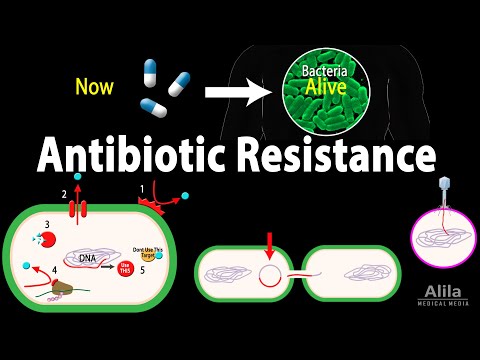
Q. How are plasmids confer antibiotic resistance in bacteria?
The plasmids can be transferred between bacteria within the same species or between different species via conjugation. Plasmids often carry multiple antibiotic resistance genes, contributing to the spread of multidrug-resistance (MDR).
Q. What role do plasmids play in antibiotic resistance?
Such plasmids, termed drug-resistance (R) factors, generally also specify the formation of sex pili, filamentous appendages on the cell surface. These promote bacterial conjugation, and hence permit the transfer of a copy of the plasmid from the resistant organism to one which may previously have been drug-sensitive.
Table of Contents
- Q. How are plasmids confer antibiotic resistance in bacteria?
- Q. What role do plasmids play in antibiotic resistance?
- Q. What are plasmids and how are they important to bacteria?
- Q. How are plasmids transferred between bacteria?
- Q. How does gene transfer work?
- Q. What are the disadvantages of gene therapy?
- Q. What diseases can be treated with gene therapy?
- Q. Why is horizontal gene transfer a problem?
- Q. How Covid-19 affect our life?
Q. What are plasmids and how are they important to bacteria?
Plasmids are important for bacterial evolution and adaptation to the changing environment, as they carry genes which carry beneficial traits for the bacterial cell. For example, plasmids can contain antibiotic resistance genes, posing a risk to public health. Plasmids carrying resistance genes are known as R plasmids.
Q. How are plasmids transferred between bacteria?
When a bacterium divides, all of the plasmids contained within the cell are copied such that each daughter cell receives a copy of each plasmid. Bacteria can also transfer plasmids to one another through a process called conjugation.
Q. How does gene transfer work?
In horizontal gene transfer, newly acquired DNA is incorporated into the genome of the recipient through either recombination or insertion. Recombination essentially is the regrouping of genes, such that native and foreign (new) DNA segments that are homologous are edited and combined.
Q. What are the disadvantages of gene therapy?
Potential Disadvantages of Gene Therapy Gene therapy poses a number of risks. The way the genes are delivered and the different vectors may present the following risks. DNA mutations The new gene might be inserted in the wrong location in the DNA, which might cause harmful mutations to the DNA or even cancer.
Q. What diseases can be treated with gene therapy?
Gene therapy holds promise for treating a wide range of diseases, such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, heart disease, diabetes, hemophilia and AIDS.
Q. Why is horizontal gene transfer a problem?
Horizontal gene transfer is common among bacteria, even among very distantly related ones. This process is thought to be a significant cause of increased drug resistance when one bacterial cell acquires resistance, and the resistance genes are transferred to other species.
Q. How Covid-19 affect our life?
COVID-19 has rapidly affected our day to day life, businesses, disrupted the world trade and movements. Identification of the disease at an early stage is vital to control the spread of the virus because it very rapidly spreads from person to person.