Q. How can we convert galvanometer into ammeter and voltmeter?
A galvanometer can be converted into ammeter by connecting a low resistance called shunt in parallel to the galvanometer. A voltmeter is a device used to measure the potential difference between two points in a circuit.
Q. How will you convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter?
A galvanometer can be converted in to a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance in series connection within it. The scale is calibrated in volt. The value of the resistance connected in series decides the range of the voltmeter. The resistance is calculated by this equation which is connected in series.
Table of Contents
- Q. How can we convert galvanometer into ammeter and voltmeter?
- Q. How will you convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter?
- Q. What modification will be required to convert galvanometer into ammeter?
- Q. How do you convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter explain with a circuit diagram?
- Q. Why do we convert galvanometer into voltmeter?
- Q. Why an ammeter is always connected in series?
- Q. What if ammeter is connected in parallel?
- Q. Does ammeter have high resistance?
- Q. What is current formula?
- Q. What is ammeter measured in?
- Q. What is the reading on ammeter A3?
- Q. At which position should an ammeter be placed?
- Q. What is the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor?
- Q. How do you find current?
- Q. Is current the same in parallel?
- Q. What is wattage formula?
- Q. What is voltage drop formula?
- Q. How much voltage drop is too much?
- Q. How do I calculate wire size?
- Q. How much voltage drop is acceptable 120v?
- Q. How much voltage drop is acceptable 24v?
- Q. How do you fix voltage drop?
- Q. How far can you go before voltage drop?
- Q. How deep do you need to bury electrical wire?
- Q. What wire size do I need to go 100 feet for a 60 amp service to a workshop?
- Q. How many feet can 12 gauge wire run?
- Q. How many outlets can I run on a 20 amp breaker?
- Q. How many outlets can you run on a 12 2 wire?
- Q. Is it OK to mix 12 and 14 gauge wire?
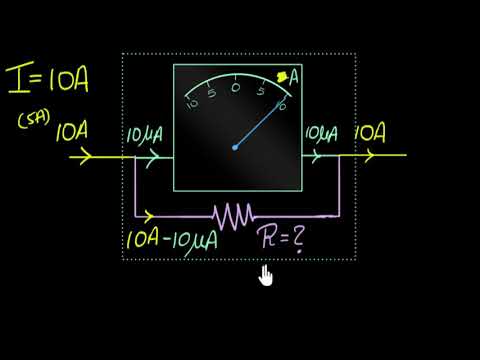
Q. What modification will be required to convert galvanometer into ammeter?
Since galvanometer is a very sensitive instrument that cannot measure heavy currents in order to convert a galvanometer into ammeter we have to put a low resistance called shunt in parallel to it so that most of the current goes through it , and our device can measure the accurate value.
Q. How do you convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter explain with a circuit diagram?
A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a large resistance in series to the galvanometer which is shown in diagram. Let G and R be the resistance of a galvanometer and a conductor connected in series with it respectively.
Q. Why do we convert galvanometer into voltmeter?
To convert a moving coil galvanometer to a voltmeter, we add a high series resistance, but why?. The high resistance causes most of the voltage to drop across it, leaving a small voltage drop across the galvanometer. This also ends up making the voltmeter have very high resistance.
Q. Why an ammeter is always connected in series?
In order for an ammeter to measure a device’s current, it must be connected in series to that device. This is necessary because objects in series experience the same current. Ammeter in Series: An ammeter (A) is placed in series to measure current. All of the current in this circuit flows through the meter.
Q. What if ammeter is connected in parallel?
When ammeter is connected in parallel to the circuit, net resistance of the circuit decreases. Hence more current is drawn from the battery, which damages the ammeter.
Q. Does ammeter have high resistance?
1 ) Resistance of an ammeter is low. As ammeter is connected in series in the circuit, effective resistance is the sum of resistance of the circuit and the resistance of ammeter. Thus small resistance of ammeter would not effect the current in the circuit. 2) Resistance of Voltmeter is High.
Q. What is current formula?
The current is the ratio of the potential difference and the resistance. It is represented as (I). The current formula is given as I = V/R. The SI unit of current is Ampere (Amp).
