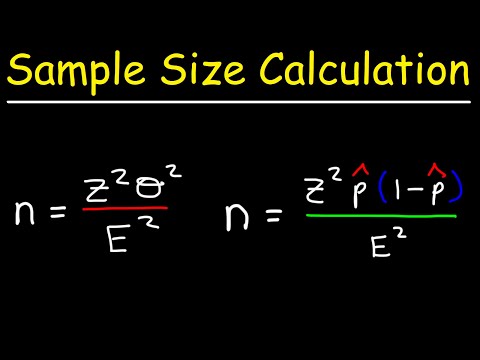
Q. How do you find the margin of error for an unknown sample size?
Here are the steps for calculating the margin of error for a sample proportion:
- Find the sample size, n, and the sample proportion.
- Multiply the sample proportion by 1 – ρ.
- Divide the result by n.
- Take the square root of the calculated value.
Q. How do you find 95% margin of error?
Divide the population standard deviation by the square root of the sample size. gives you the standard error. Multiply by the appropriate z*-value (refer to the above table). For example, the z*-value is 1.96 if you want to be about 95% confident.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you find the margin of error for an unknown sample size?
- Q. How do you find 95% margin of error?
- Q. How do you interpret the margin of error for a confidence interval?
- Q. How do you find the confidence level?
- Q. How does margin of error change with confidence interval?
- Q. How much margin of error is acceptable?
- Q. What is the z score for 92 confidence interval?
- Q. How do you compute the p value?
- Q. What do you need to know about margin of error?
- Q. How is margin of error related to confidence interval?
- Q. What is the margin of error for social media?
- Q. What is the margin of error for banana flavor?
Q. How do you interpret the margin of error for a confidence interval?
A margin of error tells you how many percentage points your results will differ from the real population value. For example, a 95% confidence interval with a 4 percent margin of error means that your statistic will be within 4 percentage points of the real population value 95% of the time.
Q. How do you find the confidence level?
Find a confidence level for a data set by taking half of the size of the confidence interval, multiplying it by the square root of the sample size and then dividing by the sample standard deviation. Look up the resulting Z or t score in a table to find the level.
Q. How does margin of error change with confidence interval?
1. Three things influence the margin of error in a confidence interval estimate of a population mean: sample size, variability in the population, and confidence level. As the variability in the population increases, the margin of error increases. As the confidence level increases, the margin of error increases.
Q. How much margin of error is acceptable?
The acceptable margin of error usually falls between 4% and 8% at the 95% confidence level. While getting a narrow margin of error is quite important, the real trick of the trade is getting that perfectly representative sample.
Q. What is the z score for 92 confidence interval?
| Confidence Level | z |
|---|---|
| 0.85 | 1.44 |
| 0.90 | 1.645 |
| 0.92 | 1.75 |
| 0.95 | 1.96 |
Q. How do you compute the p value?
The p-value is calculated using the sampling distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis, the sample data, and the type of test being done (lower-tailed test, upper-tailed test, or two-sided test). The p-value for: a lower-tailed test is specified by: p-value = P(TS ts | H 0 is true) = cdf(ts)
Q. What do you need to know about margin of error?
MOE is the margin of error, z is the z-score associated with a level of confidence, p is the sample proportion, expressed as a decimal, n is the sample size,
Q. How is margin of error related to confidence interval?
The range of values which are below and above the sample statistic in a confidence interval is known as Margin of Error. In other words, it is basically the degree of error in the sample statistic. Higher the margin of error, lesser will the confidence in the results because the degree of deviation in these results is very high.
Q. What is the margin of error for social media?
As such, the margin of error in this survey is as follows: MOE = 0.977 / 31.623 * 100 = 3.089% These results indicate that the market research company can conclude with 95% confidence that 54% of mobile phone users use their device to access social media, give or take 3%.
Q. What is the margin of error for banana flavor?
Margin of Error = 2.60% So we can say that with 90% confidence that 47% of all people liked banana flavor plus or minus 2.60%. As discussed above, the margin of error helps us understand whether the sample size of your survey is appropriate or not.