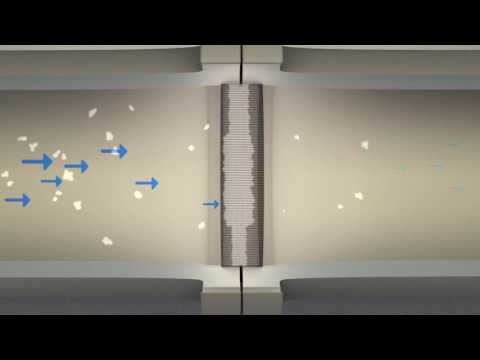
Q. How do you calculate delta P pipe?
To determine the Delta P across a valve, simply subtract the outlet pressure (P2) from the inlet pressure(P1).
Q. What is the formula for flow velocity?
Summary. Flow rate Q is defined to be the volume V flowing past a point in time t, or Q=Vt where V is volume and t is time. The SI unit of volume is m3. Flow rate and velocity are related by Q=A¯v where A is the cross-sectional area of the flow and v is its average velocity.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you calculate delta P pipe?
- Q. What is the formula for flow velocity?
- Q. What is Delta P equation?
- Q. How do you calculate air flow in a pipe?
- Q. How do you calculate gas flow rate?
- Q. How do you calculate volume flow in a pipe?
- Q. How do you calculate flow rate with pressure and pipe?
- Q. How do you write Delta P?
- Q. What is Delta P water?
- Q. How to calculate the Delta P of a pressure drop?
- Q. How to calculate the Delta P in a heat exchanger?
- Q. What does Delta P stand for in physics?
- Q. Why do we use delta P for performance monitoring?
Q. What is Delta P equation?
The equation for the pressure difference is: ΔP = P2 – P1. It is obvious that a high concentration of deposits, in pipe or exchanger, lead to a high pressure drop, ΔP. If there are deposits the water can’t flow free. Hence the outlet pressure is much lower than the inlet pressure.
Q. How do you calculate air flow in a pipe?
Plug the cross-sectional areas and the air speed in pipe one to calculate the air speed in pipe two. Assuming the air speed in pipe one is known to be 20 feet per second, you have: v2 = (19.6 square inches x 20 feet per second) / (50.2 square inches). The air speed in pipe two is 7.8 feet per second.
Q. How do you calculate gas flow rate?
R = Universal Gas Flow Constant (1545 ft•lbf/(lb•mol)(°R)) divided by M.W. As an example, let’ss assume that we have dry air flowing at 100 lb/min, 200°F and 24.7 psia. We will assume a molecular weight (M.W.) of 28.964 lb/lb•mol.
Q. How do you calculate volume flow in a pipe?
A A A is the cross sectional area of a section of the pipe, and v is the speed of the fluid in that section. So, we get a new formula for the volume flow rate Q = A v Q=Av Q=AvQ, equals, A, v that is often more useful than the original definition of volume flow rate because the area A is easy to determine.
Q. How do you calculate flow rate with pressure and pipe?
Square the pipe’s radius. With a radius, for instance, of 0.05 meters, 0.05 ^ 2 = 0.0025. Multiply this answer by the pressure drop across the pipe, measured in pascals. With a pressure drop, for instance, of 80,000 pascals, 0.0025 x 80,000 = 200.
Q. How do you write Delta P?
ΔP (Delta P) is a mathematical term symbolizing a change (Δ) in pressure (P).
Q. What is Delta P water?
Commercial divers use the phrase ‘Delta P’ (or sometimes just ‘DP’) as a shorthand for ‘Differential Pressure’, to describe a potential diving hazard in which there is water movement from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure. water is adjacent to a gaseous void at lower pressure than the water.
Q. How to calculate the Delta P of a pressure drop?
Subtract the inlet pressure (P1) at the point B, from the outlet pressure (P2) at the exit A and you will get Delta P. It is obvious that a high concentration of deposits, in pipe or exchanger, lead to a high pressure drop, ΔP.
Q. How to calculate the Delta P in a heat exchanger?
The ΔP in the heat exchanger to the left can be calculated very simple. Subtract the inlet pressure (P1) at the point B, from the outlet pressure (P2) at the exit A and you will get Delta P. It is obvious that a high concentration of deposits, in pipe or exchanger, lead to a high pressure drop, ΔP.
Q. What does Delta P stand for in physics?
Delta P (ΔP) or differential pressure usually refers to the drop of pressure in a piping system. The symbol Δ (delta) is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet and is used as a mathematical symbol which represents the „difference“ between two values.
Q. Why do we use delta P for performance monitoring?
That’s because the pressure in the plane is much lower than the atmospheric pressure at the ground. This pressure difference can be seen on the bottle. The delta P would be the difference in between the lower pressure in the airplane and the normal pressure on the ground. We at Merus use delta P for the performance monitoring.