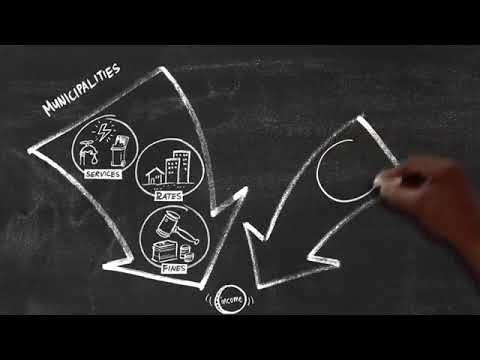
Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, value added tax (VAT) and corporation tax. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds and municipal rates.
Q. What are state governments major source of revenue?
State and local governments collect tax revenues from three primary sources: income, sales, and property taxes. Income and sales taxes make up the majority of combined state tax revenue, while property taxes are the largest source of tax revenue for local governments, including school districts.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are state governments major source of revenue?
- Q. What do state governments spend money on?
- Q. What are the 5 major sources of revenue for the government in South Africa?
- Q. Which tax base is the largest source of revenue in South Africa?
- Q. What income is not taxable in South Africa?
- Q. How much do you need to earn to pay tax in South Africa 2020?
- Q. Where does most of South Africa’s income come from?
- Q. Is South Africa economy better than Nigeria?
- Q. Is South Africa more developed than India?
- Q. What do you think is the biggest cause of unemployment in South Africa?
- Q. What are the three causes of unemployment?
- Q. What are the impacts of unemployment in South Africa?
- Q. What is the relationship between low economic growth and unemployment in South Africa?
- Q. What are the effects of unemployment on the economy?
- Q. What is unemployment and its effects?
- Q. What are four effects of unemployment?
- Q. What are the types of unemployment Class 9?
- Q. What do you mean by unemployment for Class 9?
- Q. What is poverty class 9th?
- Q. What are the major factors for unemployment in India Class 9?
- Q. How does unemployment affect the overall growth of an economy class 9?
- Q. What is the main causes of unemployment in India?
- Q. Which state in India has highest unemployment?
- Q. What poverty causes?
Q. What do state governments spend money on?
State and local governments spend most of their resources on education, health, and social service programs. In 2017, about one-third of state and local spending went toward combined elementary and secondary education (21 percent) and higher education (10 percent).
Q. What are the 5 major sources of revenue for the government in South Africa?
Some of South Africa’s main tax revenue sources
- Personal income tax: R 85 883 790 000 (42.67%)
- Value-added tax: R 48 376 840 000 (24.04%)
- Corporate income tax: R 20 971 610 000 (10.42%)
- Fuel levies: R 14 289 800 000 (7.10%)
- Specific excise duties: R 8 886 140 000 (4.42%)
- Customs duties: R 6 517 800 000 (3.24%)
Q. Which tax base is the largest source of revenue in South Africa?
Personal income tax is the largest contributor to total tax revenue, so what does this mean for Sars and those who can still contribute? In the ordinary course, National Treasury would ride to Sars’ aid and hike tax rates to increase revenue.
Q. What income is not taxable in South Africa?
Interest from a South African source, earned by any natural person under 65 years of age, up to R23 800 per annum, and persons 65 and older, up to R34 500 per annum, is exempt from income tax.
Q. How much do you need to earn to pay tax in South Africa 2020?
Who is it for? R87 300 if you are younger than 65 years. If you are 65 years of age to below 75 years, the tax threshold (i.e. the amount above which income tax becomes payable) increases to R135 150. For taxpayers aged 75 years and older, this threshold is R151 100.
Q. Where does most of South Africa’s income come from?
The highest share of tax revenues in South Africa in 2018 was contributed by personal income tax (35%). The second-highest share of tax revenues in 2018 was derived from value added taxes (VAT) (23%).
Q. Is South Africa economy better than Nigeria?
Nigeria’s GDP surpassed that of South Africa about a decade ago, according to the World Bank. Last year, Nigeria’s economy was valued at $397 billion, while South Africa – once the biggest player on the continent – had a GDP of $366 billion.
