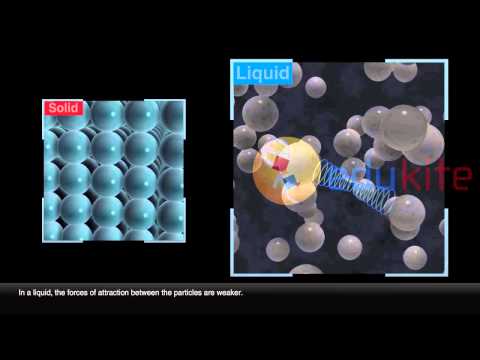
Solid – In a solid, the attractive forces keep the particles together tightly enough so that the particles do not move past each other. In the solid the particles vibrate in place. Liquid – In a liquid, particles will flow or glide over one another, but stay toward the bottom of the container.
Q. What is the relation between temperature and kinetic energy?
Temperature is directly proportional to the average translational kinetic energy of molecules in an ideal gas.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the relation between temperature and kinetic energy?
- Q. How do speed of molecules kinetic energy and temperature of matter affect each other?
- Q. What factors does molecular speed depend on?
- Q. What are the two main ideas of the kinetic molecular theory of matter?
- Q. How do changes in kinetic energy affect the state of matter?
- Q. Which state of matter is the strongest conductor of electricity?
- Q. Which solid has highest density?
- Q. What is difference between density and volume?
- Q. What is the relationship between area and volume?
- Q. What are the similarities and differences between surface area and volume?
Q. How do speed of molecules kinetic energy and temperature of matter affect each other?
If the temperature is increased, the average speed and kinetic energy of the gas molecules increase. If the volume is held constant, the increased speed of the gas molecules results in more frequent and more forceful collisions with the walls of the container, therefore increasing the pressure (Figure 1).
Q. What factors does molecular speed depend on?
The speed of the molecules in a gas is proportional to the temperature and is inversely proportional to molar mass of the gas. In other words, as the temperature of a sample of gas is increased, the molecules speed up and the root mean square molecular speed increases as a result.
Q. What are the two main ideas of the kinetic molecular theory of matter?
The simplest kinetic model is based on the assumptions that: (1) the gas is composed of a large number of identical molecules moving in random directions, separated by distances that are large compared with their size; (2) the molecules undergo perfectly elastic collisions (no energy loss) with each other and with the …
Q. How do changes in kinetic energy affect the state of matter?
Kinetic energy leads to disruptive forces in matters, which causes molecules to scatter and form gases. The state of a substance depends on the relative strength of the cohesive forces (potential energy) that hold particles together and the disruptive forces (kinetic energy) that tends to scatter them.
Q. Which state of matter is the strongest conductor of electricity?
Plasma
Q. Which solid has highest density?
The first chemical element with the lowest density is Hydrogen and the highest density is Osmium.
Q. What is difference between density and volume?
Volume – How much space an object or substance takes up. Mass – Measurement of the amount of matter in an object or substance. Density – How much space an object or substance takes up (its volume) in relation to the amount of matter in that object or substance (its mass).
Q. What is the relationship between area and volume?
The area is the amount of space occupied by a two-dimensional flat object in a plane. Volume is defined as the space occupied by the three-dimensional object. It is always measured in square units. It is always measured in cubic units.
Q. What are the similarities and differences between surface area and volume?
Finding surface area of solid figure is like finding how much wrapping paper that is required to cover the solid; it is the area of the outside faces of a box. It is measured in square units. Volume is the number of unit cubes that make up a solid figure. Volume is the amount of space inside of the solid figure.