To find the unit step response, multiply the transfer function by the unit step (1/s) and the inverse Laplace transform using Partial Fraction Expansion..
Q. How do you find unit impulse response?
To find the unit impulse response of a system we simply take the inverse Laplace Transform of the transfer function.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you find unit impulse response?
- Q. What is step response of system?
- Q. What is the use of impulse response?
- Q. How do you interpret impulse response?
- Q. How does an impulse response work?
- Q. Which is correct for impulse signal?
- Q. What is impulse input?
- Q. What is the other name of a continuous time unit impulse function?
- Q. Which is true for unit impulse function?
- Q. Is unit step function bounded?
- Q. What is unit impulse function and unit step function?
- Q. What is the Laplace transform of a unit impulse function?
- Q. What is the Laplace transform of unit step?
- Q. What is T in Laplace transform?
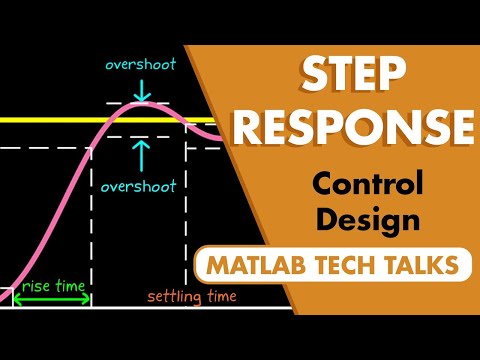
Q. What is step response of system?
In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from zero to one in a very short time. The concept can be extended to the abstract mathematical notion of a dynamical system using an evolution parameter.
Q. What is the use of impulse response?
In acoustic and audio applications, impulse responses enable the acoustic characteristics of a location, such as a concert hall, to be captured. Various packages are available containing impulse responses from specific locations, ranging from small rooms to large concert halls.
Q. How do you interpret impulse response?
Usually, the impulse response functions are interpreted as something like “a one standard deviation shock to x causes significant increases (decreases) in y for m periods (determined by the length of period for which the SE bands are above 0 or below 0 in case of decrease) after which the effect dissipates.
Q. How does an impulse response work?
Technically, an Impulse Response, or IR for short, refers to a system’s output when presented with a very short input signal called an impulse. Basically, you can send any device or chain of devices a specially crafted audio signal and the system will spit out a digital picture of its linear characteristics.
Q. Which is correct for impulse signal?
Which of the following is correct regarding to impulse signal? Explanation: When the input x[n] is multiplied with an impulse signal, the result will be impulse signal with magnitude of x[n] at that time.
Q. What is impulse input?
An impulse input is a very high pulse applied to a system over a very short time (i.e., it is not maintained). That is, the magnitude of the input approaches infinity while the time approaches zero.
Q. What is the other name of a continuous time unit impulse function?
Explanation: The continuous time unit impulse function is also known as the Dirac delta function.
Q. Which is true for unit impulse function?
Explanation: Unit impulse is an elementary signal with zero amplitude everywhere except at n = 0.
Q. Is unit step function bounded?
It’s true that the unit step function is bounded. However, a system which has the unit step function as its impulse response is not stable, because the integral (of the absolute value) is infinite.
Q. What is unit impulse function and unit step function?
In discrete time the unit step is a well-defined sequence, whereas in continuous time there is the mathematical complication of a discontinuity at the origin. In discrete time the unit impulse is the first difference of the unit step, and the unit step is the run- ning sum of the unit impulse.
Q. What is the Laplace transform of a unit impulse function?
The Unit Impulse The impulse function is drawn as an arrow whose height is equal to its area. Now we apply the sifting property of the impulse. Since the impulse is 0 everywhere but t=0, we can change the upper limit of the integral to 0+. So the Laplace Transform of the unit impulse is just one.
Q. What is the Laplace transform of unit step?
We saw some of the following properties in the Table of Laplace Transforms. Recall u(t) is the unit-step function. [You can see what the left hand side of this expression means in the section Products Involving Unit Step Functions.]
Q. What is T in Laplace transform?
The Laplace Transform of a function y(t) is defined by. if the integral exists. The notation L[y(t)](s) means take the Laplace transform. of y(t). The functions y(t) and Y(s) are partner functions.