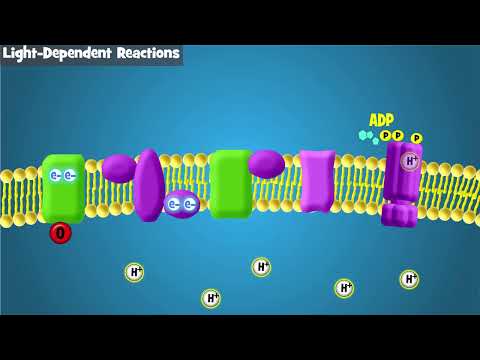
Q. How are electrons that are passed from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1 replaced?
Water is oxidized to replace the lost electron, generating H+ ions and oxygen (O-2) ions. These O-2 ions combine to form the diatomic O2. Electrons are passed from a photosystem into a redox or electron transport chain, eventually attaching to a chlorophyll molecule in Photosystem I (P700).
Q. How are photosystem 2 electrons replaced?
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. The energized electrons are replaced by oxidizing water to form hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen.
Table of Contents
- Q. How are electrons that are passed from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1 replaced?
- Q. How are photosystem 2 electrons replaced?
- Q. How does photosystem 1 replenish its electrons?
- Q. Where does photosystem I get its replacement electron?
- Q. What would happen if chloroplast stopped working?
- Q. Why the chloroplast is bad?
- Q. What year will we run out of oxygen?
- Q. What year will food run out?
- Q. What if Earth ran out of oxygen?
- Q. Will the earth ever run out of water?
- Q. What if we ran out of air?
- Q. What would happen if everyone on Earth held their breath?
- Q. What would happen if everyone stop breathing for 1 minute?
- Q. What would happen if everyone on Earth blinked at the same time?
- Q. Will the earth stop rotating?
- Q. What Year Will Earth die?
- Q. How long will it take for Earth to stop rotating?
- Q. Could the Earth survive without the moon?
Q. How does photosystem 1 replenish its electrons?
Electron transfer from P680 to electron acceptor. Travel of electrons down electron transport chain (creating ATP) Simultaneously, the excitation of pigments in Photosystem I. Transfer of these electrons to P700.
Q. Where does photosystem I get its replacement electron?
F. Photosystem I. Photosystem I receives electrons from plastocyanin or cytochrome c6 on the lumenal side of the thylakoid membrane and uses light energy to transfer them across the membrane to ferredoxin on the stromal side. It can also function in a cyclic electron transport pathway.
Q. What would happen if chloroplast stopped working?
Without chloroplasts, plants would not be able to get their energy from the sun and would cease to survive, leaving us without food. On the other hand, without mitochondria, animals would be lacking in cellular energy and would also fail to survive.
Q. Why the chloroplast is bad?
In stressful conditions such as drought and high temperature, a plant cell’s chloroplasts can become damaged and produce harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS). With these green organelles destroyed, young plants never became green.
Q. What year will we run out of oxygen?
approximately 1 billion years
Q. What year will food run out?
According to Professor Cribb, shortages of water, land, and energy combined with the increased demand from population and economic growth, will create a global food shortage around 2050.
Q. What if Earth ran out of oxygen?
Everyone would get sunburnt as oxygen makes up the ozone and normally helps to block out UV light. Water is one third oxygen, without it the Hydrogen becomes a free gas and expands, thereby destroying all living cells and evaporating the oceans. The earth below us would disappear and we would free fall.
Q. Will the earth ever run out of water?
While our planet as a whole may never run out of water, it’s important to remember that clean freshwater is not always available where and when humans need it. In fact, half of the world’s freshwater can be found in only six countries. Also, every drop of water that we use continues through the water cycle.
Q. What if we ran out of air?
Plants. Like trees, plants feed us and give us the oxygen we breathe—and if they were to run out, humans and animals would starve and suffocate. According to New Scientist, oxygen would remain in the atmosphere for quite a while, but we would run out of food long before we’d run out of air.
Q. What would happen if everyone on Earth held their breath?
The body can only live for approximately six minutes without oxygen, so if the entire human race stopped breathing for ten minutes, we would most likely all die/become unconcious.
Q. What would happen if everyone stop breathing for 1 minute?
For most people, it’s safe to hold your breath for a minute or two. Doing so for too much longer can decrease oxygen flow to the brain, causing fainting, seizures and brain damage. In the heart, a lack of oxygen can cause abnormalities of rhythm and affect the pumping action of the heart.
Q. What would happen if everyone on Earth blinked at the same time?
The ground would begin to shake, and if the jump happened near the coast, it could trigger a tsunami with 100-feet-tall waves. The shaking could also lead to an earthquake falling in the 4-8 magnitude range.
Q. Will the earth stop rotating?
The Earth will never stop rotating. Space is so empty, so devoid of anything to slow the Earth down, that it just spins and spins, practically without friction. The moon sloshing our oceans saps the tiniest amount of energy from our spin, as does space dust. But these effects are really trivial.
Q. What Year Will Earth die?
about 7.5 billion years
Q. How long will it take for Earth to stop rotating?
The moon is rotating around the Earth at a much slower pace, which like a brake being applied to the faster rotating Earth is slowing the Earth’s spin. Thus, the Earth will slow down until that moment in the future, when it will match the rotation of the moon around the Earth— 27.32 days or 559.68 hours.
Q. Could the Earth survive without the moon?
It is the pull of the Moon’s gravity on the Earth that holds our planet in place. Without the Moon stabilising our tilt, it is possible that the Earth’s tilt could vary wildly. It would move from no tilt (which means no seasons) to a large tilt (which means extreme weather and even ice ages).