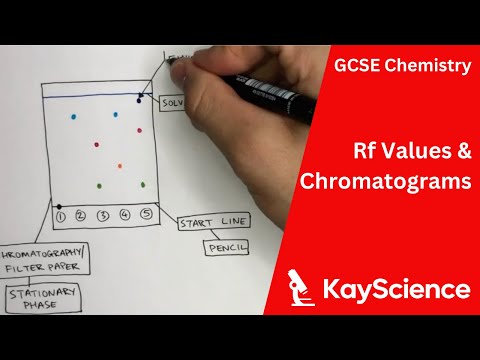
The larger an Rf of a compound, the larger the distance it travels on the TLC plate. If two substances have the same Rf value, they are likely (but not necessarily) the same compound. If they have different Rf values, they are definitely different compounds.
Q. Why do we not use pen in chromatography?
The resins and colouring agents are miscible with other polar organic solvents that we use in the chromatography. So the ink also travels along with the mobile phase. Hence, a paper or sketch pen should never be used to draw a line either on Paper chromatography or a TLC sheet.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why do we not use pen in chromatography?
- Q. Why must the solvent level be below the Coloured spots in chromatography?
- Q. What does a high RF value mean?
- Q. What is RF and how is it calculated?
- Q. What is the maximum RF value in paper chromatography?
- Q. What are the two phases of chromatography?
- Q. Why do colors separate in paper chromatography?
- Q. What is the solvent called in chromatography?
- Q. What type of mixtures can be separated by chromatography?
- Q. What are the 2 phases of chromatography?
Q. Why must the solvent level be below the Coloured spots in chromatography?
The solvent level has to be below the starting line of the TLC, otherwise the spots will dissolve away. Non-polar solvents will force non-polar compounds to the top of the plate, because the compounds dissolve well and do not interact with the polar stationary phase.
Q. What does a high RF value mean?
A high Rf (Ie 0.92) would refer to a substance that is very non-polar. Ie that substance moved a 92% of the entire distance the solvent traveled. A low Rf value (0.10) would refer to a substance that is very polar. IE that substance was only able to move 10% of the entire distance the solvent traveled. Term.
Q. What is RF and how is it calculated?
In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin).
Q. What is the maximum RF value in paper chromatography?
Size of spot may range 2-5 mm depending upon number of sample to be applied to the paper. The mobile phase which gives Rf value range between 0.2-0.8 are selected for chromatographic work.
Q. What are the two phases of chromatography?
Chromatography is essentially a physical method of separation in which the components of a mixture are separated by their distribution between two phases; one of these phases in the form of a porous bed, bulk liquid, layer or film is generally immobile (stationary phase), while the other is a fluid (mobile phase) that …
Q. Why do colors separate in paper chromatography?
Often the colors that we see are a combination of the light reflected by a mixture of different-color molecules. Different molecules run up the paper at different rates. As a result, components of the solution separate and, in this case, become visible as strips of color on the chromatography paper.
Q. What is the solvent called in chromatography?
mobile phase
Q. What type of mixtures can be separated by chromatography?
Paper chromatography is a method for separating dissolved substances from one another. It is often used when the dissolved substances are coloured, such as inks, food colourings and plant dyes.