Q. How are rocks deformed?
Rocks become deformed when the Earth’s crust is compressed or stretched. The forces needed to do this act over millions of years – deformation is a very slow process!
Q. What are the 3 types of stress in rock deformation?
Stress is the force applied to a rock and may cause deformation. The three main types of stress are typical of the three types of plate boundaries: compression at convergent boundaries, tension at divergent boundaries, and shear at transform boundaries.
Table of Contents
- Q. How are rocks deformed?
- Q. What are the 3 types of stress in rock deformation?
- Q. What are the three components of deformation geology?
- Q. What are the two ways rocks permanently deform?
- Q. What are 3 types of deformation?
- Q. What are the 2 types of deformation?
- Q. What is deformation and write its formula?
- Q. What are the four basic forms of deformation of solid bodies?
- Q. What is a deformation?
- Q. What is deformation formula?
- Q. How does deformation occur?
- Q. What is ductile deformation?
- Q. What is an example of ductile?
- Q. Where does ductile deformation occur?
- Q. What’s the difference between ductile and brittle?
- Q. Is ductile or brittle stronger?
- Q. What is ductility material?
- Q. Which material has the highest ductility?
- Q. How do you determine which material is more ductile?
- Q. What is ductility in simple words?
- Q. What is difference between ductility and malleability?
- Q. What are examples of malleability?
- Q. What do you mean by ductility class 8?
- Q. What is an element for Class 8?
- Q. What is displacement reaction for Class 8?
- Q. Why are bells made of metals Class 8?
- Q. Why are wooden bells not used in schools?
- Q. Why are metals used in Bells?
- Q. Why are the bells made of metals?
Q. What are the three components of deformation geology?
The three components of deformation: translation, strain, and rotation (Means, 1976) constitute the total displacement fi eld for material moving within an orogenic system.
Q. What are the two ways rocks permanently deform?
Rocks deform permanently in two ways: brittle deformation and ductile deformation.
Q. What are 3 types of deformation?
When a rock is subjected to increasing stress it passes through 3 successive stages of deformation. Elastic Deformation — wherein the strain is reversible. Ductile Deformation — wherein the strain is irreversible. Fracture – irreversible strain wherein the material breaks.
Q. What are the 2 types of deformation?
Deformation can be of two types as follows: Permanent Deformation – Also known as plastic deformation, it is irreversible. It is a type of deformation that stays even after the removal of applied forces. Temporary Deformation – Also known as elastic deformation, it is reversible.
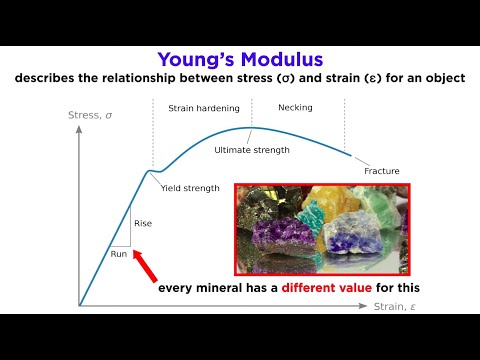
Q. What is deformation and write its formula?
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. Displacements are the absolute change in position of a point on the object. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is elastic.
Q. What are the four basic forms of deformation of solid bodies?
3 Introduction Forces result in four basic forms of deformations or displacements of structures or solid bodies and these are: TENSION COMPRESSION BENDING TWISTING Torsion is one of the common modes of deformations in which shafts are subjected to torques about its longitudinal axis resulting in twisting deformations.
Q. What is a deformation?
1 : alteration of form or shape also : the product of such alteration. 2 : the action of deforming : the state of being deformed. 3 : change for the worse.
Q. What is deformation formula?
A general deformation of a body can be expressed in the form x = F(X) where X is the reference position of material points in the body. Such a measure does not distinguish between rigid body motions (translations and rotations) and changes in shape (and size) of the body.
