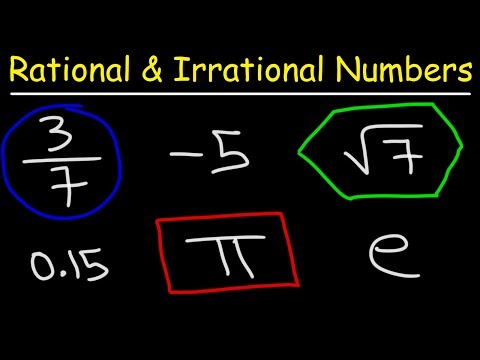
A rational number can be defined as any number that can be expressed or written in the p/q form, where ‘p’ and ‘q’ are integers and q is a non-zero number. An irrational number on the other hand cannot be expressed in p/q form and the decimal expansion of an irrational number is non-repeating and non-terminating.
Q. What can cause irrational behavior?
A person may experience a change in their demeanor after experiencing a traumatic situation or witnesses an unpleasant event. These behavioral changes may be caused by a mental health condition, such as: Anxiety: Anxiety occurs when a person feels nervous or uneasy about a situation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What can cause irrational behavior?
- Q. How do you know if it’s rational or irrational?
- Q. Are feelings irrational?
- Q. Are emotions feminine?
- Q. What does irrational love mean?
- Q. Do emotions make us irrational?
- Q. What’s another word for irrational?
- Q. What is the difference between rational and irrational decision making?
- Q. What is non rational thinking?
- Q. What is rational behavior?
- Q. What are the steps of rational decision making?
- Q. Do humans make rational decisions?
- Q. Are humans rational or emotional?
- Q. How do you help someone make a decision?
- Q. What are the factors that lead to irrational economic decisions?
- Q. Is consumer Behaviour rational or irrational?
- Q. Are consumers rational or irrational?
- Q. What is an irrational economic decision?
- Q. How do people make economic decisions?
- Q. What is behavioral decision making?
- Q. What is the rational economic man?
Q. How do you know if it’s rational or irrational?
All numbers that are not rational are considered irrational. An irrational number can be written as a decimal, but not as a fraction. An irrational number has endless non-repeating digits to the right of the decimal point.
Q. Are feelings irrational?
‘Irrational’ or ‘recalcitrant’ emotions are those emotions that are in tension with our evaluative judgements. For example, you fear flying despite judging it to be safe, you are angry at your colleague even though you know her remarks were inoffensive, and so on.
Q. Are emotions feminine?
Expressing emotion is a very feminine trait, and I think traditionally women have hidden their emotions because they’ve bought into an “act like a man” mentality in business. Many women believe this is what it takes to be successful.
Q. What does irrational love mean?
Sometimes love is illogical and foolish or even harmful, and sometimes it’s perfectly sensible. If you love someone who treats you with disdain and disrespect or who abuses you, your love is irrational. If you are in love with your own fantastical creation of your beloved, your love is irrational.
Q. Do emotions make us irrational?
Emotions can be rational or irrational. It can be rational if we are showing our positive emotion to that particular person or situation. It can also be irrational, if we are showing our negative emotions, especially if we can’t already handle or manage our actions and feelings toward that person.
Q. What’s another word for irrational?
What is another word for irrational?
| senseless | unreasonable |
|---|---|
| foolish | stupid |
| illogical | silly |
| absurd | nonsensical |
| preposterous | unwise |
Q. What is the difference between rational and irrational decision making?
Rational decisions are generally made by people who are able to determine the possibilities of an outcome, while irrational decisions are based almost entirely on emotion rather than experience. Those who make irrational decisions generally make them based on emotions and availability bias.
Q. What is non rational thinking?
Thinking is polluted by prejudices, beliefs, emotions, and dispositions. Since rational decision making is unrealistic, managers realistically make decisions through non-rational means. The non-rational models understand that making a decision is risky and that optimal decisions are difficult to make.
Q. What is rational behavior?
Rational behavior refers to a decision-making process that is based on making choices that result in the optimal level of benefit or utility for an individual. Most classical economic theories are based on the assumption that all individuals taking part in an activity are behaving rationally.
Q. What are the steps of rational decision making?
The Rational Decision-Making Process
- Step 1: Identify the Problem.
- Step 2: Establish Decision Criteria.
- Step 3: Weigh Decision Criteria.
- Step 4: Generate Alternatives.
- Step 5: Evaluate Alternatives.
- Step 6: Select the Best Alternative.
Q. Do humans make rational decisions?
Human Decision-Making is Rarely Rational Human decision-making is strongly biased by unconscious mental processes (system one) that sometimes produce good outcomes quickly but sometimes cause us to make irrational choices. Fear of loss influences human decisions more than expectation of gains.
Q. Are humans rational or emotional?
Specifically, human thought is generally not rational because much of it is unconscious (Wilson, 2002), automatic (Bargh, 1997), emotional (Zajonc, 1980), and heuristic in nature (Tversky&Kahneman, 1974).
Q. How do you help someone make a decision?
9 Ways you can help others make great decisions.
- Connect them with people that have experience and expertise.
- Help them identify the real problem/challenge.
- Explore risk tolerance.
- Inspire them to lean toward doing something.
- Help them explore, examine and then express their values.
Q. What are the factors that lead to irrational economic decisions?
There are many factors that can lead to irrational economic decisions. Many times you can overspend because of lack of availability, such as buying expensive gas because you are in the desert. Another irrational economic decision may be impulse buying or pressure.
Q. Is consumer Behaviour rational or irrational?
Time. Lastly, consumer behavior is not just irrational between emotions and situations, but also across different moments in time. As consumers, we often find ourselves faced with intertemporal choices. These are decisions in which the moment of choice and its consequence are separated by time.
Q. Are consumers rational or irrational?
Consumers and shoppers are purposeful and will more likely act consistently with their underlying preferences and motivations. This is what makes consumers neatly or broadly rational. Rationality does not assume consumers are conscious of their preferences, motives and decision processes.
Q. What is an irrational economic decision?
Classical economic theory assumes that individuals are rational. However, in the real world, we often see irrational behaviour – decisions which don’t maximise utility but can cause a loss of economic welfare. It means economists need to take into account the potential for irrationality.
Q. How do people make economic decisions?
Economists use the term marginal change to describe a small incremental adjustment to an existing plan of action. Keep in mind that margin means “edge,” so marginal changes are adjustments around the edges of what you are doing. Rational people often make decisions by comparing marginal benefits and marginal costs.
Q. What is behavioral decision making?
Behavioral style decision making describes people who prefer structure and stability and are motivated to maintain harmony. They use the information they gather to come up with solutions that they believe others will respond well to and typically ask for advice before moving forward with a decision.
Q. What is the rational economic man?
a construct introduced in the work of Scottish economist Adam Smith (1723–1790): The rational-economic man makes decisions based on the rational analysis of potential and desired outcomes and acts in his (or her) own rational self-interest. See also behavioral economics; bounded rationality. …