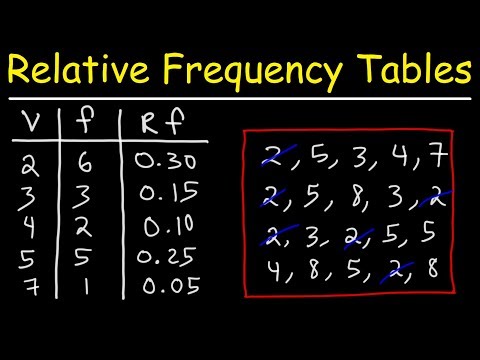
Step 1: Make a table with the category names and counts.
Q. Is a frequency table a graph?
A bar graph. Another type of graph used to represent a frequency table is the frequency polygon, which plots the frequencies of the different data values and then connects the plotted points with straight lines. Figure 2.3 presents the frequency polygon of the data of Table 2.1.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is a frequency table a graph?
- Q. How do you show frequency in data?
- Q. What do frequency tables show?
- Q. What is a frequency bar graph?
- Q. Can you use a bar graph for frequency?
- Q. What is a segmented bar graph?
- Q. Why would you draw a segmented bar graph?
- Q. What is multiple bar graph?
- Q. How do you do multiple bar graphs?
- Q. What is bar chart and its advantages and disadvantages?
Q. How do you show frequency in data?
A frequency distribution of data can be shown in a table or graph. Some common methods of showing frequency distributions include frequency tables, histograms or bar charts. A frequency table is a simple way to display the number of occurrences of a particular value or characteristic.
- Step 2: Add a second column called “relative frequency”. I shortened it to rel.
- Step 3: Figure out your first relative frequency by dividing the count by the total.
- Step 4: Complete the rest of the table by figuring out the remaining relative frequencies.
Q. What do frequency tables show?
Frequency refers to the number of times an event or a value occurs. A frequency table is a table that lists items and shows the number of times the items occur. We represent the frequency by the English alphabet ‘f’.
Q. What is a frequency bar graph?
A bar graph is a graph that displays a bar for each category with the length of each bar indicating the frequency of that category. To construct a bar graph, we need to draw a vertical axis and a horizontal axis.
Q. Can you use a bar graph for frequency?
Frequency tables, pie charts, and bar charts can be used to display the distribution of a single categorical variable. These displays show all possible values of the variable along with either the frequency (count) or relative frequency (percentage).
Q. What is a segmented bar graph?
A segmented bar graph compares two categories within a data set. The whole bar represents all the data within one category. Then, each bar is separated into parts (segments) that show the percentage of each part in the second category.
Q. Why would you draw a segmented bar graph?
The segmented bar graph uses a rectangular bar to represent the entire data set. The bar is divided into segments (just like the “slices” of a pie chart) with different segments representing different categories. Just like the pie chart, we should find the relative frequencies (decimal form) for each category.
Q. What is multiple bar graph?
A multiple bar graph shows the relationship between different values of data. Each data value is represented by a column in the graph. In a multiple bar graph, multiple data points for each category of data are shown with the addition of columns. The quantity or amount of data is listed along the vertical, or y, axis.
Q. How do you do multiple bar graphs?
To create a combo chart, select the data you want displayed, then click the dialog launcher in the corner of the Charts group on the Insert tab to open the Insert Chart dialog box. Select combo from the All Charts tab. Select the chart type you want for each data series from the dropdown options.
Q. What is bar chart and its advantages and disadvantages?
The following are advantages of bar graph: • Show each data category in a frequency distribution • Display relative numbers/proportions of multiple categories • Summarize a large amount of data in a visual, easily intepretable form • Make trends easier to highlight than tables do • Estimates can be made quickly and …