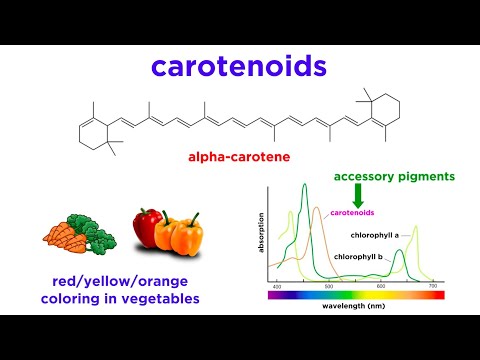
Q. How are carotenoid pigments different from chlorophyll?
Chlorophylls are greenish pigments which contain a porphyrin ring. This is a stable ring-shaped molecule around which electrons are free to migrate. Carotenoids are usually red, orange, or yellow pigments, and include the familiar compound carotene, which gives carrots their color.
Q. What is the difference between chlorophyll a chlorophyll b and beta carotene?
(a) Chlorophyll a, (b) chlorophyll b, and (c) β-carotene are hydrophobic organic pigments found in the thylakoid membrane. Chlorophyll a and b, which are identical except for the part indicated in the red box, are responsible for the green color of leaves. β-carotene is responsible for the orange color in carrots.
Table of Contents
- Q. How are carotenoid pigments different from chlorophyll?
- Q. What is the difference between chlorophyll a chlorophyll b and beta carotene?
- Q. What is the role of carotene and xanthophyll in photosynthesis?
- Q. What is the function of pigments such as β carotene and xanthophylls?
- Q. Is chlorophyll a more polar than B?
- Q. Is chlorophyll polar or nonpolar?
- Q. Is chlorophyll a or Pheophytin a more polar?
- Q. Is Pheophytin a more polar than chlorophyll?
- Q. Why is Xanthophyll so polar?
Q. What is the role of carotene and xanthophyll in photosynthesis?
Carotenes and their oxygenated derivatives, xanthophylls, are structural elements of the photosynthetic apparatus and contribute to increasing both the light-harvesting and photoprotective capacity of the photosystems.
Q. What is the function of pigments such as β carotene and xanthophylls?
In the eye, lutein and zeaxanthin are xanthophylls that protect the macula from blue and ultraviolet (UV)-light damage. All dietary carotenoids have antioxidant function; α carotene, β carotene, γ carotene, and β cryptoxanthin also have vitamin A activity.
Q. Is chlorophyll a more polar than B?
The distinctions between the chlorophylls, which are more polar than β-carotene is slight: chlorophyll a has a methyl group (Y=CH3) in a position where chlorophyll b has an aldehyde (Y=CHO). This makes chlorophyll b slightly more polar than chlorophyll a.
Q. Is chlorophyll polar or nonpolar?
Remember, chlorophylls and carotenoids are hydrophobic or nonpolar and will dissolve in less polar solvents, whereas anthocyanins are extractable and soluble in more polar solvents like water.
Q. Is chlorophyll a or Pheophytin a more polar?
Both chlorophylls contain C-O and C-N bonds, which are polar, and also contain magnesium bonded to nitrogen, which is such a polar bond it is almost ionic. Both chlorophylls are much more polar than -carotene. Pheophytin a is chlorophyll a without the Mg-ion.
Q. Is Pheophytin a more polar than chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll b and pheophytin b have one more oxygen atom around the ring than their a equivalents, making them more polar than their a equivalents, so they have smaller Rf values than their a equivalents.
Q. Why is Xanthophyll so polar?
Xanthophylls are very polar as they contain alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, acid, or epoxide groups, and thus may be extracted with ethyl alcohol or mixtures of ethyl alcohol and comparatively less polar solvents, such as chloroform (Houghton and Raman, 1998).