Q. Do plant cells have starch granules?
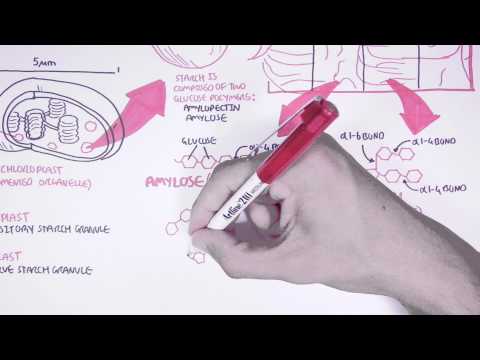
Zeeman. Background: Starch is the major form of carbohydrate storage in plants and a vital source of calories in our diet. It is produced in leaves of most plants, where it is present in chloroplasts as insoluble granules composed of glucose polymers.
Q. What are starch grains in plant cells?
Starch grains are tiny structures made by most plants as products of photosynthesis. Essentially, a starch grain is a well-packed storehouse of glucose sugar units. Many plants store starch grains in underground organs such as roots, bulbs, tubers, and rhizomes, as well as their seeds and stems.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do plant cells have starch granules?
- Q. What are starch grains in plant cells?
- Q. Do plant cells store starch?
- Q. Why some plant cells contain starch?
- Q. Which plant stores starch?
- Q. Are starch grains found in animal cells?
- Q. How can starch grains be used to identify plants?
- Q. What color are starch grains?
- Q. What are the different shapes of starch grain?
- Q. Is starch grains smaller than tracheal cell?
- Q. Is trachea an organelle?
- Q. Which cell makes food for the plant?
- Q. How do plant cells control turgor pressure?
- Q. How do plant cells maintain their shape?
- Q. What stores food in cells?
- Q. What plant organelle stores food or pigments?
- Q. Why do plant cells have cytoplasm?
- Q. Do plants have mitochondria?
- Q. Where is starch found in food?
- Q. What plant cells do?
Q. Do plant cells store starch?
Storage. In some plants, starch is stored in cell organelles called amyloplasts. Some plant roots and embryos, in the form of seeds and fruit, also serve as storage units for starch. Cells in plant leaves produce starch in the presence of sunlight.
Q. Why some plant cells contain starch?
Starch is a polymer of the sugar glucose, an important component of respiration and needed to provide plants with energy. Unlike glucose, starch is insoluble allowing it to be stored within the cell without having an osmotic effect. This allows starch to be broken down and used by the cell.
Q. Which plant stores starch?
Starch is stored in the stroma of the chloroplasts and in the cytoplasm of leaves. When plants use the process of photosynthesis to create their own…
Q. Are starch grains found in animal cells?
Animal cells never contain starch grains. Some animal cells, however, do have granules (tiny grains) of another substance similar to starch, called glycogen. These granules are found in the cytoplasm, not inside chloroplasts.
Q. How can starch grains be used to identify plants?
Features that allow identification of starch grains include: presence of hilum, layering, birefringence, and extinction cross, and also testing for presence of starch using iodine (staining black to blue in presence of starch). See below for more on the morphology.
Q. What color are starch grains?
A blue-black color results if starch is present. If starch amylose is not present, then the color will stay orange or yellow.
Q. What are the different shapes of starch grain?
The starch granules are angular-shaped for maize, and pentagonal and angular-shaped for rice. A-type granules of wheat starch are disk-like or lenticular in shape and the B-type starch granules are roughly spherical or polygonal in shape.
Q. Is starch grains smaller than tracheal cell?
Each plant species has a unique starch granular size: rice starch is relatively small (about 2μm) while potato starches have larger granules (up to 100μm). Tracheal cell has greater size compared to other organells.
Q. Is trachea an organelle?
The trachea is related posteriorly by oesophagus. The trachea contains cilia; microscopic, hairlike organelles that line the surface of cells in the trachea and bronchi. They sweep in pulsing waves to brush mucus which contains unwanted inhaled foreign particles such as dust up out of the lungs.
Q. Which cell makes food for the plant?
Chloroplast Chloroplasts
Q. How do plant cells control turgor pressure?
Turgor pressure within cells is regulated by osmosis and this also causes the cell wall to expand during growth. One mechanism in plants that regulate turgor pressure is its semipermeable membrane, which only allows some solutes to travel in and out of the cell, which can also maintain a minimum amount of pressure.
Q. How do plant cells maintain their shape?
Answer. Cell wall & cell membrane maintain the shape of cell and vacuole also maintain the shape of cells in plants. It is the cell wall structure that helps maintain the shape of cell.
Q. What stores food in cells?
Cell Structure
| A | B |
|---|---|
| vacuole | stores water, waste products, food, and other cellular materials |
| Golgi bodies | membranes that sort protein |
| lysosome | breaks down food molecules, cell wastes, and worn-out cell parts |
| compound light microscope | uses light and one or more lenses to view cells |
Q. What plant organelle stores food or pigments?
Plastids are membrane-bound organelles with their own DNA. Examples are chloroplasts and chromoplasts. Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis. Chromoplasts make and store other pigments.
Q. Why do plant cells have cytoplasm?
Plant cells have high concentrations of molecules dissolved in their cytoplasm, which causes water to come into the cell under normal conditions and makes the cell’s central vacuole swell and press against the cell wall. With a healthy supply of water, turgor pressure keeps a plant from wilting.
Q. Do plants have mitochondria?
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, so they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. Plants and animals are very different on the outside as well as on the cellular level. Both animal and plant cells have. mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts.
Q. Where is starch found in food?
Starch is the most common carbohydrate in the human diet and is contained in many staple foods. The major sources of starch intake worldwide are the cereals (rice, wheat, and maize) and the root vegetables (potatoes and cassava).
Q. What plant cells do?
Plant Cell Functions Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. Photosynthesis is the major function performed by plant cells. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cell. It is the process of preparing food by the plants, by utilizing sunlight, carbon dioxide and water.