, the histamine from the coffee causes an inflammatory reaction that can be quite severe in some people.
Q. Does exercise lower histamine levels?
Aerobic exercise results in activation of histamine H1 and H2 receptors within the previously exercised muscle, triggering vasodilation and a broad range of responses to exercise.
Q. What foods should I avoid with histamine intolerance?
Foods to avoid on a low-histamine diet
- fermented dairy products, such as cheese (especially aged), yogurt, sour cream, buttermilk, and kefir.
- fermented vegetables, such as sauerkraut and kimchi.
- pickles or pickled veggies.
- kombucha.
- cured or fermented meats, such as sausages, salami, and fermented ham.
Q. Does chocolate have histamine?
Although chocolate actually is quite low in histamine it contains two other biogenic amines, namely tyramine and phenylethylamine, both present in cocoa. Biogenic amines are histamine triggers.