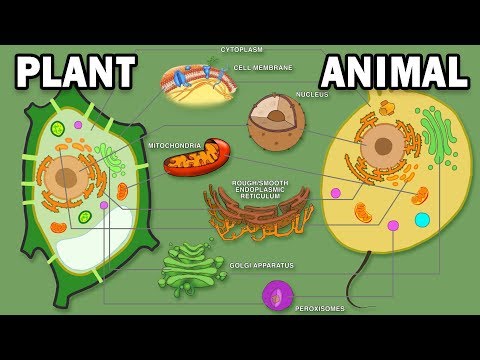
Q. Are vacuoles found in plant or animal cells?
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that can be found in both animals and plants.
Q. Do mammals have vacuoles?
Vacuoles/lysosomes share a conserved mechanism of biogenesis, and they are at the terminal of the endocytic pathways, Recent genetic studies of the mammalian orthologs of Vam/Vps genes, which have essential functions for vacuole assembly, revealed that the dynamics of vacuoles/lysosomes are important for tissue …
Table of Contents
- Q. Are vacuoles found in plant or animal cells?
- Q. Do mammals have vacuoles?
- Q. Why vacuoles are absent in animal cell?
- Q. Would an animal cell die without a vacuole?
- Q. What happens if no vacuole?
- Q. How many vacuoles are in an animal cell?
- Q. Which plant cell has no vacuoles?
- Q. Do all plant cells have vacuoles?
- Q. What are vacuoles made of?
- Q. What happens if contractile vacuole is absent?
- Q. What will happen to contractile vacuole?
- Q. Where are contractile vacuoles found?
- Q. What will happen if a contact I’ll vacuole is absent in amoeba?
- Q. What would happen if the contractile vacuole stopped working in amoeba?
- Q. Why contractile vacuole is absent in protozoa?
- Q. What is the function of vacuoles present in amoeba?
- Q. What is food vacuole function?
- Q. What are some examples of vacuole?
- Q. What is a contractile vacuole and why is it important?
- Q. What is contractile vacuole give example?
- Q. Why are contractile vacuoles useless in salt water?
- Q. What is the difference between contractile vacuole and food vacuole?
- Q. What are the 3 types of vacuoles?
- Q. Where is the food vacuole located?
- Q. Where do food vacuoles end up?
- Q. Is food vacuole an organelle?
- Q. Is food vacuole present in amoeba?
- Q. What happens to the food in the food vacuole of an amoeba?
Q. Why vacuoles are absent in animal cell?
In animal cells, vacuoles are present but are smaller in size compared to plant cells. Compared to other cells, animal cells have smaller vacuoles, as they do not require the storage of more water, organic and inorganic for the proper functioning of the cell. …
Q. Would an animal cell die without a vacuole?
Conclusion: A plant cell would die without a vacuole. An animal cell that normally has a vacuole would die too, yet it wouldn’t be that drastical.
Q. What happens if no vacuole?
If a cell did not have a vacuole, then it would be unable to carry out its usual functions and would eventually die. In plants, the vacuole plays an important role in water storage and the maintenance of structure.
Q. How many vacuoles are in an animal cell?
Also in a Plant Cell there is only one vacuole the Large Central Vacuole. Yes, animal cells do have vacuoles. They just have a larger number of them and some sites call them with different names. In a plant cell there is just one vacuole.
Q. Which plant cell has no vacuoles?
So, the correct answer is ‘Xylem vessels’
Q. Do all plant cells have vacuoles?
Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells. They are found in both animal and plant cells but are much larger in plant cells. Vacuoles might store food or any variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive. In that fluid are nutrients or waste products.
Q. What are vacuoles made of?
Vacuoles are closed sacs, made of membranes with inorganic or organic molecules inside, such as enzymes. They have no set shape or size, and the cell can change them as needed. They are in most eukaryotic cells and do many things. They can store waste.
Q. What happens if contractile vacuole is absent?
(cytosol) Without a contractile vacuole, the cell would fill with excess water and, eventually, burst, because the surrounding water is hypotonic when considered with respect to the contents of the cell, water is transferred or passed across the amoeba’s cell membrane by osmosis.
Q. What will happen to contractile vacuole?
What would happen if the contractile vacuole stopped working? If there is too much water, the contractile vacuole works to pump out the water. This helps to protect the cell: if there is too much water in the cell, it will swell and swell until eventually it ruptures, destroying the cell.
