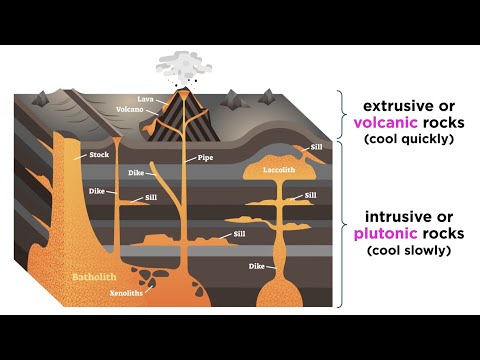
Q. At which tectonic settings do igneous rocks form?
Igneous rocks—tectonic setting
- Ocean–ocean island arc.
- Continent–ocean arc. Divergent(constructive)
- Mid-ocean ridge.
- Back-arc basin. Within plate. Tensional.
- Intracontinental rift.
- Intramontane rift. Neutral.
- Oceanic hot spot (ocean island)
- Continental hot spot.
Q. At what type of plate tectonic boundary would you expect to find the igneous rock known as basalt?
Divergent Boundaries
Table of Contents
- Q. At which tectonic settings do igneous rocks form?
- Q. At what type of plate tectonic boundary would you expect to find the igneous rock known as basalt?
- Q. Which igneous rock type is associated with divergent plate boundaries?
- Q. What are the igneous processes?
- Q. How are igneous rocks used by humans?
- Q. Where are the igneous rocks found?
- Q. What are igneous rocks characteristics?
- Q. What are two common uses of igneous rocks?
- Q. What do igneous rocks tend to be?
- Q. Are igneous rocks radioactive?
Q. Which igneous rock type is associated with divergent plate boundaries?
Most rocks formed at divergent boundaries are categorized as malefic igneous rocks, which are dark-colored due to their high magnesium and iron content. This category includes basalt, gabbro and peridotites, which are often found at these boundaries.
Q. What are the igneous processes?
Igneous rock is formed when liquid rock freezes into solid rock. This molten material is called magma when it is in the ground and lava when it is on the surface. Only the Earth’s outer core is liquid; the Earth’s mantle and crust are naturally solid. Volcanism is the process in which lava has erupted.
Q. How are igneous rocks used by humans?
One of the most common igneous rocks is granite (Figure 4.9). Granite is used extensively in building materials and making statues. Perhaps you have used a pumice stone to smooth your skin or to do jobs around the house. Figure 4.10: Pumice is a light igneous rock used for abrasive materials.
Q. Where are the igneous rocks found?
Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust. All magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle, because of the intense heat there.
Q. What are igneous rocks characteristics?
Igneous rocks can be easily identified with their texture, density, color, and mineral composition. Its texture depends on the shape, size, time period to cool down and solidify, and the arrangement of crystals in the rock.
Q. What are two common uses of igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks have a wide variety of uses. One important use is as stone for buildings and statues. Diorite was used extensively by ancient civilizations for vases and other decorative artwork and is still used for art today (Figure 1). Granite (figure 2) is used both in building construction and for statues.
Q. What do igneous rocks tend to be?
Felsic igneous rocks, as a whole rock, tend to have light colors or shades: white, pink, light brown, light gray. Mafic igneous rocks, on the whole, tend to be dark colored, commonly black or dark gray. Most mafic magma originates by melting of rocks in the mantle that are extremely rich in iron and magnesium.
Q. Are igneous rocks radioactive?
Radioactive atoms are inherently unstable; over time, radioactive “parent atoms” decay into stable “daughter atoms.” When molten rock cools, forming what are called igneous rocks, radioactive atoms are trapped inside. Afterwards, they decay at a predictable rate.