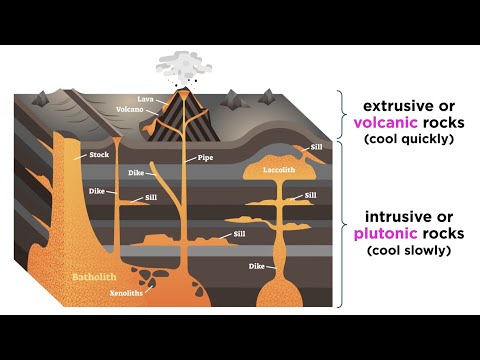
Q. Does rhyolite or basalt have more mafic composition?
Compilations of many rock analyses show that rhyolite and granite are felsic, with an average silica content of about 72 percent; syenite, diorite, and monzonite are intermediate, with an average silica content of 59 percent; gabbro and basalt are mafic, with an average silica content of 48 percent; and peridotite is …
Q. Which rock is most felsic?
granite
Table of Contents
- Q. Does rhyolite or basalt have more mafic composition?
- Q. Which rock is most felsic?
- Q. What is the difference between rhyolite and basalt?
- Q. Is Rhyolite a felsic rock?
- Q. Why is rhyolite so high in silica?
- Q. How can you tell if a rock is rhyolite?
- Q. What can rhyolite turn into?
- Q. What does rhyolite look like?
- Q. What is rhyolite used for today?
- Q. Why is rhyolite lava so explosive?
- Q. What are the characteristics of Rhyolite?
- Q. Where are rhyolite found?
- Q. What mineral is in rhyolite and andesite?
- Q. Why is rhyolite red?
- Q. How do you cleanse Rhyolite?
- Q. Is Obsidian Rhyolite?
- Q. Is Jasper a rhyolite?
- Q. Is Rainforest Jasper the same as Rhyolite?
- Q. Is Bloodstone a crystal?
Q. What is the difference between rhyolite and basalt?
The main difference between basalt and rhyolite is that basalt usually appears in dark colours, while rhyolite usually appears in light colours. Basalt is an extrusive igneous rock type. Rhyolite is considered as an extrusive volcanic rock that is equivalent to granite.
Q. Is Rhyolite a felsic rock?
Most rhyolites are light gray to pinkish in color, but red or even black rhyolites are not rare.
Q. Why is rhyolite so high in silica?
oʊˌlaɪt, -ə-/ RY-oh-lyte, -ə-) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. Magma with the composition of rhyolite is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so rhyolitic magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows.
Q. How can you tell if a rock is rhyolite?
Rhyolite comes from the same lava as granite but with smaller crystals because it has cooled quickly on the surface. The crystal size is one of the keys to identifying it as an extrusive igneous rock. It is a viscous lava so it is slow flowing and often displays flow banding from solidifying as it moves.
Q. What can rhyolite turn into?
If rhyolite magma is gas rich it can erupt explosively, forming a frothy solidified magma called pumice (a very lightweight, light-coloured, vesicular form of rhyolite) along with ash deposits, and / or ignimbrite. In certain situations extremely porous rhyolite lava flows may develop.
Q. What does rhyolite look like?
Rhyolite is a fine-grained extrusive igneous rock or volcanic rock. It is pale coloured, often light grey, tan or pinkish. Rhyolite is made up of quartz and feldspar crystals, and occasionally contains some mafic (dark coloured) minerals.
Q. What is rhyolite used for today?
4.33) with relatively large thickness and small propagation due to the high viscosity and low capacity of lava flow. Rhyolite is suitable as aggregate, fill-in construction, building material and road industries, decorative rock in landscaping, cutting tool, abrasive and jewelry.
Q. Why is rhyolite lava so explosive?
Explosive eruptions are favored by high gas content and high viscosity (andesitic to rhyolitic magmas). Explosive bursting of bubbles will fragment the magma into clots of liquid that will cool as they fall through the air.
Q. What are the characteristics of Rhyolite?
Rhyolite is an extrusive igneous rock with a very high silica content. It is usually pink or gray in color with grains so small that they are difficult to observe without a hand lens. Rhyolite is made up of quartz, plagioclase, and sanidine, with minor amounts of hornblende and biotite.
Q. Where are rhyolite found?
Rhyolite is found in volcanic arcs where crustal rocks have been subducted under continental crust and melted into a lighter magma rich in silica.
Q. What mineral is in rhyolite and andesite?
Andesite (/ˈæn. dɪˌsaɪt, -də-, -ˌzaɪt/) is an extrusive volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between basalt and rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende.
Q. Why is rhyolite red?
Description: Rhyolite cobbles are river-worn cobbles of igneous rock. In Sonora these purplish-red rocks were originally formed from the cooling magma of volcanoes. They are especially rich in silica.
Q. How do you cleanse Rhyolite?
Clean rhyolite jewelry with a soft dry cloth to preserve polish. Clean quickly if the jewelry becomes soiled, as jaspers can be porous and easily stained. Wash with warm, soapy water and a soft cloth or soft brush. Dry thoroughly.
Q. Is Obsidian Rhyolite?
Obsidian sample – dense volcanic glass, rhyolite composition. Obsidian is dense volcanic glass, usually rhyolite in composition and typically black in color. Obsidian forms in lava flows where the lava cools so fast that crystals do not have time to grow.
Q. Is Jasper a rhyolite?
Rhyolite is a rock but Ocean Jasper is Jasper (quartz). Ocean Jasper has Rhyolite in it.
Q. Is Rainforest Jasper the same as Rhyolite?
Rainforest Jasper is the green form of Rhyolite and comes from Western Australia. The Green Rhyolite is quite different to the more yellow form of Rhyolite that comes from Mexico and the USA, although they often may be fairly similar looking.
Q. Is Bloodstone a crystal?
Bloodstone is a Seeker Transformer crystal. Seekers contain a crystal energy structure that aligns the natural energy of the crystal to the natural power of the human mind in finding the way to new horizons and new capabilities.