Q. Where are contractile vacuoles found?
freshwater protozoa
Q. What will happen if a contact I’ll vacuole is absent in amoeba?
Answer: The contractile vacuole is present in amoeba but absent in Entamoeba because Amoeba lives in water and needs osmotic regulation. Since the osmotic concentration of its body remains equal to its surroundings entry of water through osmosis will not happen.
Q. What would happen if the contractile vacuole stopped working in amoeba?
The cell would have no chance to repair that damage as it would not be able to break down any complex molecules and transform them into what is needed. Moreover, the cell would “starve” as it wouldn’t be able to store all nutrients properly. Conclusion: A plant cell would die without a vacuole.
Q. Why contractile vacuole is absent in protozoa?
Answer: The marine protozoa do not have contractile vacuole because the marine protozoa live in a hypertonic environment. Marine protozoa do not need to remove excess water out of the cell, instead, they need to conserve water from getting lost in the hypertonic environment. Hence, they do not need contractile vacuole.
Q. What is the function of vacuoles present in amoeba?
In Amoeba contractile vacuoles collect excretory waste, such as ammonia, from the intracellular fluid by both diffusion and active transport.
Q. What is food vacuole function?
Function of Food Vacuole Food vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs within a cell, which contain food matter to be digested. These can be thought of as intracellular “stomachs,” where food is stored while it is broken down and its nutrients are extracted.
Q. What are some examples of vacuole?
Examples include the lytic vacuole, the storage vacuole and the lutoid. One important function of plant vacuoles is the maintenance of hydrostatic pressure. Other eukaryotes employ vacuoles for a variety of purposes, including storage (as in the yeast lysosome/vacuole), secretion and phagocytosis.
Q. What is a contractile vacuole and why is it important?
A contractile vacuole (CV) is an organelle, or sub-cellular structure, that is involved in osmoregulation and waste removal. Thus, the CV acts as a protective mechanism against cellular expansion (and possibly explosion) from too much water; it expels excess water from the cell by contracting.
Q. What is contractile vacuole give example?
Examples. Examples of cells that contain this contractile vacuole are amoeba, paramecium, and some types of algae. Some sponges (including amoebocytes, pinacocytes, and choanocytes), singled-celled fungi, and hydra also have contractile vacuoles. Some species, like giant amoeba, have numerous contractile vacuoles.
Q. Why are contractile vacuoles useless in salt water?
In salt water, the solute concentration outside the cell is more than inside the cell so the water flows out of the cell down the concentration gradient. Therefore contractile vacuoles are not required for expelling water.
Q. What is the difference between contractile vacuole and food vacuole?
Food vacuoles are membranous structures that participate in the process of digestion. Contractile vacuoles are membranous structures which participate in osmoregulation of the cell and prevent the bursting of cells.
Q. What are the 3 types of vacuoles?
I know of only three types: central vacuole – helps maintain plants’ shape and structure by storing water (hypotonic). contractile vacuole – pumps water out of protist cells to maintain a suitable concentration. food vacuole – storage for molecules that is a food source for the cell (phagocytosis).
Q. Where is the food vacuole located?
Food vacuoles are found in cells of plants, protists, animals and fungi. Food vacuoles are circular portions of the plasma membrane that capture or encircle food particles when they enter the cell.
Q. Where do food vacuoles end up?
Food vacuoles form when the food is pushed toward the cell where the membrane bends inward. As the food pushes against the membrane, the membrane stretches inward until the food particle is completely in the cell, where the membrane then pinches off, forming a vacuole. This form of eating is called phagocytosis.
Q. Is food vacuole an organelle?
The food vacuole, or digestive vacuole, is an organelle found in simple eukaryotes such as protists.
Q. Is food vacuole present in amoeba?
amoeba. The endoplasm contains food vacuoles, a granular nucleus, and a clear contractile vacuole. The amoeba has no mouth or anus; food is taken in and material excreted at any point on the cell surface.
Q. What happens to the food in the food vacuole of an amoeba?
Answer: Food vacuoles of amoeba are fluid filled membrane bound structures present inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The fluid inside vacuole contains several enzymes that digest the food and digested parts are absorbed into the cytoplasm. Undigested waste parts are thrown out of the cell.