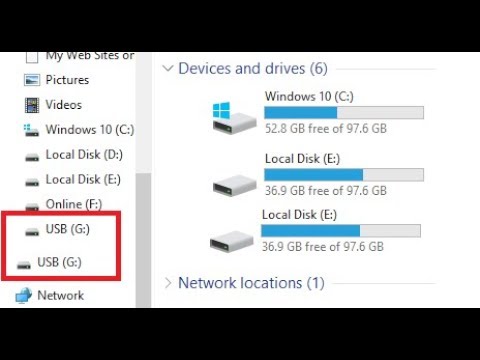
Yes Huckleberry,you can have 2 drives with the same letter, that will not be a problem. However, if you connect both drives at the same time by accident, Windows will automatically assign a different drive letter to one of the drives . . . Power to the Developer!
Q. Do hard drives have separate read and write heads?
A hard drive with five platters thus has ten read/write heads. However, all of these heads are attached to a single common actuator arm assembly (sometimes called a head stack assembly), meaning they all move together. If read/write head #1 is on track 0, so are all of the other read/write heads.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do hard drives have separate read and write heads?
- Q. Can SSD read and write simultaneously?
- Q. How does a hard disk read and write data?
- Q. What disk writes?
- Q. Who read and writes data on disk?
- Q. What is the mechanism that use to prevents the head crashing on the disk?
- Q. How data is stored on a disk?
- Q. Are used to read and write data on disks?
- Q. When the computer is on does the hard disk spin all the time?
- Q. What is the purpose of ROM?
- Q. What devices use ROM?
- Q. Why do we need both RAM and ROM?
- Q. Can a computer run without rom?
- Q. Will a computer post without RAM?
- Q. Can a laptop run without RAM?
Q. Can SSD read and write simultaneously?
According to Enterprise Storage, a typical 7200 RMP has a read/write speed of 125MBps, SATA SSDs can read at up to 550MBps and write at 520MBps, and M. 2 NVMe SSDs that use the PCIe 3.0 interface are up to five times faster than a standard SATA SSD and twenty-five times faster than a 7200 RPM HDD.
Q. How does a hard disk read and write data?
The hard drive contains a spinning platter with a thin magnetic coating. A “head” moves over the platter, writing 0’s and 1’s as tiny areas of magnetic North or South on the platter. To read the data back, the head goes to the same spot, notices the North and South spots flying by, and so deduces the stored 0’s and 1’s.
Q. What disk writes?
Disk read/write heads are the small parts of a disk drive which move above the disk platter and transform the platter’s magnetic field into electrical current (read the disk) or, vice versa, transform electrical current into magnetic field (write the disk).
Q. Who read and writes data on disk?
– In a hard disk information / data is written on the rotating platters by the read and write heads. – The heads are not in actual contact with the disk they are actually slightly above the magnetic surface of the platter. – The heads detects the magnetization of the platter right below them.
Q. What is the mechanism that use to prevents the head crashing on the disk?
This safety process is known as the parking technology. Most modern disk that uses the voice-coil or giant magneto-resistive head, supports auto-parking. In an event of power loss to the disk, a retract mechanism moves and secures the head to its landing zone without the use of external power.
Q. How data is stored on a disk?
Data is stored on a hard drive in binary code, using 1s and 0s. The information is spread out on the magnetic layer of the disk(s) and are read or written by the read heads that ‘float’ above the surface thanks to the layer of air produced by the ultra fast rotation of the disk.
Q. Are used to read and write data on disks?
A read/write head is a specific physical part of a hard disk that is responsible for reading data from, and writing data to, the disk. Read/write heads are typically made up of a thin horizontal magnetic blade attached to an actuator arm.
Q. When the computer is on does the hard disk spin all the time?
Standard computer hard drives spin continuously at 7200 RPM, only stopping after a prolonged period of disuse. When you hear your hard drive hard at work, you’re actually hearing the movement of a mechanical arm containing the read/write head, which glides across the drive’s platters.
Q. What is the purpose of ROM?
ROM stands for read-only memory. It’s used to store the start-up instructions for a computer, also known as the firmware. Most modern computers use flash-based ROM. It is part of the BIOS chip, which is located on the motherboard.
Q. What devices use ROM?
Read-Only Memory (ROM), is a type of electronic storage that comes built in to a device during manufacturing. You’ll find ROM chips in computers and many other types of electronic products; VCRs, game consoles, and car radios all use ROM to complete their functions smoothly.
Q. Why do we need both RAM and ROM?
The TL;DR answer is that RAM is volatile and contents disappear when powered down, so a computer with only RAM would have be be kept powered up all the time. ROM is “read only” so a computer with only ROM would not be able to manipulate or alter any data. If only it were that simple! RAM means random access memory.
Q. Can a computer run without rom?
Yes, you can design a computer without any kind of ROM. But you need to remember that a CPU is just a hunk of silicon until you give it instructions. If you’re not getting those instructions form ROM, you’ll need to get them from a block storage device like a hard drive and load them into ram.
Q. Will a computer post without RAM?
The computer cannot run without RAM. When you power up your computer, the CPU will jump to the firmware (BIOS/UEFI). Next, POST (Power On Self Test) step will run as part of those firmwares and detect that there is no RAM and as a result will send beeps to your speaker.
Q. Can a laptop run without RAM?
No, a laptop (or a desktop) will not start without RAM. If RAM is not installed when a laptop (or a desktop) is switched on, nothing would appear on the screen.