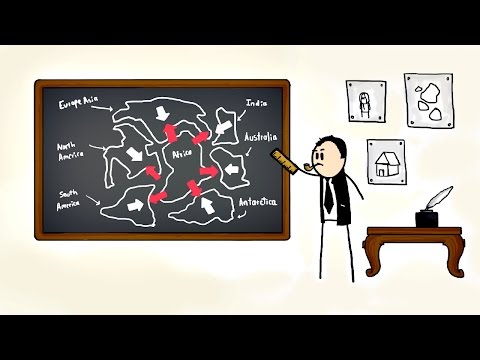
Q. How did plate tectonics affect evolution?
Plate tectonic processes such as the redistribution of continents, growth of mountain ranges, formation of land bridges, and opening and closing of oceans provide a continuous but moderate environmental pressure that stimulates populations to adapt and evolve.
Q. What is the effect of the movement of plates on the evolution and diversity of living things on different parts of the world?
As continents broke apart from Pangaea, species got separated by seas and oceans and speciation occurred. Individuals that were once able to interbreed were reproductively isolated from one another and eventually acquired adaptations that made them incompatible. This drove evolution by creating new species.
Table of Contents
- Q. How did plate tectonics affect evolution?
- Q. What is the effect of the movement of plates on the evolution and diversity of living things on different parts of the world?
- Q. How is the process of plate tectonics related to geologic events?
- Q. What would happen if the tectonic plates continue to move?
- Q. Will plate tectonics ever stop?
- Q. Why will Plate tectonics eventually end?
- Q. What is the fastest moving plate?
- Q. What don’t we know about plate tectonics?
- Q. Does Earth become smaller or bigger when plates move?
- Q. What are the 3 theories of plate tectonics?
- Q. What are the two theories of plate tectonics?
- Q. Which best describes the theory of plate tectonics?
- Q. How many tectonic plates are there?
- Q. Do smaller plates make you eat less?
- Q. What happens to the plate once it Submerages under another plate?
- Q. What will happen when two continental plates collide?
- Q. What zone is created when two plates move apart?
Q. How is the process of plate tectonics related to geologic events?
These tectonic plates rest upon the convecting mantle, which causes them to move. The movements of these plates can account for noticeable geologic events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and more subtle yet sublime events, like the building of mountains.
Q. What would happen if the tectonic plates continue to move?
Plate tectonics moves the continents around on a scale of 100s of millions of year. Plate tectonics also has an impact on longer-term climate patterns and these will change over time. It also changes ocean current patterns, heat distribution over the planet, and the evolution and speciation of animals.
Q. Will plate tectonics ever stop?
After the planet’s interior cooled for some 400 million years, tectonic plates began shifting and sinking. This process was stop-and-go for about 2 billion years. In another 5 billion years or so, as the planet chills, plate tectonics will grind to a halt.
Q. Why will Plate tectonics eventually end?
Instead of a gradual slowdown, Scotese predicts that plate tectonics will be invigorated during the next one to two billion years, before the conveyor belt ends. He reasons that as the mantle heat flow diminishes, the slabs will become extremely cool and dense, allowing them to subduct faster.
Q. What is the fastest moving plate?
The Cocos and Nazca plates (in the pacific ocean) are right now the quickest, moving at over 10 cm/yr.
Q. What don’t we know about plate tectonics?
“We don’t really know when plate tectonics as it looks today got started, but we do know that we have continental crust that was likely scraped off a down-going slab [a tectonic plate in a subduction zone] that is 3.8 billion years old,” Van der Elst said.
Q. Does Earth become smaller or bigger when plates move?
But the Earth isn’t getting any bigger. In locations around the world, ocean crust subducts, or slides under, other pieces of Earth’s crust. The boundary where the two plates meet is called a convergent boundary. Deep trenches appear at these boundaries, caused by the oceanic plate bending downward into the Earth.
Q. What are the 3 theories of plate tectonics?
Plates of lithosphere move because of convection currents in the mantle. One type of motion is produced by seafloor spreading. Plate boundaries can be located by outlining earthquake epicenters. Plates interact at three types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent and transform.
Q. What are the two theories of plate tectonics?
Plate Tectonics Theory The plates are moved around on Earth’s surface by seafloor spreading. Convection in the mantle drives seafloor spreading. Oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges.
Q. Which best describes the theory of plate tectonics?
The statement that best describes the theory of plate tectonics is the one that says that sections of Earth’s continents are in slow constant movement. Explanation: According to plate tectonic theory, the outermost part of the earth’s interior consists of two layers, the outer lithosphere and the inner asthenosphere.
Q. How many tectonic plates are there?
seven
Q. Do smaller plates make you eat less?
Smaller plates might not help us to eat any less, or at least not a meaningful reduction. One important thing to keep in mind when interpreting this result is that we conducted our study in a laboratory setting, where people only ate one type of food and ate alone in front of a TV.
Q. What happens to the plate once it Submerages under another plate?
A convergent plate boundary is where one of the tectonic plates submerge under the other. This could happen with multiple plates but in the diagrams shown there are only two. When an ocean plate is pushed under another ocean plates it goes right into the mantle and also has a subduction zone.
Q. What will happen when two continental plates collide?
What happens when two continental plates collide? Instead, a collision between two continental plates crunches and folds the rock at the boundary, lifting it up and leading to the formation of mountains and mountain ranges.
Q. What zone is created when two plates move apart?
Divergent boundaries