Q. Is South Africa more developed than India?
Out of 133 countries ranked by per capita GNP, India ranks as one of the poorest low-income countries, at position 23, above the very poorest. South Africa ranks at position 93, in the group of upper-middle-income countries. South Africa’s per capita income is close to 10 times that of India’s.
Q. What do you think is the biggest cause of unemployment in South Africa?
• Legacy of apartheid and poor education and training Inadequate education and lack of productivity is costing jobs. Unemployment increases progressively with decreased educational levels; and the education system is not producing the skills for the labour market.
Q. What are the three causes of unemployment?
The following are the main causes of unemployment:
- (i) Caste System:
- (ii) Slow Economic Growth:
- (iii) Increase in Population:
- (iv) Agriculture is a Seasonal Occupation:
- (v) Joint Family System:
- (vi) Fall of Cottage and Small industries:
- (vii) Slow Growth of Industrialisation:
- (ix) Causes of Under Employment:
Q. What are the impacts of unemployment in South Africa?
Unemployment has both individual and social consequences that require public policy interventions. For the individual, unemployment can cause psychological distress, which can lead to a decline in life satisfaction. It can also lead to mood disorders and substance abuse.
Q. What is the relationship between low economic growth and unemployment in South Africa?
Theoretically, economic growth is viewed as the most prominent instrument for reducing unemployment, poverty and to help improve the living standards of people. Kreishan (2011) states that an increase in the growth rate of GDP of an economy is expected to increase employment levels thus reducing unemployment.
Q. What are the effects of unemployment on the economy?
Key Takeaways. The unemployment rate is the proportion of unemployed persons in the labor force. Unemployment adversely affects the disposable income of families, erodes purchasing power, diminishes employee morale, and reduces an economy’s output.
Q. What is unemployment and its effects?
Unemployment causes workers to suffer financial hardship that impacts families, relationships, and communities. When it happens, consumer spending, which is one of an economy’s key drivers of growth, goes down, leading to a recession or even a depression when left unaddressed.
Q. What are four effects of unemployment?
There is a feeling of hopelessness and despair among the youth. People do not have enough money to support their family. Inability of educated people who are willing to work to find gainful employment implies a great social waste. (ii) Unemployment tends to increase economic overload.
Q. What are the types of unemployment Class 9?
Answer. There are three main types of Unemployment: structural ,frictional and cyclical.
Q. What do you mean by unemployment for Class 9?
Unemployment exists when a person, 15 to 59 years of age, is willing to work at acceptable wages, cannot find a job. Such a person is called an unemployed person. The unemployment faced by people who are matriculates, graduates or post-graduates is called educated unemployment.
Q. What is poverty class 9th?
Answer: Poverty is a situation in which a person is unable to get the minimum basic necessities of life, i.e., food, clothing and shelter for his or her sustenance. Mass poverty is a situation in which a large section of people in economy are deprived of the basic necessities.
Q. What are the major factors for unemployment in India Class 9?
The following are the main causes of unemployment:
- The Caste System.
- Increased Population Growth.
- Slow Economic Growth.
- Slow Industrial Growth.
- Seasonality of Agricultural Occupations.
- Joint Family System.
- Loss of Small-Scale/Cottage Industries.
- Low Rates of Saving and Investment.
Q. How does unemployment affect the overall growth of an economy class 9?
Unemployment affects the overall growth of an economy. People who are an asset for the nation turn into a liability for an organization. It leads to wastage of manpower resources. It tends to increase economic overload.
Q. What is the main causes of unemployment in India?
Causes of Unemployment in India:
- Rapid growth of population and increase in labour force.
- Underdevelopment of the economy.
- Slow growth in the agricultural sector.
- Defective system of education.
- Absence of manpower planning.
- Degeneration of village industries.
- Inappropriate technology.
- Slow growth of industrial sector.
Q. Which state in India has highest unemployment?
Haryana
Q. What poverty causes?
According to the United Nations Social Policy and Development Division, “inequalities in income distribution and access to productive resources, basic social services, opportunities, markets, and information have been on the rise worldwide, often causing and exacerbating poverty.” The U.N. and many aid groups also …