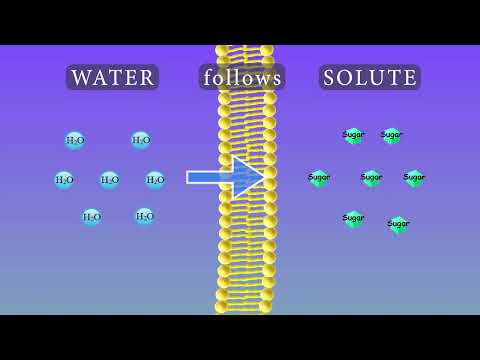
Q. How does a membrane deal with materials?
1. Lipid diffusion (the only substances that can through the membrane on this way are lipid-soluble molecules such as steroids, or very small molecules, such as water, oxygen and carbon dioxide); 2. Osmosis (the diffusion of water across a membrane);
Q. What are the 4 ways materials enter and leave a cell?
Your answer must include two passive and active transport methodsDiffusionno energy is required; transports gases and other small particles; moves from high to lowOsmosisno energy required; only transports water; moves from high to lowActive Transportmoves particles through proteins; requires energy; low to highPassive …
Table of Contents
- Q. How does a membrane deal with materials?
- Q. What are the 4 ways materials enter and leave a cell?
- Q. Why is it necessary for wastes to be removed from the body?
- Q. How do plant cells remove waste?
- Q. What happens to the waste produced in a plant body?
- Q. Are waste products stored in flowers?
- Q. Which plant waste products are stored in the old xylem?
- Q. How many products are stored in old xylem in plants?
- Q. Where are resin and gums preserved?
- Q. What is translocation Why is it essential for plants?
- Q. What happens during translocation in plants?
- Q. What is difference between transpiration and translocation?
- Q. What is translocation How does it take place in plants?
- Q. What is translocation short answer?
- Q. What is translocation and how does it occur?
- Q. How does translocation occur?
Q. Why is it necessary for wastes to be removed from the body?
Excretion is the removal from the body of waste products which result from normal life processes. Waste products such as carbon dioxide must be removed. If they are allowed to accumulate they cause poisoning which slows down vital chemical reactions.
Q. How do plant cells remove waste?
Plants excrete through stomatal pores on their leaves. The major metabolic reactions occurring in a plant that produce this waste are cellular respiration and photosynthesis. One of these methodical systems that remove the waste that accumulates throughout the body is the excretory system.
Q. What happens to the waste produced in a plant body?
Answer: Plants major of their waste into useful substances a metabolic process called photosynthesis in which the gaseous wastes in side the plants are are excreted during respiration. This happens through their stomata via transpiration and through root cell walls.
Q. Are waste products stored in flowers?
In plant cell. Hint: Plants excreted the main waste products like carbon dioxide, water vapour and oxygen through gaseous exchange through stomata and lenticels. Some wastes are stored in plants in the form of gums and resins.
Q. Which plant waste products are stored in the old xylem?
Complete answer: The resins and gums are stored in the plant part called Old Xylem.
Q. How many products are stored in old xylem in plants?
Two
Q. Where are resin and gums preserved?
Xylem
Q. What is translocation Why is it essential for plants?
Translocation is defined as “the transport of soluble products of photosynthesis”. The translocation in plants takes place by vascular tissue called phloem. The translocation is essential since without it, food prepared by leaves of plants could not reach other parts of plant.
Q. What happens during translocation in plants?
Photosynthesis produces glucose in the green parts of plants, which are often leaves. This is then converted into sucrose. The movement of sucrose and other substances like amino acids around a plant is called translocation . …
Q. What is difference between transpiration and translocation?
Transpiration is a biological process in which the water molecules are lost in the form of water vapours from the aerial parts of the plants Whereas translocation is also a biological mechanism involving the transfer of water and other soluble nutrients from one part of the plant to another through the xylem and phloem …
Q. What is translocation How does it take place in plants?
Transport of soluble product of photosynthesis or food from leaves to other parts of plants is called translocation. For translocation, food molecules enter the part of the phloem called the sieve tubes where they can be transported upwards or downwards to all the parts of the plant including roots.
Q. What is translocation short answer?
Answer: Translocation is a biological mechanism involving the transfer of water and other soluble nutrients from one part of the plant to another through the xylem and phloem, which occurs in all plants.
Q. What is translocation and how does it occur?
Translocation is the movement of materials in plants from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Nutrients, mainly sugars, are created in the leaves during photosynthesis. These are then transported throughout the plant through phloem, which are a long series of connected cells.
Q. How does translocation occur?
Translocation occurs within a series of cells known as the phloem pathway, or phloem transport system, with phloem being the principal food-conducting tissue in vascular plants. Nutrients are translocated in the phloem as solutes in a solution called phloem sap.