Q. How do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another quizlet?
How do the electron-dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another? Elements of the same group have the same number of valence electrons. The number of electrons in the electron-dot-structure will equal the group number for each element of the group.
Q. How do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another how do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another?
How does the electrondot structure of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another? In the periodic table the electron-dot structure of elements compare with one another by knowing how many valence electrons are paired and unpaired. To become a negative ion, an atom gains electrons.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another quizlet?
- Q. How do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another how do the electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another?
- Q. How do electron dot diagrams work?
- Q. Why do elements in the same group have similar Lewis dot structures?
- Q. What is a structure of an element?
- Q. What is carbons structure?
- Q. What’s the meaning of structure?
- Q. What are 3 types of structures?
- Q. What is an example of structure?
- Q. What are some examples of structures?
- Q. What are examples of natural structures?
- Q. What are the four types of structures?
- Q. What are the two types of structure?
- Q. What are the 5 types of structures?
- Q. What is meant by framed structure?
- Q. What are the different classifications of structure?
- Q. What is an example of a combination structure?
- Q. What are the types of framed structures?
- Q. What are the types of framing?
- Q. What is frame structure example?
- Q. What are some examples of combination structures?
- Q. What’s the difference between a shell structure and a frame structure?
- Q. What three properties do all structures have in common?
- Q. What makes a structure strong and stable?
- Q. What is the purpose of a solid structure?
- Q. What are examples of solid structures?
- Q. What are some disadvantages of solid structures?
- Q. What is a solid structure Grade 8?
- Q. How does the Lewis electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another?
- Q. What is the hybridization of SCl2?
- Q. What shape is CH2Cl2?
- Q. What shape is bf3?
- Q. What shape is alcl3?
- Q. What is the name for Li2S?
- Q. What is the chemical name of CCl₄?
- Q. What is the name of mgh2?
- Q. Is carbon tetrachloride used in fire extinguishers?
- Q. Why CCl₄ is used as fire extinguisher?
- Q. Is CCl4 flammable?
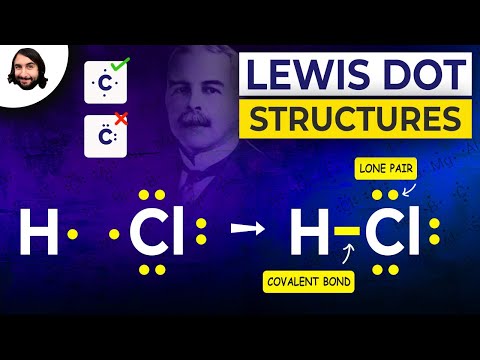
Q. How do electron dot diagrams work?
Electron dot diagrams are diagrams in which the valence electrons of an atom are shown as dots distributed around the element’s symbol. A beryllium atom, with two valence electrons, would have the electron dot diagram below. Electron dot diagrams would be the same for each element in the representative element groups.
Q. Why do elements in the same group have similar Lewis dot structures?
The columns are called GROUPS! (Columns go up and down.) Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the only electrons that are involved in bonding.
Q. What is a structure of an element?
Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Structure of an atom: Elements, such as helium, depicted here, are made up of atoms. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.
Q. What is carbons structure?
Every carbon atom is covalently bonded at the four corners of the tetrahedron to four other carbon atoms. The crystal structure of graphite amounts to a parallel stacking of layers of carbon atoms. Within each layer the carbon atoms lie in fused hexagonal rings that extend infinitely in two dimensions.
Q. What’s the meaning of structure?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 : the action of building : construction. 2a : something (such as a building) that is constructed. b : something arranged in a definite pattern of organization a rigid totalitarian structure— J. L. Hess leaves and other plant structures.
Q. What are 3 types of structures?
There are three basic types of structures: shell structures, frame structures and solid structures.
Q. What is an example of structure?
Structure is a constructed building or a specific arrangement of things or people, especially things that have multiple parts. An example of structure is a newly built home. An example of structure is the arrangement of DNA elements. Something composed of interrelated parts forming an organism or an organization.
Q. What are some examples of structures?
Structure
- A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized.
- Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures.
Q. What are examples of natural structures?
Natural Structures: Shells, trees, skeletons, nests, etc. Natural animal structures: nests, beaver dams, termite hills, coral, wasp nests, bee, hives, tunnels made by moles, mice, rabbits, birds’ eggs, tortoise shells, etc. Natural geological structures: caves, mountains, etc.
Q. What are the four types of structures?
There are four types of structures;
- Frame: made of separate members (usually thin pieces) put together.
- Shell: encloses or contains its contents.
- Solid (mass): made almost entirely of matter.
- liquid (fluid): braking fluid making the brakes.
Q. What are the two types of structure?
One-dimensional: Ropes, cables, struts, columns, beams, arches. Two-dimensional: Membranes, plates, slabs, shells, vaults, domes, synclastic, anticlastic. Three-dimensional: Solid masses. Composite.
Q. What are the 5 types of structures?
Let’s go through the seven common types of org structures and reasons why you might consider each of them.
- Hierarchical org structure.
- Functional org structure.
- Horizontal or flat org structure.
- Divisional org structure.
- Matrix org structure.
- Team-based org structure.
