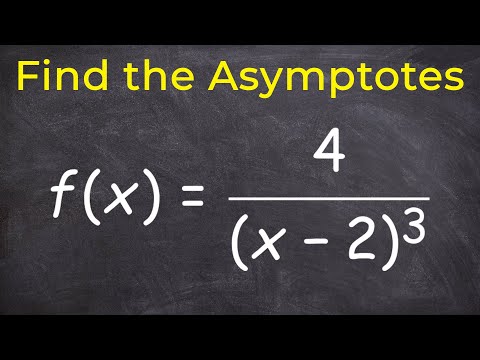To find the vertical asymptote(s) of a rational function, simply set the denominator equal to 0 and solve for x. We mus set the denominator equal to 0 and solve: This quadratic can most easily be solved by factoring the trinomial and setting the factors equal to 0. There are vertical asymptotes at .
Q. Can a graph have more than one vertical asymptote?
A graph can have an infinite number of vertical asymptotes, but it can only have at most two horizontal asymptotes. The graph of y = f(x) will have vertical asymptotes at those values of x for which the denominator is equal to zero.
Table of Contents
- Q. Can a graph have more than one vertical asymptote?
- Q. Can a function have more than one asymptote?
- Q. Will all rational functions have at least one vertical asymptote?
- Q. Can a vertical asymptote be imaginary?
- Q. What is the difference between a vertical and horizontal asymptote?
- Q. How do you find the horizontal asymptote of an exponential graph?
- Q. How do you know if a graph is exponential or logarithmic?
- Q. What is the difference between exponential and logarithmic growth?
- Q. What is difference between linear and logarithmic scale?
- Q. How do you tell if a graph is an exponential function?
- Q. What is an exponential graph?
- Q. How do you plot an exponential graph?
- Q. What is the difference between an exponential function and a linear function?
- Q. How do you read an exponential graph?
- Q. What is the general equation for exponential growth?
Q. Can a function have more than one asymptote?
A function can have at most two different horizontal asymptotes. A graph can approach a horizontal asymptote in many different ways; see Figure 8 in §1.6 of the text for graphical illustrations. In particular, a graph can, and often does, cross a horizontal asymptote.
Q. Will all rational functions have at least one vertical asymptote?
No. Not all rational functions will have at least one vertical asymptote. Algebraically, for a rational function to have a vertical asymptote, the denominator must be able to be set to zero while the numerator remains a non-zero value.
Q. Can a vertical asymptote be imaginary?
Vertical asymptotes apply to real functions. For complex, the corresponding concept is called a ‘pole’. tachu101 said: But the Vertical if (x^2+9)=0 then x is an imaginary number.
Q. What is the difference between a vertical and horizontal asymptote?
Vertical asymptotes mark places where the function has no domain. You solve for the equation of the vertical asymptotes by setting the denominator of the fraction equal to zero. Horizontal asymptotes, on the other hand, indicate what happens to the curve as the x-values get very large or very small.
Q. How do you find the horizontal asymptote of an exponential graph?
Exponential Functions A function of the form f(x) = a (bx) + c always has a horizontal asymptote at y = c. For example, the horizontal asymptote of y = 30e–6x – 4 is: y = -4, and the horizontal asymptote of y = 5 (2x) is y = 0.
Q. How do you know if a graph is exponential or logarithmic?
As you can tell from the graph to the right, the logarithmic curve is a reflection of the exponential curve….Comparison of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions.
| Exponential | Logarithmic | |
|---|---|---|
| Function | y=ax, a>0, a≠1 | y=loga x, a>0, a≠1 |
| Domain | all reals | x > 0 |
| Range | y > 0 | all reals |
Q. What is the difference between exponential and logarithmic growth?
Exponential growth is where the rate of increase in something is proportional to the amount present. ie . This has a solution of the form and hence the term “exponential”. Logarithmic growth is where the rate of increase in something is inversely proportional to the amount of time that has expired.
Q. What is difference between linear and logarithmic scale?
Linear graphs are scaled so that equal vertical distances represent the same absolute-dollar-value change. The logarithmic scale reveals percentage changes. A change from 100 to 200, for example, is presented in the same way as a change from 1,000 to 2,000.
Q. How do you tell if a graph is an exponential function?
Graphs of Exponential Functions
- The graph passes through the point (0,1)
- The domain is all real numbers.
- The range is y>0.
- The graph is increasing.
- The graph is asymptotic to the x-axis as x approaches negative infinity.
- The graph increases without bound as x approaches positive infinity.
- The graph is continuous.
Q. What is an exponential graph?
Differences • In Example 1, the graph goes upwards as it goes from left to right making it an increasing function. An exponential function that goes up from left to right is called “Exponential Growth”. • In Example 2, the graph goes downwards as it goes from left to right making it a decreasing function.
Q. How do you plot an exponential graph?
Graphing Exponential Functions
- Replacing x with −x reflects the graph across the y -axis; replacing y with −y reflects it across the x -axis.
- Replacing x with x+h translates the graph h units to the left.
- Replacing y with y−k (which is the same as adding k to the right side) translates the graph k units up.
Q. What is the difference between an exponential function and a linear function?
What is the difference between linear and exponential functions? Linear functions change at a constant rate per unit interval. An exponential function changes by a common ratio over equal intervals.
Q. How do you read an exponential graph?
Graphical Features of Exponential Functions
- a is the vertical intercept of the graph.
- b determines the rate at which the graph grows:
- The graph will have a horizontal asymptote at y = 0.
- The domain of the function is all real numbers.
- The range of the function is (0,∞) if a > 0, and (−∞,0) if a < 0.
Q. What is the general equation for exponential growth?
Exponential Function exponential growth or decay function is a function that grows or shrinks at a constant percent growth rate. The equation can be written in the form f(x) = a(1 + r)x or f(x) = abx where b = 1 + r.