It is not much possible to divide a helium atom of mass number 4 into two atoms. As fissioning it with beta particles gives one hydrogen atom. As fissioning it with protons gives three hydrogen atoms. As fissioning it with alpha particles gives four hydrogen atoms.
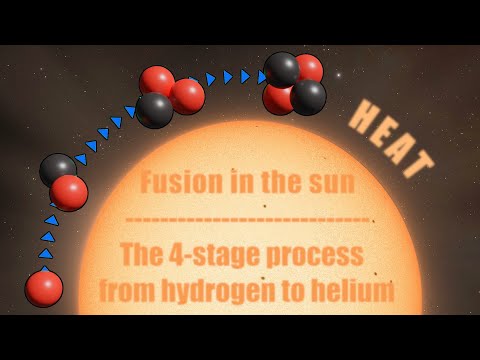
Q. What is the fuel for the sun?
hydrogen
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the fuel for the sun?
- Q. How much hydrogen does the Sun convert to helium every second?
- Q. How many hydrogens make a helium?
- Q. What has an outer shell of burning hydrogen and a core of helium?
- Q. What causes a high-mass star to explode as a Type II supernova?
- Q. What will happen to the sun’s core after the double shell burning stage?
- Q. Why do high-mass stars burn faster?
- Q. What is the last stage of a high mass star?
- Q. How do high mass stars die?
Q. How much hydrogen does the Sun convert to helium every second?
In each nuclear conversion 4 hydrogen atoms are combined to produce a helium atom. This reaction occurs throughout the Sun and by this process our Sun converts 600 million tons of hydrogen into 596 million tons of helium every second.
Q. How many hydrogens make a helium?
four hydrogen
Q. What has an outer shell of burning hydrogen and a core of helium?
Such a star tracks across to the left along the horizontal branch on the HR diagram. HB stars have helium core-burning and hydrogen shell-burning. A solar-mass star has sufficient helium fuel for core-burning to last for about 100 million years.
Q. What causes a high-mass star to explode as a Type II supernova?
For a star to explode as a Type II supernova, it must be at several times more massive than the sun (estimates run from eight to 15 solar masses). Like the sun, it will eventually run out of hydrogen and then helium fuel at its core. However, it will have enough mass and pressure to fuse carbon.
Q. What will happen to the sun’s core after the double shell burning stage?
The core reverts back into a (spectacularly dense) normal gas, and powerfully expands. The enormous gravitational energy needed to expand 100,000 Earth masses out of degeneracy and up to several times their original volume is on a par with the energy release of the helium flash.
Q. Why do high-mass stars burn faster?
When the core hydrogen is exhausted a high-mass star behaves like a low- mass star, only faster. – Outer layers expand producing a supergiant star. Core temperature increases – helium burning in the core. Carbon burning in a shell around the inert core.
Q. What is the last stage of a high mass star?
Stage 9 – The remaining core (thats 80% of the original star) is now in its final stages. The core becomes a White Dwarf the star eventually cools and dims. When it stops shining, the now dead star is called a Black Dwarf.
Q. How do high mass stars die?
All stars eventually run out of their hydrogen gas fuel and die. When a high-mass star has no hydrogen left to burn, it expands and becomes a red supergiant. While most stars quietly fade away, the supergiants destroy themselves in a huge explosion, called a supernova.