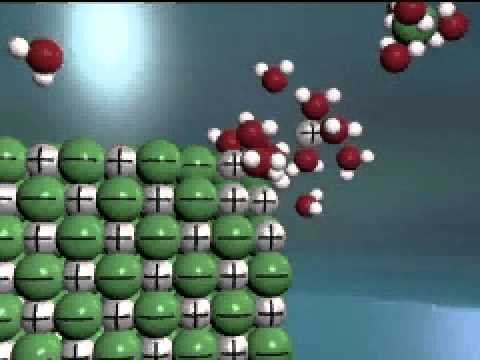
Q. Does NaCl dissociate or ionize?
Dissociation occurs when atoms or groups of atoms break off from molecules and form ions. Consider table salt (NaCl, or sodium chloride): when NaCl crystals are added to water, the molecules of NaCl dissociate into Na+ and Cl– ions, and spheres of hydration form around the ions.
Q. How does sodium chloride dissociate in water?
In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. This property makes the Na+ and Cl- ions break apart under the stronger attractions provided by the water molecules.
Table of Contents
- Q. Does NaCl dissociate or ionize?
- Q. How does sodium chloride dissociate in water?
- Q. Is dissociation of NaCl reversible?
- Q. How many ions does NaNO3 dissociate into?
- Q. What is the formula for sodium phosphate?
- Q. Why do ions dissociate?
- Q. What is an example of dissociation in chemistry?
- Q. Why do most ionic compounds dissociate?
- Q. What is the degree of dissociation?
- Q. Can degree of dissociation be greater than 1?
- Q. What is the degree of dissociation of sodium chloride?
- Q. What is the van’t Hoff factor of NaCl?
- Q. What is abnormal molar mass of NaCl?
- Q. Are equimolar solutions of sodium chloride and urea isotonic?
- Q. Why is equimolar solution of sodium chloride and sodium sulphate not isotonic?
- Q. What is isotonic solution?
- Q. Why are the equimolar solutions of NaCl and glucose not isotonic?
- Q. Why equimolar NaCl and cane sugar do not have same osmotic pressure?
- Q. What are equimolar solutions?
- Q. Why equimolar solution of NaCl and cane sugar do not have the same osmotic pressure?
- Q. What is mean by equimolar proportion?
- Q. How do you make an equimolar solution?
- Q. Which is a Colligative property?
- Q. What are the 4 Colligative properties?
- Q. Which is the most important Colligative property?
- Q. What does Raoult’s law state?
- Q. What is Raoult’s Law and its application?
- Q. In which case Raoult’s Law is not applicable?
Q. Is dissociation of NaCl reversible?
This process is called dissociation. Note that the positive side of the water molecule will be attracted to the negative chlorine ion and the negative side of the water molecule to the positive sodium ions. It can be reversed by removing (evaporating) the water.
Q. How many ions does NaNO3 dissociate into?
Why Na2SO4 dissociate into 3 while NaNO3 dissociate into 2? Na2SO4 dissociates into 3 ions becasue in water it results in 2Na+ and SO42-. Likewise, NaNO3 results in Na+ and NO3-. Remember, you have to add the coefficients of the ions to get the sum of all ions.
Q. What is the formula for sodium phosphate?
Na₃PO₄
Q. Why do ions dissociate?
In electrolytic, or ionic, dissociation, the addition of a solvent or of energy in the form of heat causes molecules or crystals of the substance to break up into ions (electrically charged particles). Most dissociating substances produce ions by chemical combination with the solvent.
Q. What is an example of dissociation in chemistry?
Dissociation Reaction Examples The reaction in which water breaks into hydrogen and hydroxide ions is a dissociation reaction. When a molecular compound undergoes dissociation into ions, the reaction can also be called ionization. When acids undergo dissociation, they produce hydrogen ions. HCl → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Q. Why do most ionic compounds dissociate?
Every ionic compound has an energy holding the lattice structure of the compound, known as lattice energy. If the hydration energy of an ionic compound exceeds its lattice energy, the lattice is broken and the ions in the compound separate, causing the compound to dissolve.
Q. What is the degree of dissociation?
The degree of dissociation is the phenomenon of generating current carrying free ions, which are dissociated from the fraction of solute at a given concentration.
