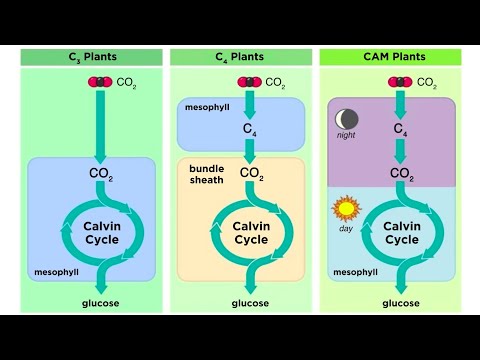
Q. How are C4 and CAM photosynthesis similar?
C3 photosynthesis produces a three-carbon compound via the Calvin cycle while C4 photosynthesis makes an intermediate four-carbon compound that splits into a three-carbon compound for the Calvin cycle. Plants that use CAM photosynthesis gather sunlight during the day and fix carbon dioxide molecules at night.
Q. What does photosynthesis in C4 plants and CAM plants have in common?
C4 and CAM plants are plants that use certain special compounds to gather carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) during photosynthesis. Using these compounds allows these plants to extract more CO 2 from a given amount of air, helping them prevent water loss in dry climates.
Table of Contents
- Q. How are C4 and CAM photosynthesis similar?
- Q. What does photosynthesis in C4 plants and CAM plants have in common?
- Q. What are the similarities and differences between C3 C4 and CAM plants?
- Q. What is an example of a C3 C4 and CAM plant?
- Q. What is the biggest difference between the C4 and CAM pathways?
- Q. Which is better C3 or C4 plants?
- Q. Is Banana C3 or C4?
- Q. Is tomato An example of C4 plant?
- Q. Is sugar beet C3 or C4?
- Q. How C3 and C4 plants are different?
- Q. Why do C4 plants are more expensive than C3 plants?
- Q. What is the meaning of C4 plant?
- Q. Do C4 plants use the Calvin cycle?
- Q. What are the characteristics of C4 plants?
- Q. Do C4 plants produce oxygen?
- Q. Why do C4 plants grow well in summer?
- Q. Why C4 plants are more efficient?
- Q. Why C4 plants are more productive class 11?
- Q. Why is Photorespiration absent in C4 plants?
- Q. Why C4 cycle is important?
- Q. Where does the C4 cycle get its name?
Q. What are the similarities and differences between C3 C4 and CAM plants?
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | C3 pathway | CAM |
|---|---|---|
| Cells involved | Mesophyll cells. | Both C3 and C4 in same mesophyll cells. |
| Example | Sunflower, Spinach, Beans, Rice, Cotton. | Cacti, orchids. |
| Can be seen in | All photosynthetic plants. | Semi-arid condition. |
| Types of plants using this cycle | Mesophytic, hydrophytic, xerophytic. | Xerophytic. |
Q. What is an example of a C3 C4 and CAM plant?
C4 plant, drawing of leaf anatomy: Most plants have C3 photosynthesis, eg. rice, wheat, barley and oats; tropical grasses for example are C4, sorghum, sugarcane and corn (maize); and CAM plants such as pineapple, agave and prickly pear cactus are found in very dry conditions.
Q. What is the biggest difference between the C4 and CAM pathways?
The main difference between C4 and CAM plants is the way they minimize water loss. C4 plants relocate the CO2 molecules to minimize photorespiration while CAM plants choose when to extract CO2 from the environment. Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plants where oxygen is added to RuBP instead of CO2.
Q. Which is better C3 or C4 plants?
The leaves possess kranz anatomy, and the chloroplasts of these plants are dimorphic. About 5% of plants on earth are C4 plants. Let us have a detailed look at the important difference between C3 and C4 plants….C3 vs C4 Plants.
| C3 Plants | C4 Plants |
|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide fixation is slow. | Carbon dioxide fixation is faster. |
Q. Is Banana C3 or C4?
CAM photosynthesis
| Characteristic | C3 Species | C4 Species |
|---|---|---|
| Crops | rice, wheat, barley, soybean, peanut, potato, sweet potato, taro, banana, bean, most vegetables, beet, cabbage, sunflower, all fruit trees studied, etc | corn, sugarcane, sorghum, millets, tropical grasses, Chinese spinach (an amaranth) |
Q. Is tomato An example of C4 plant?
C3 plants are those, in which the first stable product of carbon fixation is 3-carbon compound 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). Tomato is a C3 plant. Around 85% of plants are C3 plants. …
Q. Is sugar beet C3 or C4?
Peanuts, cotton, sugar beets, tobacco, spinach, soybeans, and most trees are C3 plants. Most lawn grasses such as rye and fescue are C3 plants. C3 plants have the disadvantage that in hot dry conditions their photosynthetic efficiency suffers because of a process called photorespiration.
