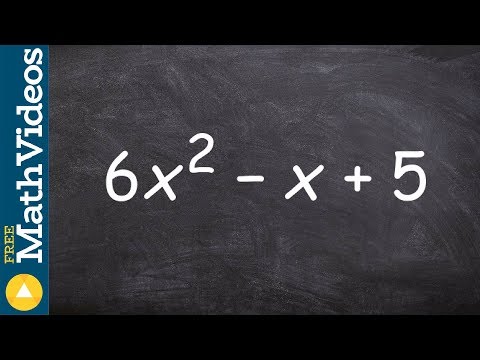Q. How do you know if the polynomial is Factorable?
2 Answers. The most reliable way I can think of to find out if a polynomial is factorable or not is to plug it into your calculator, and find your zeroes. If those zeroes are weird long decimals (or don’t exist), then you probably can’t factor it. Then, you’d have to use the quadratic formula.
Q. How do you know if an expression is Factorable?
If Δ<0 then ax2+bx+c has two distinct Complex zeros and is not factorable over the reals. It is factorable if you allow Complex coefficients.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you know if the polynomial is Factorable?
- Q. How do you know if an expression is Factorable?
- Q. What polynomials Cannot be factored?
- Q. How do you identify the degree of the polynomial?
- Q. How do you know if you can Factorise a quadratic?
- Q. How do you find the discriminant?
- Q. What is a discriminant example?
- Q. What does the discriminant tell you?
- Q. What happens if the discriminant is negative?
- Q. Is the discriminant negative or positive?
- Q. How do you get a negative discriminant?
- Q. What happens when B 2 4ac 0?
- Q. What does it mean if the discriminant is less than 0?
- Q. Do quadratic equations always have two real solutions?
- Q. What is the root of B² 4ac 0?
Q. What polynomials Cannot be factored?
A polynomial with integer coefficients that cannot be factored into polynomials of lower degree , also with integer coefficients, is called an irreducible or prime polynomial .
Q. How do you identify the degree of the polynomial?
Explanation: To find the degree of the polynomial, add up the exponents of each term and select the highest sum. The degree is therefore 6.
Q. How do you know if you can Factorise a quadratic?
So, after calculating the square root (Step 3), one integer is divided by another, and the solutions are rational numbers. Which Quadratic Expressions Are Factorable? BIG IDEA A quadratic expression with integer coefficients is factorable over the integers if and only if its discriminant is a perfect square.
Q. How do you find the discriminant?
The discriminant is the part under the square root in the quadratic formula, b²-4ac. If it is more than 0, the equation has two real solutions. If it’s less than 0, there are no real solutions. If it’s equal to 0, there is one real solution.
Q. What is a discriminant example?
For example, the discriminant of a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0 is in terms of a,b, and c . the discriminant of a cubic equation ax3+bx2+cx+d=0 a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d = 0 is in terms of a,b,c a , b , c and d .
Q. What does the discriminant tell you?
The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula underneath the square root symbol: b²-4ac. The discriminant tells us whether there are two solutions, one solution, or no solutions.
Q. What happens if the discriminant is negative?
If the discriminant is negative, that means there is a negative number under the square root in the quadratic formula. The square root of a negative number will involve the imaginary number i. This means that if you have a negative discriminant, you will get two complex solutions.
Q. Is the discriminant negative or positive?
The discriminant is negative, meaning there are no real solutions.
Q. How do you get a negative discriminant?
Having a negative discriminant means that b2−4ac<0 , and the polynominal doesn’t have real solutions.
Q. What happens when B 2 4ac 0?
If (b2 – 4ac) > 0.0, two real roots exist (i.e, the equation crosses the x-axis in two places — the x-intercepts). root of a negative number). If (b2-4ac) = 0, then only one real root exists — where the parabola touches the x-axis at a single point.
Q. What does it mean if the discriminant is less than 0?
If the discriminant of a quadratic function is less than zero, that function has no real roots, and the parabola it represents does not intersect the x-axis.
Q. Do quadratic equations always have two real solutions?
Conclusion: The number of solutions of a quadratic equation is always two, (follows from the fundamental theorem of algebra), however their nature may vary.
Q. What is the root of B² 4ac 0?
In a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 the coefficients a, b and c are real. We know, the roots (solution) of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are given by x = −b±√b2−4ac2a. 1. If b2 – 4ac = 0 then the roots will be x = −b±02a = −b−02a, −b+02a = −b2a, −b2a.