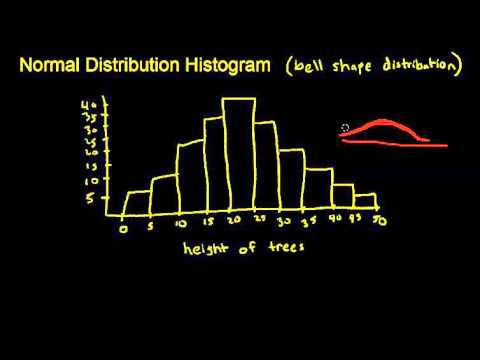
The most obvious way to tell if a distribution is approximately normal is to look at the histogram itself. If the graph is approximately bell-shaped and symmetric about the mean, you can usually assume normality.
Q. Which of the following best describes the purpose of a histogram?
Which of the following BEST describes the purpose of a histogram? The best answer is that a histogram measures distribution of continuous data. A histogram is a special type of bar chart. It can be used to display variation in weight — but can also be used to look at other variables such as size, time, or temperature.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following best describes the purpose of a histogram?
- Q. What is a symmetric histogram?
- Q. When would you choose to use a histogram to represent data?
- Q. What is the bin width of the histogram?
- Q. How do you find classes in statistics?
- Q. How do you calculate an interval?
- Q. What is the difference between class limit and class interval?
- Q. What is the class size of the class interval 100 120?
Q. What is a symmetric histogram?
A symmetric distribution is one in which the 2 “halves” of the histogram appear as mirror-images of one another. A skewed (non-symmetric) distribution is a distribution in which there is no such mirror-imaging.
Q. When would you choose to use a histogram to represent data?
When you are unsure what to do with a large set of measurements presented in a table, you can use a Histogram to organize and display the data in a more user- friendly format. A Histogram will make it easy to see where the majority of values falls in a measurement scale, and how much variation there is.
Q. What is the bin width of the histogram?
A histogram displays numerical data by grouping data into “bins” of equal width. Each bin is plotted as a bar whose height corresponds to how many data points are in that bin. Bins are also sometimes called “intervals”, “classes”, or “buckets”.
Q. How do you find classes in statistics?
Find the class width: Determine the range of the data and divide this by the number of classes. Round up to the next convenient number (if it’s a whole number, also round up to the next whole number). 3. Find the class limits: You can use the minimum data entry as the lower limit of the first class.
Q. How do you calculate an interval?
The steps in grouping may be summarized as follows:
- Decide on the number of classes.
- Determine the range, i.e., the difference between the highest and lowest observations in the data.
- Divide range by the number of classes to estimate approximate size of the interval (h).
Q. What is the difference between class limit and class interval?
Corresponding to a class interval, the class limits may be defined as the minimum value and the maximum value the class interval may contain. The minimum value is known as the lower class limit (LCL) and the maximum value is known as the upper class limit (UCL).
Q. What is the class size of the class interval 100 120?
⇒Class mark of 60-80 is 70. ⇒Class mark of 80-100 is 90. ⇒Class mark of 100-120 is 110….
| Class | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 80-100 | 7 |
| 100-120 | 8 |
| Total | 50 |