Q. How does deformation occur?
When a sufficient load is applied to a metal or other structural material, it will cause the material to change shape. This change in shape is called deformation. A temporary shape change that is self-reversing after the force is removed, so that the object returns to its original shape, is called elastic deformation.
Q. What is ductile deformation?
Ductile deformation involves the production of large, open folds in the sediments or rocks in front of an advancing glacier, which may develop into overfolds or begin to undergo internal thrusting due to continued ice advance.
Q. What is an example of ductile?
Materials that have relatively large plastic regions under tensile stress are known as ductile . Examples of ductile materials include aluminum and copper.
Q. Where does ductile deformation occur?
Ductile deformation occurs in the deeper regions of the Earth due to two comtributing factors – pressure and temperature. When a rock is burried the weight of the overlying material puts a pressure on the rock that acts in all direction and confines it.
Q. What’s the difference between ductile and brittle?
Ductile: A material that can be easy bent or material can be drawn into wires. Brittle: A material that instantly snaps by external load application. Ductile: Such material will undergo plastic deformation before fracture. Brittle: These material show zero plastic deformation after stress and instantly break.
Q. Is ductile or brittle stronger?
In general, soft tough metals will be ductile. Harder, stronger metals tend to be more brittle. The relationship between strength and hardness is a good way to predict behavior. Mild steel (AISI 1020) is soft and ductile; bearing steel, on the other hand, is strong but very brittle.
Q. What is ductility material?
4 Ductility and malleability. Ductility is the ability of a material to sustain a large permanent deformation under a tensile load up to the point of fracture, or the relative ability of a material to be stretched plastically at room temperature without fracturing.
Q. Which material has the highest ductility?
platinum
Q. How do you determine which material is more ductile?
The reduction of area, being measured at the minimum diameter of the neck, is a better indicator of ductility. Ductility is more commonly defined as the ability of a material to deform easily upon the application of a tensile force, or as the ability of a material to withstand plastic deformation without rupture.
Q. What is ductility in simple words?
: the quality or state of being ductile especially : the ability of a material to have its shape changed (as by being drawn out into wire or thread) without losing strength or breaking When certain alloys are added to metal, hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. —
Q. What is difference between ductility and malleability?
A malleable material is one in which a thin sheet can be easily formed by hammering or rolling. In contrast, ductility is the ability of a solid material to deform under tensile stress. Practically, a ductile material is a material that can easily be stretched into a wire when pulled as shown in the figure below.
Q. What are examples of malleability?
Examples of malleable metals are gold, iron, aluminum, copper, silver, and lead. Gold and silver are highly malleable. When a piece of hot iron is hammered it takes the shape of a sheet.
Q. What do you mean by ductility class 8?
The property which allow the metals to be drawn into wires is called ductility.
Q. What is an element for Class 8?
A substance which cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by chemical reactions is called an element. For Example: Iron,hydrogen,helium,oxygen,phosphorus,sulphur,chlorine,bromine,gold,silver,mercury, aluminium etc.
Q. What is displacement reaction for Class 8?
In displacement reaction a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal but a less rwactive metal cannot displace a more reactive metal.
Q. Why are bells made of metals Class 8?
bells are made from metals because metals have a property of producing a ringing on striking called sonorous property. metals are also very strong and light.
Q. Why are wooden bells not used in schools?
Answer Expert Verified Bells are made up of metals Rather than wood because according to the physical properties of metals, they have highly sonorous….and if you would bang a piese of wood instead of wood , no voice will be produced and hence your bell will be of no use…..!!!!!!!!!!
Q. Why are metals used in Bells?
Metals are used in making bellsbecause they are sonorous that is they produce a ringing sound when we strike them. Because they are sonorous ie they make sound. Metalsused for bells are specially designed alloys that make a nice ringing sound. Small bellsmay be made of glass or ceramic.
Q. Why are the bells made of metals?
The reason that bells are made of metals is that metals are sonorous. Hence, metals can make the deep ringing sound, the sound of the bell you’re familiar with.