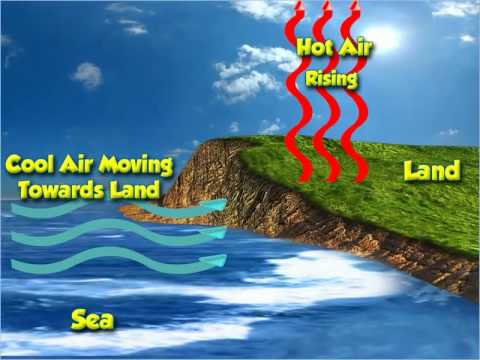
Q. Does air heat up faster than land?
During the typical day the surface heats and during the night it cools. Solar heating of the Earth’s surface is uneven because land heats faster than water, and this causes air to warm, expand and rise over land while it cools and sinks over the cooler water surfaces.
Q. Has the air warmed over land or ocean more?
Heat capacity Simple physics suggests that when you put more heat into the climate system, land should warm more quickly than oceans. This is because land has a smaller “heat capacity” than water, which means it needs less heat to raise its temperature.
Table of Contents
- Q. Does air heat up faster than land?
- Q. Has the air warmed over land or ocean more?
- Q. Why does the temperature change more rapidly over the land than over the ocean?
- Q. What does the uneven heating of Earth cause?
- Q. What is the hottest layer in the atmosphere?
- Q. Which is the coldest layer in the atmosphere?
- Q. Which is the hottest layer of the atmosphere Why?
- Q. What are 3 facts about the exosphere?
- Q. Can you breathe in the exosphere?
- Q. Can you breathe in the mesosphere?
- Q. What is a fact about the exosphere?
- Q. Is the exosphere the thinnest layer?
- Q. Is the exosphere the coldest layer?
- Q. Why is the exosphere cold?
- Q. How hot is the exosphere?
- Q. What layer is the ozone?
- Q. What are the 2 types of ozone?
- Q. Is the ozone hole bad?
- Q. Where is the ozone layer most damaged?
- Q. Is there no ozone layer in Canada?
- Q. Which country has no ozone layer?
- Q. How long until the ozone layer is gone?
Q. Why does the temperature change more rapidly over the land than over the ocean?
When the earth’s surface cools or is heated by the sun, the temperature change is greater – and faster – over the land than over the oceans. Because it is a fluid, the ocean diffuses the effects of a temperature change for great distances via vertical mixing and convective movements.
Q. What does the uneven heating of Earth cause?
Usually when we talk about uneven heating of the Earth’s surface we are discussing convection. The uneven heating results in some of the atmosphere to be warmer than other parts and changes in volume and pressure which result in updrafts and can cause thunderstorms and other violent weather.
Q. What is the hottest layer in the atmosphere?
thermosphere
Q. Which is the coldest layer in the atmosphere?
mesosphere
Q. Which is the hottest layer of the atmosphere Why?
the thermosphere
Q. What are 3 facts about the exosphere?
The air in the exosphere is very thin, and is made up mostly of helium, and hydrogen. Traces of other gases such as atomic oxygen and carbon dioxide can also be found. The upper level of the exosphere is the farthest point from earth that is still affected by earth’s gravity.
Q. Can you breathe in the exosphere?
The exosphere is really, really big. The exosphere has gases like hydrogen and helium, but they are very spread out. There is a lot of empty space in between. There is no air to breathe, and it’s very cold.
Q. Can you breathe in the mesosphere?
The mesosphere lies between the thermosphere and the stratosphere. The mesosphere is 22 miles (35 kilometers) thick. The air is still thin, so you wouldn’t be able to breathe up in the mesosphere. But there is more gas in this layer than there is out in the thermosphere.
Q. What is a fact about the exosphere?
The exosphere is the highest and top layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. It marks the edge of space. There are very few molecules in this layer. The lightest atmospheric gases such as hydrogen and helium exist throughout the exosphere.
Q. Is the exosphere the thinnest layer?
The air in the exosphere is extremely thin – in many ways it is almost the same as the airless void of outer space. The layer directly below the exosphere is the thermosphere; the boundary between the two is called the thermopause. However, other scientists do consider the exosphere part of our planet’s atmosphere.
Q. Is the exosphere the coldest layer?
exosphere—contains few particles that move into and from space. mesopause—the boundary between the mesosphere and the thermosphere; the coldest place on Earth. mesosphere—the layer in which most meteors burn up after entering Earth’s atmosphere and before reaching Earth’s surface.
Q. Why is the exosphere cold?
When particles are bouncing around more slowly, the temperature is cooler. The particles in the exosphere are moving very quickly, so the temperature there is quite hot. However, the exosphere would feel quite cold to us.
Q. How hot is the exosphere?
Temperature of the Exosphere The exosphere is closer to the Sun than the other layers of the atmosphere and therefore is the warmest. However, the temperature of the exosphere varies greatly, usually between 0 °C and 1700 °C, and can even experience very cold temperatures, which is attributed to several factors.
Q. What layer is the ozone?
the stratosphere
Q. What are the 2 types of ozone?
Ozone or “O3” is a colorless gas composed of three atoms of oxygen (O3). There are two types of ozone, both “good” ozone and “bad” ozone.
Q. Is the ozone hole bad?
Ozone layer depletion causes increased UV radiation levels at the Earth’s surface, which is damaging to human health. Negative effects include increases in certain types of skin cancers, eye cataracts and immune deficiency disorders.
Q. Where is the ozone layer most damaged?
lower stratosphere
Q. Is there no ozone layer in Canada?
The ozone layer over southern Canada has thinned by an average of about 7% since the 1980s. In the late 1990s, average ozone depletion in the summer over Canada was between 3% and 7%. Ozone depletion in Canada is usually greatest in the late winter and early spring. Large Antarctic ozone holes continue to occur.
Q. Which country has no ozone layer?
Antarctica
Q. How long until the ozone layer is gone?
The ozone layer is expected to return to normal levels by about 2050. But, it is very important that the world comply with the Montreal Protocol; delays in ending production and use of ozone-depleting substances could cause additional damage to the ozone layer and prolong its recovery.