Q. Can degree of dissociation be greater than 1?
Why is the degree of dissociation of acids more than 1? (amount of the reactant dissociated) / (amount of the reactant present initially). This ratio cannot be greater than 1, since you can’t dissociate more than is present. Degree of dissociation is basically the fraction of a mole of a reactant that has dissociated.
Q. What is the degree of dissociation of sodium chloride?
0.84
Q. What is the van’t Hoff factor of NaCl?
Sodium chloride consists of two ions i.e. the sodium ion and the chlorine ion. So, the Van’t Hoff factor for NaCl considering complete dissociation is 2.
Q. What is abnormal molar mass of NaCl?
Thus, the experimental molar mass of NaCl is 117. Thus, the experimental molar mass is greater than the calculated molar mass. Thus, the molar mass of NaCl determined experimentally following elevation in the boiling point or depression in freezing point method is >58.5 g mol−1.
Q. Are equimolar solutions of sodium chloride and urea isotonic?
In case you know about Vant off’s factor (i), then this question is easier to solve. And if osmotic pressure of 2 solutions is same then they are considered as isotonic solutions. Clearly, they are not equal. They are not isotonic evenafter being equimolar.
Q. Why is equimolar solution of sodium chloride and sodium sulphate not isotonic?
Explain why equimolar aqueous solution chloride and sodium sulphate are not isotonic? Thus, equimolar solution of NaCl and Na2SO4 have different concentrations of ions in the solution. As osmotic pressure depends upon concentration of particles in the solution, they have different osmotic pressures.
Q. What is isotonic solution?
Isotonic solution: A solution that has the same salt concentration as cells and blood. Isotonic solutions are commonly used as intravenously infused fluids in hospitalized patients.
Q. Why are the equimolar solutions of NaCl and glucose not isotonic?
glucose is non electrolyte and when added in water, it does not break into ions. nacl is an electrolyte and when added to water, it dissociates into ions of na+ and cl- ions completely. the two solutions will have different osmotic pressures, but same concentration.
Q. Why equimolar NaCl and cane sugar do not have same osmotic pressure?
Isotonic solutions are those having same concentrations and osmotic pressure but NaCl and Glucose have not the same osmotic pressure due to the different Van’t Hoff factor.
Q. What are equimolar solutions?
Hint:Equimolar solutions are the solution which contains the same number of moles of solute dissolved in a solvent. Hence the concentration of the solution or molarity or molality will be the same.
Q. Why equimolar solution of NaCl and cane sugar do not have the same osmotic pressure?
one mole of sugar in water gives only one mole of solute species. Common salt(NaCl) is an ionic compound, and in aqueous solution it completely dissociates into Na+ and Cl- ions. Hence, the two solutions will have different osmotic pressures, despite having the same concentration.
Q. What is mean by equimolar proportion?
The definition of equimolar is having the same amount of moles. An example of equimolar substances are ones that both have five moles.
Q. How do you make an equimolar solution?
It is a mixture of the same number of moles (gram molecular weights) of two or more compounds. Could be dry, but usually in solution. E.g., take 58.5g NaCl and 74.5g KCl and dissolve to make up a liter of water. This would be an equimolar mixture of one mole each of sodium and potassium chloride.
Q. Which is a Colligative property?
Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions, but not upon the identity of the solute. Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
Q. What are the 4 Colligative properties?
There are four colligative properties: vapor pressure lowering, boiling point ele- vation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. This means that a solution shows a decreased vapor pressure, an increased boiling point and a decreased freez- ing point in comparison to the pure solvent (water in our case).
Q. Which is the most important Colligative property?
Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and membrane osmometry. The latter property is considered here, since it is the most important of the group as far as synthetic polymers are concerned. Figure 3.1. System for demonstration of osmotic pressure.
Q. What does Raoult’s law state?
Assuming γ1 = γ2 = 1, equations for y1P and y2P express what is commonly known as Raoult’s law, which states that at constant temperature the partial pressure of a component in a liquid mixture is proportional to its mole fraction in that mixture (i.e., each component exerts a pressure that depends directly on the …
Q. What is Raoult’s Law and its application?
One of the simplest and most widely applied for non- aqueous mixtures is Raoult’s law. It is used to estimate the contribution of individual components of a liquid or solid mixture to the total pressure exerted by the system, espe- cially for discrete mixtures where the quantity of each com- ponent is known.
Q. In which case Raoult’s Law is not applicable?
Raoults law is not applicable if the total number of particles of solute changes in the solution due to association or dissociation.