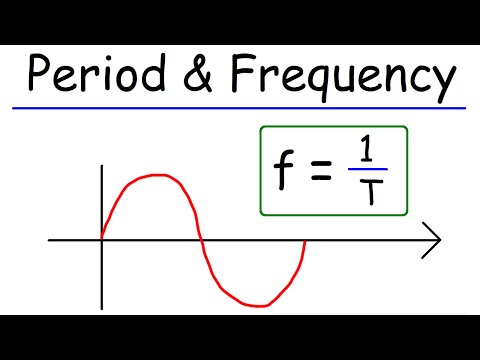
Q. How do you calculate frequency and phase?
Calculating Phase Shift Dividing the frequency into 1 gives the period, or duration of each cycle, so 1/100 gives a period of 0.01 seconds. The phase shift equation is ps = 360 * td / p, where ps is the phase shift in degrees, td is the time difference between waves and p is the wave period.
Q. What does 180 degree out of phase mean?
A phrase used to characterize two or more signals whose phase relationship with each other is such that when one is at its positive peak the other is at (or near) its negative peak. This is also commonly referred to as being 180 degrees out of phase. Polarity refers to one signal being “backwards” from another.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you calculate frequency and phase?
- Q. What does 180 degree out of phase mean?
- Q. How does frequency affect phase angle?
- Q. How do you calculate phase difference?
- Q. What is the formula for phase shift?
- Q. What is the formula of phase angle?
- Q. What is a healthy phase angle?
- Q. What is the phase angle?
- Q. How do you find the phase angle on a calculator?
- Q. What is phase angle of a wave?
- Q. What is phase angle in SHM?
- Q. How do you find power angle?
- Q. How do you find apparent power?
- Q. What is the power factor for 3 phase?
- Q. How many volts is a 3 phase line?
- Q. What is the ideal power factor?
- Q. What causes low power factor?
- Q. What happens at low power factor?
- Q. How can we improve power factor?
- Q. How do you fix a bad power factor?
- Q. Why do we need power factor correction?
- Q. Is reactive power wasted?
- Q. Why is reactive power bad?
- Q. What is reactive power Example?
- Q. Do capacitors absorb reactive power?
Q. How does frequency affect phase angle?
The time interval for 1° of phase is inversely proportional to the frequency. If the frequency of a signal is given by f, then the time tdeg (in seconds) corresponding to 1° of phase is tdeg = 1 / (360f) = T / 360. Therefore, a 1° phase shift on a 5 MHz signal corresponds to a time shift of 555 picoseconds.
Q. How do you calculate phase difference?
Phase difference can be measured on an oscilloscope by determining the time delay between two waveforms along with their period. All periodic signals can be described in terms of amplitude and phase. We all learned that in basic circuit theory.
Q. What is the formula for phase shift?
where |A| is the amplitude, B gives you the period, D gives you the vertical shift (up or down), and C/B is used to find the phase shift. So the phase shift, as a formula, is found by dividing C by B. For F(t) = A f(Bt – C) + D, where f(t) is one of the basic trig functions, we have: the amplitude is |A|
Q. What is the formula of phase angle?
Calculation of Phase Angle The phase angle is equal to the arctangent of the ratio of the capacitive current to the resistive current. Thus, the phase angle, θ, is equal to the arctangent of 3 amperes divided by 4 amperes which equals the arctangent 0.75.
Q. What is a healthy phase angle?
Phase angle has been utilized to discriminate between normal subjects and patients, and between septic and non-septic critically ill patients. It indicates alterations in either body composition or in cellular membrane function. Phase angle varies between 3-15 degrees (the average is 5-7).
Q. What is the phase angle?
It describes the phase shift between total voltage and total electric current. In the voltage triangle this matches the phase shift between total voltage and active voltage. For the resistance triangle the phase shift lies between the impedance and effective resistance vector.