Q. How C3 and C4 plants are different?
In C4 plants, the bundle sheath cells contain chloroplasts. In C3 plants, the carbon dioxide fixation takes place only at one place. In C4 plants, the carbon dioxide fixation takes places twice (one in mesophyll cells, second in bundle sheath cells). C3 plants possess only one CO2 acceptor.
Q. Why do C4 plants are more expensive than C3 plants?
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. How is C4 pathway more energy expensive that C3 ? C3 Cycle needs 18 ATP molecules for synthesis of one molecule of glucose whereas the C4 cycle needs 30 ATP molecules. Due to high energy requirement C4 cycle is more energy expensive than the C3 cycle.
Q. What is the meaning of C4 plant?
(2) A plant in which the CO2 is first fixed into a compound containing four carbon atoms before entering the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis. Supplement. A C4 plant is better adapted than a C3 plant in an environment with high daytime temperatures, intense sunlight, drought, or nitrogen or CO2 limitation.
Q. Do C4 plants use the Calvin cycle?
C4 plants are unique because they incorporate another type of carbon fixation that forms a four-carbon sugar (hence their name) before they undergo the Calvin cycle. In the C4 plants, the Calvin cycle occurs in the bundle-sheath cells (in C3 plants this occurs in the mesophyll cells).
Q. What are the characteristics of C4 plants?
Characteristics of C4 Plants
- C4 plants use C4 photosynthesis to avoid photorespiration.
- C4 plants make a four-carbon sugar during the Calvin cycle.
- C4 plants are suited for hot, dry climates and produce higher amounts of energy than C3 plants.
Q. Do C4 plants produce oxygen?
They are called C4 plants because the first product of carbon dioxide fixation is a 4-carbon compound, not PGA as it is in C3 plants. The answer is simple – C4 plants separate the site of oxygen production (PSII) from rubisco (Calvin cycle).
Q. Why do C4 plants grow well in summer?
C4 photosynthesis is an adaptation for plants living in hot, arid climates. Some plants that live in hot, dry climates maintain low oxygen levels in their leaves by keeping the stomata closed to prevent water loss. C4 plants have a special leaf anatomy, with prominent bundle sheath cells surrounding the leaf veins.
Q. Why C4 plants are more efficient?
C4 plants are more efficient than C3 due to their high rate of photosynthesis and reduced rate of photorespiration. The main enzyme of carbon fixation (Calvin cycle) is RuBisCO, i.e. ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase.
Q. Why C4 plants are more productive class 11?
C4 plants have a mechanism for increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide. The increase in CO2 ensures that the enzyme RuBisCo does not act as an oxygenase, but as a carboxylase. This prevents photorespiration and increases the rate of photosynthesis. Thus, C4 plants are highly productive.
Q. Why is Photorespiration absent in C4 plants?
The C4 plants have a unique krantz anatomy with agranal chloroplasts in bundle sheath cells. These plants maintain high concentration of carbon dioxide in the bundle sheath cells and absence of grana ensures no release of oxygen due to photolysis. Thus photorespiration is absent in C4 plants.
Q. Why C4 cycle is important?
When the stomata are open CO2 can diffuse in to be used in photosynthesis and O2, a product of photosynthesis can diffuse out. Plants that perform C4 photosynthesis can keep their stomata closed more than their C3 equivalents because they are more efficient in incorporation CO2. This minimizes their water loss.
Q. Where does the C4 cycle get its name?
Word origin: from the intermediate organic compound, which contains four carbon atoms, hence the name C4. Synonym: hatch slack kortshak pathway, Hatch-Slack pathway. Compare: C3 carbon fixation pathway, Crassulacean acid metabolism. See also: C4 plant.