Q. How do you find average orbital speed?
Orbital speed Formula
- orbital speed = square root (gravitational constant * mass of the attractive body / radius of the orbit)
- Orbital speed Questions:
- Answer: First, we look for default values for the earth, such as mass and its approximate radius.
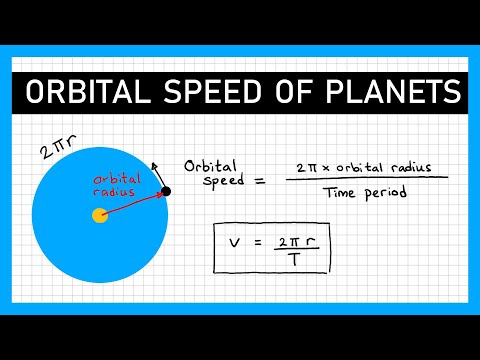
Q. How do you calculate orbital speed GCSE?
- momentum = mass X velocity p = mv.
- (kg m/s) (kg) (m/s)
- Force = change in momentum / time F = (mv – mu) / t.
- Orbital speed = 2 X π X orbital radius / time period v = 2 π r / T.
- (m / s) (m) (s)
- moment = Force X perpendicular distance between force and pivot, moment = Fd.
Q. What is the average speed of Earth’s orbit?
30 kilometers per second
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you find average orbital speed?
- Q. How do you calculate orbital speed GCSE?
- Q. What is the average speed of Earth’s orbit?
- Q. Does the moon have a dark side?
- Q. Is there a month with 2 new moons?
- Q. Does the Moon slow down Earth rotation?
- Q. What would happen if the moon revolved fast or slower?
- Q. Is the moon getting slower?
- Q. Can a moon have a moon?
- Q. What are moons of moons called?
- Q. Can a moon have a ring?
- Q. What is that circle around the moon?
- Q. Why is there a big ring around the moon tonight?
Q. Does the moon have a dark side?
The ‘dark side’ of the Moon refers to the hemisphere of the Moon that is facing away from the Earth. In reality it is no darker than any other part of the Moon’s surface as sunlight does in fact fall equally on all sides of the Moon.
Q. Is there a month with 2 new moons?
Month with two new moons February is too short for a second new moon to occur. This event occurs about every 29 months. The assignment of a calendar date to a new moon, and in which month a second new moon occurs, depends on the time zone.
Q. Does the Moon slow down Earth rotation?
The Earth’s rotation is indeed being slowed down by the presence of the Moon – every year, the Moon gains a little energy from the Earth, and drifts a little farther away from us. As a point of reference, this rate of slowing means that it will take 25,000 years to add a half a second to the Earth’s day.
Q. What would happen if the moon revolved fast or slower?
The moon would sail off into space (slowing down as it is dragged back by the Earth, and end up orbiting the sun). The escape velocity is √2 times the orbital velocity, so if you are in orbit, and double the speed, you are sure to escape. If you gave it a more gentle push it would enter an elliptical orbit.
Q. Is the moon getting slower?
But the energy gained as the Moon is pushed higher is balanced by a reduction in the energy of its motion – so an acceleration provided by the Earth’s tides is actually slowing the Moon down.
Q. Can a moon have a moon?
Yes, in theory, moons can have moons. The region of space around a satellite where a sub-satellite can exist is called the Hill sphere. Outside the Hill sphere, a sub-satellite would be lost from its orbit about the satellite. An easy example is the Sun-Earth-Moon system.
Q. What are moons of moons called?
A subsatellite, also known as a submoon or moonmoon, is a natural or artificial satellite that orbits a natural satellite, i.e. a “moon of a moon”.
Q. Can a moon have a ring?
Rings around the Moon are caused when moonlight passes through thin clouds of ice crystals high in Earth’s atmosphere. As moonlight passes through the ice crystals, it is bent in a way similar to light passing through a lens. The shape of the ice crystals causes the moonlight to be focused into a ring.
Q. What is that circle around the moon?
A 22° halo is an optical phenomenon that belongs to the family of ice-crystal halos. When visible around the Moon, it is called a moon ring or winter halo. It forms as direct sunlight or moonlight is refracted in millions of hexagonal ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere.
Q. Why is there a big ring around the moon tonight?
But what causes a ring to appear around the moon? This phenomenon is called a “moon halo.” According to the National Weather Service, this ring of light, which is actually an optical illusion, forms around the moon when moonlight refracts off ice crystals in cirrus clouds, high up in the Earth’s atmosphere.