Q. What is ammeter measured in?
amperes
Q. What is the reading on ammeter A3?
Answer. Answer: the ammeter readings would be where A1 shows 1 ampere, A2 shows zero as bulb B2 blows off, A3 shows 1 ampere and A shows 2 amperes, the total current in the circuit.
Q. At which position should an ammeter be placed?
position 1
Q. What is the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor?
Now potential difference across 3 ohm resistor, V = IR. so Potential difference across 3 ohm resistor V = 3*1/3 = 1 Volt.
Q. How do you find current?
The current can be found from Ohm’s Law, V = IR. The V is the battery voltage, so if R can be determined then the current can be calculated.
Q. Is current the same in parallel?
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents flowing through each component.
Q. What is wattage formula?
The formula for calculating wattage is: W (joules per second) = V (joules per coulomb) x A (coulombs per second) where W is watts, V is volts, and A is amperes of current. In practical terms, wattage is the power produced or used per second. For example, a 60-watt light bulb uses 60 joules per second.
Q. What is voltage drop formula?
Voltage drop of the circuit conductors can be determined by multiplying the current of the circuit by the total resistance of the circuit conductors: VD = I x R.
Q. How much voltage drop is too much?
The NEC recommends that the maximum combined voltage drop for both the feeder and branch circuit shouldn’t exceed 5%, and the maximum on the feeder or branch circuit shouldn’t exceed 3% (Fig. 1). This recommendation is a performance issue, not a safety issue.
Q. How do I calculate wire size?
Wire Sizing Chart and Formula
- Calculate the Voltage Drop Index (VDI) using the following formula:
- VDI = AMPS x FEET ÷ (% VOLT DROP x VOLTAGE)
- Determine the appropriate wire size from the chart below.
Q. How much voltage drop is acceptable 120v?
4) in the National Electrical Code states that a voltage drop of 5% at the furthest receptacle in a branch wiring circuit is acceptable for normal efficiency. In a 120 volt 15 ampere circuit, this means that there should be no more than a 6 volt drop (114 volts) at the furthest outlet when the circuit is fully loaded.
Q. How much voltage drop is acceptable 24v?
The acceptable maximum voltage drop for DC loads is 5% of nominal battery voltage.
Q. How do you fix voltage drop?
The simplest way to reduce voltage drop is to increase the diameter of the conductor between the source and the load, which lowers the overall resistance. In power distribution systems, a given amount of power can be transmitted with less voltage drop if a higher voltage is used.
Q. How far can you go before voltage drop?
As an example, for a 120-volt circuit, you can run up to 50 feet of 14 AWG cable without exceeding 3 percent voltage drop….For 120-volt circuits:
| 14 AWG | 50 feet |
|---|---|
| 12 AWG | 60 feet |
| 10 AWG | 64 feet |
| 8 AWG | 76 feet |
| 6 AWG | 94 feet |
Q. How deep do you need to bury electrical wire?
In general, bury metal conduits at least 6 inches below the soil surface. You may also run them at a depth of 4 inches under a 4-inch concrete slab. Under your driveway, the conduits must be below a depth of 18 inches, and under a public road or alleyway, they must be buried below 24 inches.
Q. What wire size do I need to go 100 feet for a 60 amp service to a workshop?
If the circuit is 100 amp or less you have to size the conductors based on the 60-degree celsius column unless the breaker and the equipment terminations are rated for 75 or 90 degrees. You have to use a #4 conductor to feed a 60 amp circuit.
Q. How many feet can 12 gauge wire run?
A 12 gauge wire is typically good for 15 amp at 100 feet. For your 160 feet, they suggest a 6 gauge.
Q. How many outlets can I run on a 20 amp breaker?
10 outlets
Q. How many outlets can you run on a 12 2 wire?
For general use receptacles, In commercial buildings it is limited to 180VA per duplex or single receptacle, therefore on a 12/2 Romex cable not otherwise subject to ampacity derating and protected by a 20 amp circuit breaker, that would allow a maximum of 13 receptacles.
Q. Is it OK to mix 12 and 14 gauge wire?
Yes you can mix 12 and 14 gauge wire with a 15 amp breaker on the circuit. But it is not recommended because the next homeowner or electrician may be confused and put a 20 amp breaker on it again.