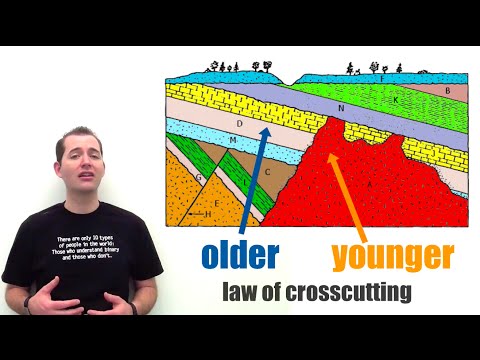
Geologists are able to ‘read’ the rock layers using relative and absolute dating techniques. Relative dating arranges geological events – and the rocks they leave behind – in a sequence. The method of reading the order is called stratigraphy (layers of rock are called strata).
Q. What is correlation of rock layers?
The process of showing that rocks or geologic events occurring at different locations are of the same age is called correlation. Geologists have developed a system for correlating rocks by looking for similarities in composition and rock layer sequences at different locations.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is correlation of rock layers?
- Q. What are rock layers?
- Q. Why are rock layers different colors?
- Q. What makes one rock green and another red?
- Q. What can be concluded if a dike protrudes through several layers of rock?
- Q. Is Granite older than sandstone?
- Q. How is the principle of original horizontality describe?
- Q. What is the principle of original horizontality examples?
- Q. What is the principle of inclusions?
- Q. What is the principle of original horizontality quizlet?
- Q. Which of the following is an example of nonconformity?
- Q. How is nonconformity formed?
- Q. What is another word for nonconformity?
- Q. Is there value in nonconformity?
- Q. Is nonconformity good or bad?
- Q. Why is nonconformity dangerous?
- Q. Why is it important to not conform?
Q. What are rock layers?
Layered rocks form when particles settle from water or air. Rock layers are also called strata (the plural form of the Latin word stratum), and stratigraphy is the science of strata. Stratigraphy deals with all the characteristics of layered rocks; it includes the study of how these rocks relate to time.
Q. Why are rock layers different colors?
The type of sediment that is deposited will determine the type of sedimentary rock that can form. Different colors of sedimentary rock are determined by the environment where they are deposited. Red rocks form where oxygen is present. Darker sediments form when the environment is oxygen poor.
Q. What makes one rock green and another red?
With the exception of gray and black, which mostly results from partially decayed organic matter, most rock colors are the result of iron staining. Ferric iron (Fe+3) produces red, purple, and yellow colors (from minerals like hematite and limonite). Ferrous iron (Fe+2) produces greenish colors.
Q. What can be concluded if a dike protrudes through several layers of rock?
radioactivity
Q. Is Granite older than sandstone?
Sandstone Sandstone is younger than phyllite (deposited and formed on top of phyllite, therefore younger) but is cut by granite and is therefore older than granite. Granite Granite dyke cuts across sandstone and phyllite (therefore younger than both) and then a sill of granite forms parallel to sandstone layer.
Q. How is the principle of original horizontality describe?
The Principle of Original Horizontality states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity. It is a relative dating technique. The principle is important to the analysis of folded and tilted strata.
Q. What is the principle of original horizontality examples?
The principle of original horizontality states that sediment is deposited horizontally. This is sometimes easier to envision with liquids: imagine pouring water into a cup. The surface of the water is perfectly flat – horizontal. If you dump that water into a bowl, the surface remains flat.
Q. What is the principle of inclusions?
The principle of inclusions and components states that, with sedimentary rocks, if inclusions (or clasts) are found in a formation, then the inclusions must be older than the formation that contains them. A similar situation with igneous rocks occurs when xenoliths are found.
Q. What is the principle of original horizontality quizlet?
The principle of original horizontality states that sediments are deposited in horizontal layers that are parallel to the surface on which they were deposited. This implies that tilted or folded layers indicate that the crust has been deformed.
Q. Which of the following is an example of nonconformity?
Nonconformity is defined as a failure to match or act like other people or things, or a conscious refusal to accept generally accepted beliefs. When you dress differently and wear your hair differently than the popular styles because you want to reflect only your own taste, this is an example of nonconformity.
Q. How is nonconformity formed?
Nonconformity: develops where sediments are deposited on top of an eroded surface of igneous or metamorphic rocks. Paraconformity: strata on either side of the unconformity are parallel, there is little apparent erosion. Angular unconformity: strata is deposited on tilted and eroded layers (such as at Siccar Point)
Q. What is another word for nonconformity?
What is another word for nonconformity?
| dissent | noncompliance |
|---|---|
| exception | negation |
| nonconformism | defiance |
| nonconformance | schism |
| apostasy | revolt |
Q. Is there value in nonconformity?
Just because something you might do is different doesn’t mean it’s wrong, yes there is value in nonconformity, there is even a beauty to it. If everything conforms to society’s wants, there would be no individuality in the world, no left-handed people, no change, and no rock music.
Q. Is nonconformity good or bad?
Our studies found that nonconformity leads to positive inferences of status and competence when it is associated with deliberateness and intentionality. In contrast, when observers perceive a nonconforming behavior as unintentional, it does not result in enhanced perceptions of status and competence.
Q. Why is nonconformity dangerous?
Although some believe that nonconformity is fundamentally nonviolent, it is more often the case that both the nonconformists’ predisposed vice and the vindictive nature of those wishing to conform them lead to inherent volatility, persecution, or physical danger.
Q. Why is it important to not conform?
Not conforming helps us grow emotionally, physically and spiritually because we’re free to do our own thing. We must try not to care about what other people think. You’ll stop conforming, and as long as you’re not rejecting other people out of spite, no one should have an opinion on it or make you feel bad.