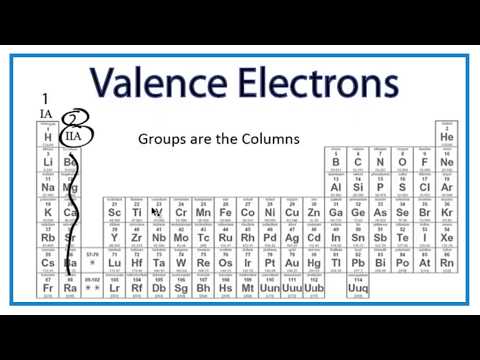
Q. How can you predict how many valence electrons an element has?
Explanation: For the first 3 short Periods, the Group, i.e. the column in which the element lies, tells you precisely how many valence electrons on the element.
Q. How many valence electrons are in a neutral atom of silicon?
four valence electrons
Table of Contents
- Q. How can you predict how many valence electrons an element has?
- Q. How many valence electrons are in a neutral atom of silicon?
- Q. How many valence electrons are in a neutral atom of phosphorus?
- Q. How many electrons are in an oxygen atom?
- Q. How do you identify an electron donor and acceptor?
- Q. Is Magnesium an electron donor?
- Q. Why is magnesium an electron donor?
- Q. Is chlorine an electron donor or acceptor?
- Q. Is Iodine an electron donor?
- Q. Is helium an electron donor?
- Q. How does iodine stain starch?
- Q. What is a charge-transfer process?
- Q. What is the difference between charge transfer and energy transfer?
- Q. How do you calculate transfer charges?
- Q. Can electrons be transferred without contact?
- Q. What is the transfer of charge from a distance?
- Q. What is electron transfer in physics?
- Q. What happens during an electron transfer?
- Q. How does an electron transfer?
Q. How many valence electrons are in a neutral atom of phosphorus?
5 valence electrons
Q. How many electrons are in an oxygen atom?
2, 6
Q. How do you identify an electron donor and acceptor?
Electron acceptors are ions or molecules that act as oxidizing agents in chemical reactions. Electron donors are ions or molecules that donate electrons and are reducing agents. In the combustion reaction of gaseous hydrogen and oxygen to produce water (H2O), two hydrogen atoms donate their electrons to an oxygen atom.
Q. Is Magnesium an electron donor?
In the [MgCl2(DEEDA)2] complex, magnesium is octahedrally coordinated by two chloride ligands trans to each other and two DEEDA molecules. The structures of the obtained magnesium chloride–electron donor complexes clearly show how diether and diamine electron donors can dictate the crystal structure of MgCl2.
Q. Why is magnesium an electron donor?
Mg donates two electrons to Fe2+ in FeO to give Mg2+ and Fe and O2–. The Mg2+ is combined with O2– in MgO. Thus the charge on both magnesium and iron change as a result of the electron transfer.
Q. Is chlorine an electron donor or acceptor?
Each chlorine atom can only accept 1 electron before it can achieve its noble gas configuration; therefore, 2 atoms of chlorine are required to accept the 2 electrons donated by the magnesium.
Q. Is Iodine an electron donor?
Electron donor-acceptor complexes of iodine with imidazole and some of its derivatives have been studied spectrophotometrically in chloroform. It is found that the equilibrium constants increase regularly as the electron donating character of the substituent is increased.
Q. Is helium an electron donor?
Helium compounds are best understood as donor-acceptor molecules consisting of He as electron donor and the respective acceptor fragment. The structures and energies of the helium compounds are rationalized by molecular orbital arguments and by analysis of the electron density and its associated Laplace field.
Q. How does iodine stain starch?
Amylose in starch is responsible for the formation of a deep blue color in the presence of iodine. The iodine molecule slips inside of the amylose coil. This makes a linear triiodide ion complex with is soluble that slips into the coil of the starch causing an intense blue-black color.
Q. What is a charge-transfer process?
A charge-transfer (CT) complex or electron-donor-acceptor complex is an association of two or more molecules, in which a fraction of electronic charge is transferred between the molecular entities. The resulting electrostatic attraction provides a stabilizing force for the molecular complex.
Q. What is the difference between charge transfer and energy transfer?
The charge transfer state can be probed with various time resolved techniques, like transient absorption. In case of Forster energy transfer, there has to be spectral overlap between the emission of the donor and the absorption of the acceptor.
Q. How do you calculate transfer charges?
Please note, that the total charge transfer is equal to charge (surface—molecule) minus [charge (molecule alone + surface alone)].
Q. Can electrons be transferred without contact?
Whenever electrons are transferred between objects, neutral matter becomes charged. For example, when atoms lose or gain electrons they become charged particles called ions. Three ways electrons can be transferred are conduction, friction, and polarization. It occurs without direct contact between the two objects.
Q. What is the transfer of charge from a distance?
Process of transferring charge by touching or rubbing is called charging by contact. Electrical forces act at a distance, charged objects brought near a neutral object will cause electrons to rearrange their position on that neutral object.
Q. What is electron transfer in physics?
Electron transfer is a fundamental process which plays a central role in physics, chemistry, and biology. Biological electron transfer reactions are required for respiration, photosynthesis, and redox reactions of intermediary metabolism.
Q. What happens during an electron transfer?
During electron transfer, an electron is accepted by an iron atom in the pigment portion of a cytochrome molecule, which thus is reduced; then the electron is transferred to the iron atom in the next cytochrome carrier in the electron transfer chain, thus oxidizing the first…
Q. How does an electron transfer?
Electron transfer (ET) occurs when an electron relocates from an atom or molecule to another such chemical entity. ET is a mechanistic description of a redox reaction, wherein the oxidation state of reactant and product changes. Numerous biological processes involve ET reactions.