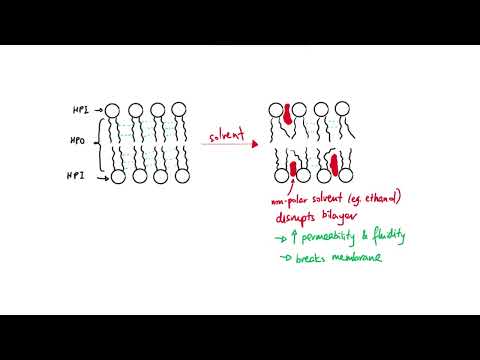
Q. How do phospholipids affect the permeability of the membrane?
Permeability of phospholipid bilayers. They contain multiple membrane-spanning regions that form a passage through the lipid bilayer, allowing polar or charged molecules to cross the membrane through a protein pore without interacting with the hydrophobic fatty acid chains of the membrane phospholipids.
Q. How does lipid structure affect membrane permeability?
At higher temperatures, lipid bilayers become more fluid (think about butter melting on a hot day), and more permeable or leaky. In mammals, cholesterol increases membrane packing to reduce membrane fluidity and permeability. The fatty acids tails of phospholipids also affect membrane fluidity.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do phospholipids affect the permeability of the membrane?
- Q. How does lipid structure affect membrane permeability?
- Q. How does phospholipid structure relate to the selective permeability?
- Q. How does the structure of the phospholipid help contribute to the structure of the phospholipid bilayer?
- Q. Which is a component of a phospholipid?
- Q. What can pass through phospholipid bilayer?
- Q. What is the role of a phospholipid?
- Q. What is the major phospholipid found in cell membranes?
- Q. Why is the membrane called a phospholipid bilayer?
- Q. Are roses prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Q. How does phospholipid structure relate to the selective permeability?
How does phospholipid structure relate to the selective permeability of the plasma membrane? Explanation: The structure of the plasma membrane makes it selectively permeable, enabling it to regulate the transport of substances into and out of the cell.
Q. How does the structure of the phospholipid help contribute to the structure of the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Structure Phospholipids are able to form cell membranes because the phosphate group head is hydrophilic (water-loving) while the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic (water-hating). This double layer, called a lipid bilayer, forms the main part of the cell membrane.
Q. Which is a component of a phospholipid?
A phospholipid molecule is constructed from four components: fatty acids, a platform to which the fatty acids are attached, a phosphate, and an alcohol attached to the phosphate (Figure 12.3).
Q. What can pass through phospholipid bilayer?
A pure artificial phospholipid bilayer is permeable to small hydrophobic molecules and small uncharged polar molecules. It is slightly permeable to water and urea and impermeable to ions and to large uncharged polar molecules.
Q. What is the role of a phospholipid?
Phospholipids play multiple roles in cells in forming the permeability barrier of the cell membrane and intracellular organdies, in providing the supporting matrix and surface for many catalytic processes, in actively participating in signal transduction in response to both external and internal stimuli, and in …
Q. What is the major phospholipid found in cell membranes?
Four major phospholipids predominate in the plasma membrane of many mammalian cells: phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin.
Q. Why is the membrane called a phospholipid bilayer?
The structure is called a “lipid bilayer” because it is composed of two layers of fat cells organized in two sheets. The lipid bilayer is typically about five nanometers thick and surrounds all cells providing the cell membrane structure.
Q. Are roses prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Rose petals are Eukaryotic, because they are multicelluar.