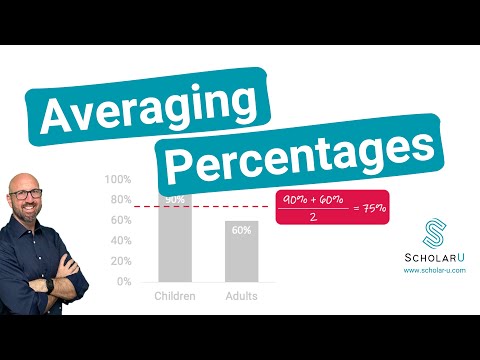
Q. Can you ever average percentages?
Calculate the percentage average To find the average percentage of the two percentages in this example, you need to first divide the sum of the two percentage numbers by the sum of the two sample sizes. So, 95 divided by 350 equals 0.27. You then multiply this decimal by 100 to get the average percentage.
Q. Is an average of an average accurate?
I frequently create reports that show the average (mean) value of a metric based on any number of dimensions. These numbers rarely match because taking an average of averages is wrong. The reason an average of averages is wrong is that it doesn’t take into account how many units went into each average.
Table of Contents
- Q. Can you ever average percentages?
- Q. Is an average of an average accurate?
- Q. How do I calculate the average percentage increase?
- Q. How do I calculate annual increase?
- Q. How do I calculate growth?
- Q. What is annual percentage change?
- Q. How do you calculate population?
- Q. What is the population mean formula?
- Q. What is the formula to calculate sample size?
- Q. What are 4 methods of determining population size?
- Q. What are 3 limiting factors?
- Q. What are the 3 types of population distribution?
- Q. What are the 3 methods of calculating population density?
Q. How do I calculate the average percentage increase?
To calculate the percentage increase:
- First: work out the difference (increase) between the two numbers you are comparing.
- Increase = New Number – Original Number.
- Then: divide the increase by the original number and multiply the answer by 100.
- % increase = Increase ÷ Original Number × 100.
Q. How do I calculate annual increase?
To calculate the annual growth rate formula, follow these steps:
- Find the ending value of the amount you are averaging.
- Find the beginning value of the amount you are averaging.
- Divide the ending value by the beginning value.
- Subtract the new value by one.
- Use the decimal to find the percentage of annual growth.
Q. How do I calculate growth?
The basic growth rate formula takes the current value and subtracts that from the previous value. Then, this difference is divided by the previous value and multiplied by 100 to get a percentage representation of the growth rate.
Q. What is annual percentage change?
Annual Percent Change (APC) is one way to characterize trends in cancer rates over time. With this approach, the cancer rates are assumed to change at a constant percentage of the rate of the previous year. Rates that change at a constant percentage every year change linearly on a log scale.
Q. How do you calculate population?
If the data is being considered a population on its own, we divide by the number of data points, N. If the data is a sample from a larger population, we divide by one fewer than the number of data points in the sample, n − 1 n-1 n−1 .
Q. What is the population mean formula?
The formula to find the population mean is: μ = (Σ * X)/ N. where: Σ means “the sum of.” X = all the individual items in the group.
Q. What is the formula to calculate sample size?
n = N*X / (X + N – 1), where, X = Zα/22 *p*(1-p) / MOE2, and Zα/2 is the critical value of the Normal distribution at α/2 (e.g. for a confidence level of 95%, α is 0.05 and the critical value is 1.96), MOE is the margin of error, p is the sample proportion, and N is the population size.
Q. What are 4 methods of determining population size?
Four methods of determining population size are direct and indirect observations, sampling, and mark-and-recapture studies.
Q. What are 3 limiting factors?
In the natural world, limiting factors like the availability of food, water, shelter and space can change animal and plant populations. Other limiting factors, like competition for resources, predation and disease can also impact populations.
Q. What are the 3 types of population distribution?
Individuals of a population can be distributed in one of three basic patterns: uniform, random, or clumped.
Q. What are the 3 methods of calculating population density?
The three methods for calculating population densities are arithmetic, physiological, and agricultural. Arithmetic density tell us how many people are living per square of land, while physiological density tells us how many people are living per square of arable land.