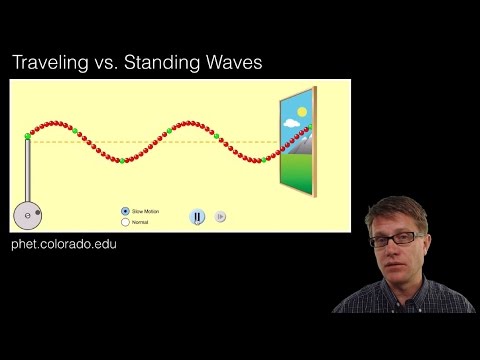
How to determine whether a wave is travelling or standing?
Q. What are the types of Travelling wave?
There are three basic types of waves: mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, and matter waves.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the types of Travelling wave?
- Q. What are the characteristics of Travelling wave?
- Q. What is speed of Travelling wave?
- Q. What are Travelling waves Class 11?
- Q. What is meant by a continuous Travelling wave?
- Q. Which of the following does not provide protection against Travelling wave?
- Q. Which of the following is a non linear diverter?
- Q. Which one of the following represents a Travelling wave?
- Q. Which relay is used for feeder?
- Q. Where is MHO relay used?
- Q. Which relay is used for protection of 11kv feeders?
- Q. Which is not an advantage of static relay?
- Q. Where static relay can be installed?
- Q. Which type of static relay is used very first?
- Q. Which components are used for static relay?
- Q. What are the limitation of relays?
- Q. What is power consumption of static relay?
- Q. Why do static relays require DC supply?
- Q. What is a DC fail relay?
Q. What are the characteristics of Travelling wave?
A wave can be described as a disturbance in a medium that travels transferring momentum and energy without any net motion of the medium. A wave in which the positions of maximum and minimum amplitude travel through the medium is known as a travelling wave.
- Well no, it isn’t of the form you suggest, it is f(kx−ωt)+f(kx+ωt), which is two waves of equal amplitude and frequency travelling in opposite directions, which superpose to give a standing wave.
- Yes, you are right.
- Closely related: physics.stackexchange.com/q/56338 – ProfRob Oct 15 ’16 at 16:45.
Q. What is speed of Travelling wave?
In the case of a wave, the speed is the distance traveled by a given point on the wave (such as a crest) in a given interval of time. In equation form, If the crest of an ocean wave moves a distance of 20 meters in 10 seconds, then the speed of the ocean wave is 2.0 m/s.
Q. What are Travelling waves Class 11?
Travelling Waves. The speed of a travelling wave. Speed of a transverse wave in a stretched string. Speed of a longitudinal wave in a stretched string. The principle of superposition of waves.
Q. What is meant by a continuous Travelling wave?
If we continue to shake the free end rope or spring we will generate a continuous traveling wave. A continuously traveling wave can be thought of as a series of wave pulses. Or vice versa a wave pulse could be thought of as a segment (one wavelength) of a continuously traveling wave.
Q. Which of the following does not provide protection against Travelling wave?
For representing a wave function must be finite everywhere,so logrithmic function can not represent a travelling wave.
Q. Which of the following is a non linear diverter?
Which of the following is a non-linear diverter ? Expulsion type arrester.
Q. Which one of the following represents a Travelling wave?
Althrough all the four functions are written in the form f(ax±bt), only (c) among the four functions is finite everywhere at all times, Hence only (c) represents a travelling wave.
Q. Which relay is used for feeder?
Buchholz relay
Q. Where is MHO relay used?
Abstract: Mho distance relays are widely used for the protection of uncompensated and series compensated transmission lines in order to determine the presence and location of faults.
Q. Which relay is used for protection of 11kv feeders?
Protection of Parallel Feeders One of the simplest methods for the protection of the relay is the time graded overload relay with inverse time characteristic at the sending end and instantaneous reverse power or directional relays at the receiving end as shown in the figure below.
Q. Which is not an advantage of static relay?
The working of the relay depends on the electrical components. The relay has less overloading capacity. The static relay is more costly as compared to the electromagnetic relay. The construction of the relay is easily affected by the surrounding interference.
Q. Where static relay can be installed?
There is no effect of gravity on operation of static relays and, therefore, they can be installed in vessels, aircrafts etc.
Q. Which type of static relay is used very first?
1. Electronic Relays: These were the first to be developed in the series of static relays. Fitzgerald presented a carrier current pilot relaying scheme for the protection of transmission lines in 1928.
Q. Which components are used for static relay?
The static relay is the combination of both the static and the electromagnetic relay. In this relay, there is no armature and moving contacts and response is developed by the components without mechanical motion. The solid state components used are transistors, diodes, resistors, 0and capacitor and so on.
Q. What are the limitation of relays?
Disadvantages of relays:
- Relays are bulkier than transistors for switching small currents.
- Relays cannot switch rapidly (except reed relays), transistors can switch many times per second.
- Relays use more power due to the current flowing through their coil.
Q. What is power consumption of static relay?
Static Relays power consumption is one mill watt. EMR consumes 2 Watts. In statics Relays, there are no moving parts and hence associated problems of arcing erosion of contacts, replacement of contacts, as in the case of EM relays, do not exists.
Q. Why do static relays require DC supply?
In a protection relay, the term ‘static’ refers to the absence of moving parts to create the relay characteristic. In particular, the relays generally require a reliable source of d.c. power and measures to prevent damage to vulnerable electronic circuits had to be devised.
Q. What is a DC fail relay?
We design and manufacture Microcontroller based DC Failure Relay to monitor the DC supply / station batteries voltage and DC Protection Fuses in Control & relay panels. When DC supply fails and need the attention of the operators in the substations, DC failure relay gives Indication & output contacts.