Q. How do you find the phase angle on a calculator?
Phase Angle Calculator
- Formula. A = tan^-1(XL-XC/R)
- Inductive Reactance (Ohms)
- Capacitive Reactance (Ohms)
- Resistance (Ohms)
Q. What is phase angle of a wave?
In a sinusoidal wave. the angle giving the phase of the wave (i.e., its shift relative to the wave with ) is called the phase angle. It represents the fraction of the period that y lags or leads the function .
Q. What is phase angle in SHM?
Phase of a point in SHM is the angle made by the point, in uniform circular motion whose projection is that simple harmonic motion, with the initial point of motion at the centre of the circular motion or the mean position of the simple harmonic motion.
Q. How do you find power angle?
Power Triangle of an AC Circuit
- Where:
- P is the I2*R or Real power that performs work measured in watts, W.
- Q is the I2*X or Reactive power measured in volt-amperes reactive, VAr.
- S is the I2*Z or Apparent power measured in volt-amperes, VA.
- Φ is the phase angle in degrees.
- Cos(Φ) = P/S = W/VA = power factor, p.f.
Q. How do you find apparent power?
Apparent power (VA) is the easiest to measure; it is what you get when you measure the rms volts with one meter and the rms amps with another meter and multiply the two. The measurements must be made with “True RMS” meters.
Q. What is the power factor for 3 phase?
An operating three phase motor has voltages measured with a voltmeter on each phase of 453, 458, and 461 volts, amperage measured on each phase with an ammeter are 14.1, 13.9, and 13.8 amps, power factor was measured as 0.82. The average voltage is 453 plus 458 plus 461 divided by 3 which equals 457 volts.
Q. How many volts is a 3 phase line?
3 phase system is expressed with line voltages. The line votage is 440 volt. Also the voltage between any one phase and neutral for a 3 phase system is 240 volts.
Q. What is the ideal power factor?
The ideal power factor is unity, or one. Anything less than one means that extra power is required to achieve the actual task at hand. All current flow causes losses both in the supply and distribution system. A load with a power factor of 1.0 results in the most efficient loading of the supply.
Q. What causes low power factor?
The main cause of low Power factor is Inductive Load. As in pure inductive circuit, Current lags 90° from Voltage, this large difference of phase angle between current and voltage causes zero power factor.
Q. What happens at low power factor?
A power factor of less than one indicates the voltage and current are not in phase, reducing the average product of the two. In an electric power system, a load with a low power factor draws more current than a load with a high power factor for the same amount of useful power transferred.
Q. How can we improve power factor?
You can improve power factor by adding power factor correction capacitors to your plant distribution system. When apparent power (kVA) is greater than working power (kW), the utility must supply the excess reactive current plus the working current . Power capacitors act as reactive current generators .
Q. How do you fix a bad power factor?
The simplest way to improve power factor is to add PF correction capacitors to the electrical system. PF correction capacitors act as reactive current generators. They help offset the non-working power used by inductive loads, thereby improving the power factor.
Q. Why do we need power factor correction?
Power factor correction (PFC) aims to improve power factor, and therefore power quality. It reduces the load on the electrical distribution system, increases energy efficiency and reduces electricity costs. It also decreases the likelihood of instability and failure of equipment.
Q. Is reactive power wasted?
The strength of the pull on the rope is the apparent power; only a portion of this power is “working” (real) power that pulls the railcar forward. Due to the angle of the horse’s pull, some of the energy expended is wasted as “non-working” (reactive) power.
Q. Why is reactive power bad?
When reactive power supply lower voltage, as voltage drops current must increase to maintain power supplied, causing system to consume more reactive power and the voltage drops further . If the current increase too much, transmission lines go off line, overloading other lines and potentially causing cascading failures.
Q. What is reactive power Example?
An example is powering an incandescent light bulb; in a reactive load energy flows toward the load half the time, whereas in the other half power flows from it, which gives the illusion that the load is not dissipating or consuming power.
Q. Do capacitors absorb reactive power?
Capacitor absorb lagging reactive power and return leading reactive power and inductor do opposite of it. Resistor absorb active power and does not return any other power. They are loads not any generating elements.