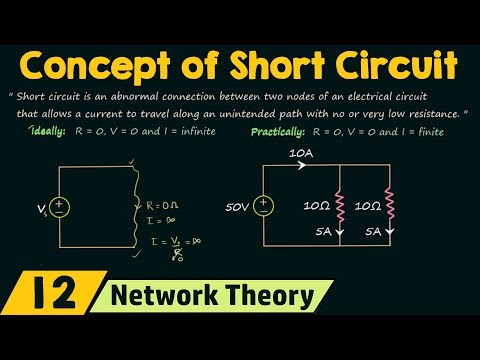
If there is a short directly across a voltage source, this can be a dangerous situation. The reason for this is that Ohm’s Law states that current through a resistor is the voltage across the resistor divided by the resistance, I=V/R. In the case of a short, the resistance is typically considered to be zero.
Q. Do amps go up as more parallel paths?
In a series circuit, if there is more than one resistance in the circuit, those resistances are connected one after the other; thus, the resistances add up. Tech A says an example of a series-parallel circuit is the brake light circuit. Tech B says that total amperage goes up as more parallel paths are added.
Table of Contents
Q. What is the value power when voltage source is short circuited?
When connected to an open circuit, there is zero current and thus zero power. When connected to a load resistance, the current through the source approaches infinity as the load resistance approaches zero (a short circuit). Thus, an ideal voltage source can supply unlimited power.
Q. Why do we zero a voltage source with a short circuit?
An ideal voltage source has zero internal impedance by definition of being “ideal”, so if we reduce its voltage to zero, we are left with a zero impedance source, which is a short circuit. An ideal voltage source can produce whatever current it needs to keep its terminal voltage at its specified value.
Q. Can we short voltage source?
If we could short a voltage source, it would mean that there was a voltage difference of x volts between A and B (because of the voltage source), and simultaneously that A and B would be at the same voltage level (because of the short circuit), which is impossible!
Q. Why current source is open?
An ideal current source has infinite internal impedance, so when you make its current zero, you are left with an infinite impedance, which is an open circuit. An idea current source has the property that it can produce whatever voltage it needs to to force its specified current to flow through it.
Q. How do I delete voltage source?
To turn off a voltage source, you replace it with a short circuit. Circuit A contains two voltage sources, vs1 and vs2, and you want to find the output voltage vo across the 10-kΩ resistor.