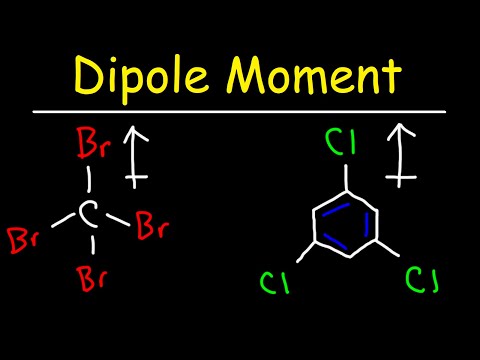
Q. How can you determine which way to draw a bond dipole?
A bond dipole is represented an arrow. The direction of the arrow always points the the negative end of the bond. A “+” is placed at the tail of the arrow to indicate the positive end of the bond.
Q. How are bond dipoles represented in Lewis structure diagrams?
Dipole vectors are shown as arrows pointing along the bond from the less electronegative atom toward the more electronegative atom. A small plus sign is drawn on the less electronegative end to indicate the partially positive end of the bond.
Table of Contents
- Q. How can you determine which way to draw a bond dipole?
- Q. How are bond dipoles represented in Lewis structure diagrams?
- Q. How do you know if a molecule has a dipole moment?
- Q. What can be used to represent bond dipole moments?
- Q. What is the symbol of dipole moment?
- Q. What is a dipole moment unit?
- Q. What is dipole moment explain with example?
- Q. What is dipole moment and its application?
- Q. What is the importance of dipole moment?
- Q. What is resultant dipole moment?
- Q. What is the dipole moment of HCl?
- Q. Is dipole moment a scalar or vector?
- Q. What is a dipole moment of zero?
- Q. Why the dipole moment of CCl4 is zero?
- Q. How do you calculate dipole moment?
- Q. Why is it called a dipole moment?
- Q. Is a dipole moment a vector?
- Q. What is P in a dipole?
- Q. How dipole is formed?
- Q. What is a dipole in a molecule?
- Q. What does dipole mean?
- Q. What is another word for dipole?
- Q. What is the charge of a dipole?
Q. How do you know if a molecule has a dipole moment?
The dipole moment of a molecule can be predicted by looking at the molecule’s structure and the location of the dipoles within the molecule. When a molecule has no dipole moment, it will be nonpolar. A molecule with a dipole moment will be polar.
Q. What can be used to represent bond dipole moments?
SO2 – has polar bonds and a bent structure, so it will have a new dipole. The magnitude of a bond dipole moment is represented by the Greek letter mu (u)and is a function of the magnitudes of the partial charges (Q), and the distance between the charge (r).
Q. What is the symbol of dipole moment?
μ
Q. What is a dipole moment unit?
The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system, that is, a measure of the system’s overall polarity. The SI units for electric dipole moment are coulomb-meter (C⋅m); however, a commonly used unit in atomic physics and chemistry is the debye (D).
Q. What is dipole moment explain with example?
A dipole moment is simply the measure of net polarity in a molecule. Polar molecules exhibit a large difference in electrical charge (a positive end and a negative end), otherwise known as a dipole moment. For example, ammonia (NHsub3) is a polar molecule.
Q. What is dipole moment and its application?
Application of dipole moment It is used for the calculation of the percentage ionic character, bond angle, electric polarization, and residual charge on the atoms in the molecules. It also helps to determine the size or shape of molecules and the arrangements of chemical bonds in the molecules.
Q. What is the importance of dipole moment?
The significance/applications of dipole moment are as follows: > Dipole moment is useful in finding the polar nature of the chemical bond: As the magnitude of dipole moment increases, the polar nature of the bond increases. Molecules with zero dipole moment are non-polar in nature.
Q. What is resultant dipole moment?
Resultant dipole moment was defined as net dipole moment of those receptor backbone atoms which interacts with the bonded ligand.
Q. What is the dipole moment of HCl?
1.08 D
Q. Is dipole moment a scalar or vector?
The simplest example is a pair of electric charges of two opposite signs and equal magnitude separated by distance. Electric dipole moment. Electric dipole moment is a vector quantity and it is represented as →p=q×→d in vector form.
Q. What is a dipole moment of zero?
A dipole moment of zero indicates that there is no partial charge on either end of a covalent bond.
Q. Why the dipole moment of CCl4 is zero?
Carbon tetrachloride molecule has zero dipole moment even though C and Cl have different electronegativities and each of the C – Cl bond is polar and has some dipole moment. This is because the individual dipole moments cancel out because of the symmetrical tetrahedral shape of the molecule.
Q. How do you calculate dipole moment?
A dipole moment is the product of the magnitude of the charge and the distance between the centers of the positive and negative charges. It is denoted by the Greek letter ‘µ’. It is measured in Debye units denoted by ‘D’. 1 D = 3.33564 × 10-30 C.m, where C is Coulomb and m denotes a meter.
Q. Why is it called a dipole moment?
When atoms in a molecule share electrons unequally, they create what is called a dipole moment. The differences in electronegativity and lone electrons give oxygen a partial negative charge and each hydrogen a partial positive charge.
Q. Is a dipole moment a vector?
Mathematically, dipole moments are vectors; they possess both a magnitude and a direction. The dipole moment of a molecule is therefore the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds in the molecule.
Q. What is P in a dipole?
The magnitude of the dipole moment vector p is the magnitude of the charge q times the distance d between them, p = qd. The vector points from the negative towards the positive charge.
Q. How dipole is formed?
An electric dipole is formed in a neutral system if the center of positive charge and the center of negative charge do not coincide. At the atomic scale, a molecule may have a permenant dipole moment if the electronic charge distribution is displaced with respect to the nuclear charge distribution.
Q. What is a dipole in a molecule?
Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. The partially positive end of a polar molecule is attracted to the partially negative end of another.
Q. What does dipole mean?
1a : a pair of equal and opposite electric charges or magnetic poles of opposite sign separated especially by a small distance. b : a body or system (such as a molecule) having such charges or poles.
Q. What is another word for dipole?
n. electric dipole, magnetic dipole, electric doublet.
Q. What is the charge of a dipole?
An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.)