- Network org structure.
Q. What is meant by framed structure?
A framed structure in any material is one that is made stable by a skeleton that is able to stand by itself as a rigid structure without depending on floors or walls to resist deformation.
Q. What are the different classifications of structure?
A structure can be classified as a solid, frame, or shell structure. Think about at least six different structures that you can use as a seat. Make a list of them. Some can be indoors, some can be outdoors.
Q. What is an example of a combination structure?
Most structures are combination structures. They have solid, shell, and frame parts. For example, most buildings have a solid foundation. They also have a frame of wood or metal that supports a shell of brick or concrete.
Q. What are the types of framed structures?
What are the Types of Frame Structures?
- 1: Rigid Frame Systems (Home Issurance Building, Chicago, USA)
- 2: Fixed Ended Rigid Frame Structure.
- 3: Pin Ended Rigid Frame Structure.
- 4: Braced Structural Frames with Various Types of Bracings.
- 5: Gable Frame Steel Structure.
Q. What are the types of framing?
Framing consists of light, heavy, and expedient framing. There are three principal types of framing for light structures: western, balloon, and braced.
Q. What is frame structure example?
Some of the most recognizable examples of frame structures include spider webs, ladders, bicycles and the Eiffel Tower. In each case, the frame of the structure fulfills its load-bearing requirements and remains unadorned while strictly meeting those needs.
Q. What are some examples of combination structures?
A house is an example a combination structure: The walls and roof of a house are primarily a frame structure with wooden beams nailed together. The foundation/basement of a house is a mass structure made up of concrete which is solid.
Q. What’s the difference between a shell structure and a frame structure?
Some of the main differences between shell structures and frame structures are: – Frame structures have joins which keep them together whereas shell structures have no joins. – Shell structures usually only support their own weight while frame structures support other loads as well as themselves.
Q. What three properties do all structures have in common?
All structures have a definite size, shape, and are capable of holding a load. It’s shape, size and the materials it is made of depends on the structure’s function. They also determine how strong it is. Forces like compression and tension are always acting on structures.
Q. What makes a structure strong and stable?
A structure which will not topple over easily when acted upon by a load is said to be stable. It is more difficult to make a structure with a wide base topple over so, the wider the base therefore, the more stable the structure. The shape and the material used to built a structure determine its resistance.
Q. What is the purpose of a solid structure?
A solid structure uses solid construction materials to support loads. A solid structure usually has a large mass. A well-made solid structure can last a long time. A concrete dam, a wooden telephone pole, and a marble statue are examples of solid structures.
Q. What are examples of solid structures?
Definition: A solid structure is strong relying on solid construction materials to support loads. Examples of solid structure: Dams, bridges, granite and literate rocks, mountains, door. The force that solid structures must resist are, natural disasters, heavy winds, lots of weight pressured against it.
Q. What are some disadvantages of solid structures?
In addition to these (more or less) advantages, solid structures also have some disadvantages when considered as a whole. On the one hand, the primary energy consumption and CO2 emissions in the production of the raw materials are significantly higher than with timber structures.
Q. What is a solid structure Grade 8?
A shell structure is more enclosing than a frame structure – it surrounds and encloses something. Solid/mass Structures. Solid structures rely heavily on solid construction such as masonry to support. loads and to transfer these loads safely to the ground.
Q. How does the Lewis electron dot structures of elements in the same group in the periodic table compare with one another?
What do the electron – dot structure of elements in the same group in periodic table have in common witth each other? They have the same number of valence electrons. Elements on opposite sides of the periodic chart. What kind of force holds two atoms together within a ionic bond?
Q. What is the hybridization of SCl2?
Answer: The hybridisation can explicitly found out once we write up the general electronic configuration. and, 4 corresponds to sp3 hybridisation. Hope this helps you !
Q. What shape is CH2Cl2?
tetrahedral
Q. What shape is bf3?
The geometry of the BF 3 molecule is called trigonal planar (see Figure 5). The fluorine atoms are positioned at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The F-B-F angle is 120° and all four atoms lie in the same plane.
Q. What shape is alcl3?
Aluminium chloride
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Coordination geometry | Octahedral (solid) Tetrahedral (liquid) |
| Molecular shape | Trigonal planar (monomeric vapour) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 91.1 J/mol·K |
Q. What is the name for Li2S?
Lithium sulfide (Li2S)
Q. What is the chemical name of CCl₄?
Carbon tetrachloride
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | CCl4 |
| Molar mass | 153.81 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Sweet, chloroform-like odor |
Q. What is the name of mgh2?
Magnesium hydride
Q. Is carbon tetrachloride used in fire extinguishers?
Carbon tetrachloride is a manufactured chemical and does not occur naturally in the environment, Carbon tetrachloride was also used in fire extinguishers and as a fumigant to kill insects in grain.
Q. Why CCl₄ is used as fire extinguisher?
Explanation: CCl₄ is used as fire extinguishers under the name pyrene. The dense vapours form protective layer on the burning objects and Prevent the oxygen or air to come in contact with the burning objects and gives incombustible vapours.
Q. Is CCl4 flammable?
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a manufactured chemical. CCl4 is not flammable and does not dissolve very easily in water.