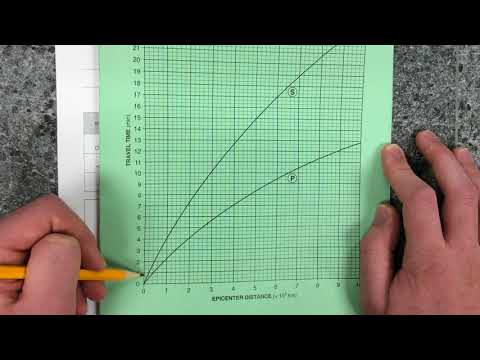
Q. How do scientists determine the distance from a seismic station to the epicenter of an earthquake?
Each seismograph records the times when the first (P waves) and second (S waves) seismic waves arrive. To determine the direction each wave traveled, scientists draw circles around the seismograph locations. The radius of each circle equals the known distance to the epicenter.
Q. How do scientists determine the location of an earthquake?
By looking at the amount of time between the P and S wave on a seismogram recorded on a seismograph, scientists can tell how far away the earthquake was from that location. Scientists then use a method called triangulation to determine exactly where the earthquake was (see image below).
Table of Contents
- Q. How do scientists determine the distance from a seismic station to the epicenter of an earthquake?
- Q. How do scientists determine the location of an earthquake?
- Q. How do scientists measure the distance earthquake waves travel?
- Q. What can one seismic station determine?
- Q. Which wave comes first in an earthquake?
- Q. What does a seismic station?
- Q. How many seismic stations are needed to locate an earthquake?
- Q. What is seismic period?
- Q. Who is responsible for seismic design?
- Q. What is fundamental period of vibration?
- Q. What is the fundamental period?
- Q. What is the formula for period of oscillation?
- Q. What is the period formula?
- Q. What is the period of oscillation?
- Q. What unit is period measured in?
- Q. What is the period of motion?
- Q. What does period of pendulum depend on?
- Q. What are the 6 types of motion?
- Q. What is the period of simple harmonic motion?
- Q. What is the formula of simple harmonic motion?
- Q. What is K in SHM?
- Q. How do you calculate period of motion?
- Q. What is the time period of a simple pendulum?
- Q. What is the equation for tangential acceleration?
- Q. What is the formula of circular motion?
- Q. What are the 3 equations of motion?
- Q. What can you say about objects moving in circular motion?
- Q. What is circular motion class 9?
Q. How do scientists measure the distance earthquake waves travel?
A seismograph produces a graph-like representation of the seismic waves it receives and records them onto a seismogram. This animation shows how distance is determined using P, S, and surface waves. The scientist then draws a circle with a radius equal to the distance from the epicenter for that seismograph.
Q. What can one seismic station determine?
One seismic station can give information about how far away the earthquake occurred, but yields little other information. The cartoonish amplified ground motions show the compressive P wave, the shearing S wave, and the rolling surface wave motions recorded by many stations with their characteristic seismograms.
Q. Which wave comes first in an earthquake?
P waves
Q. What does a seismic station?
Seismometers measure motions of the ground, including seismic waves generated by earthquakes, nuclear explosions, and other seismic sources.
Q. How many seismic stations are needed to locate an earthquake?
Three seismographs
Q. What is seismic period?
The time taken by the wave to complete one cycle of motion is called period of the earthquake wave. In general, earthquake shaking of the ground has waves whose periods vary in the range 0.03-33sec. Even within this range, some earthquake waves are stronger than the others.
Q. Who is responsible for seismic design?
At a high level, the responsibilities naturally lie with the person who will suffer loss in a disaster, which is ultimately the client, asset owner or tenant. However, the quality of construction, and therefore the seismic design, is regulated through federal, state and local governments.
Q. What is fundamental period of vibration?
Real structures are multi-degree-of freedom systems, and have several vibration modes, each with its own period of vibration. The mode with the longest period is called the fundamental period or natural period. High frequency loads such as walking or exercise (1 Hz – 3 Hz) can resonate with floor systems.
Q. What is the fundamental period?
According to periodic function definition the fundamental period of a function can be defined as the period of the function which are of the form, f(x+k)= f(x) f(x+k)=f(x), then k is known as the period of the function and the function f is known as a periodic function.
Q. What is the formula for period of oscillation?
This is the precise definition of “period”. The period formula, T = 2π√m/k, gives the exact relation between the oscillation time T and the system parameter ratio m/k.
Q. What is the period formula?
The period of a function f(x) is p, if f(x + p) = f(x), for every x. A function is said to be periodic if its value repeats after regular periods (intervals). The formula is Period, P = Period of parent function/ |Coefficient of x|
Q. What is the period of oscillation?
The period is the time it takes for an oscillating system to complete a cycle, whereas the frequency (f) is the number of cycles the system can complete in a given time period. For example, the Earth rotates once each day, so the period is 1 day, and the frequency is also 1 cycle per day.
Q. What unit is period measured in?
Period refers to the time for something to happen and is measured in seconds/cycle.
Q. What is the period of motion?
The period of the object’s motion is defined as the time for the object to complete one full cycle. Being a time, the period is measured in units such as seconds, milliseconds, days or even years. The standard metric unit for period is the second. An object in periodic motion can have a long period or a short period.
Q. What does period of pendulum depend on?
The period of a pendulum does not depend on the mass of the ball, but only on the length of the string. Two pendula with different masses but the same length will have the same period. Two pendula with different lengths will different periods; the pendulum with the longer string will have the longer period.
Q. What are the 6 types of motion?
Types of Motion
- Rectilinear motion,
- Circular motion,
- Periodic motion and.
- Rotational motion.
Q. What is the period of simple harmonic motion?
Since simple harmonic motion is a periodic oscillation, we can measure its period (the time it takes for one oscillation) and therefore determine its frequency (the number of oscillations per unit time, or the inverse of the period).
Q. What is the formula of simple harmonic motion?
That is, F = −kx, where F is the force, x is the displacement, and k is a constant. This relation is called Hooke’s law. A specific example of a simple harmonic oscillator is the vibration of a mass attached to a vertical spring, the other end of which is fixed in a ceiling.
Q. What is K in SHM?
Graph of displacement against time in simple harmonic motion. where F is force, x is displacement, and k is a positive constant. This is exactly the same as Hooke’s Law, which states that the force F on an object at the end of a spring equals -kx, where k is the spring constant.
Q. How do you calculate period of motion?
each complete oscillation, called the period, is constant. The formula for the period T of a pendulum is T = 2π Square root of√L/g, where L is the length of the pendulum and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Q. What is the time period of a simple pendulum?
A mass m suspended by a wire of length L is a simple pendulum and undergoes simple harmonic motion for amplitudes less than about 15º. The period of a simple pendulum is T=2π√Lg T = 2 π L g , where L is the length of the string and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Q. What is the equation for tangential acceleration?
The tangential acceleration = radius of the rotation * its angular acceleration. It is always measured in radian per second square. Its dimensional formula is [T-2].
Q. What is the formula of circular motion?
Equations
| Equation | Symbol breakdown |
|---|---|
| v = r ω v = r /omega v=rω | v v v is linear speed, r is radius, ω is angular speed. |
| T = 2 π ω = 1 f T = /dfrac{2/pi}{/omega} = /dfrac{1}{f} T=ω2π=f1 | T T T is period, ω is angular speed, and f is frequency |
Q. What are the 3 equations of motion?
Three Equations of Motion are v = u + at; s = ut + (1/2) at² and v² = u² + 2as and these can be derived with the help of velocity time graphs using definition acceleration.
Q. What can you say about objects moving in circular motion?
Uniform circular motion can be described as the motion of an object in a circle at a constant speed. As an object moves in a circle, it is constantly changing its direction. An object undergoing uniform circular motion is moving with a constant speed. Nonetheless, it is accelerating due to its change in direction.
Q. What is circular motion class 9?
The movement of a body following a circular path is called a circular motion. Now, the motion of a body moving with constant speed along a circular path is called Uniform Circular Motion. Here, the speed is constant but the velocity changes.