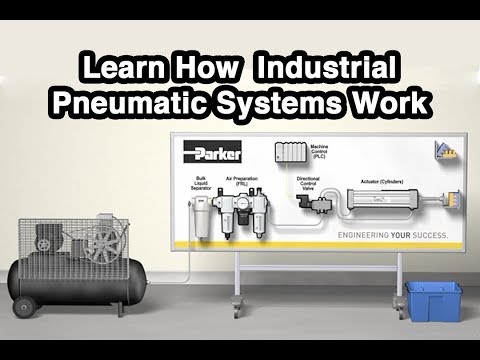
Pneumatics makes use of an air compressor to reduce the volume of the air in order to increase its pressure. This then moves through a filter into pneumatic tubing, where it’s controlled by valves before reaching an actuator which does the work at the end of the process.
Q. What is the principle of pneumatic power system?
The principles of pneumatics are the same as those for hydraulics, but pneumatics transmits power using a gas instead of a liquid. Compressed air is usually used, but nitrogen or other inert gases can be used for special applications. With pneumatics, air is usually pumped into a receiver using a compressor.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the principle of pneumatic power system?
- Q. What is the principle of air compressor?
- Q. What is pneumatic device?
- Q. What devices use pneumatics?
- Q. What products use pneumatics?
- Q. How do we use pneumatics in everyday life?
- Q. What are the advantages of pneumatics?
- Q. What is the purpose of pneumatics?
- Q. What fluid is most commonly used in pneumatics?
- Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems?
- Q. What are two advantages of a hydraulic system?
- Q. What are the disadvantages of a hydraulic system?
- Q. What are the pros and cons of using a hydraulic system?
- Q. What are the applications of fluid power?
- Q. Where are fluid power systems used?
- Q. What are the three types of fluids?
- Q. What are the 2 types of fluid power?
Q. What is the principle of air compressor?
Air compressors work by forcing air into a container and pressurizing it. Then, the air is forced through an opening in the tank, where pressure builds up. Think of it like an open balloon: the compressed air can be used as energy as it’s released.
Q. What is pneumatic device?
A pneumatic device is a tool or instrument that generates and utilizes compressed air. Some examples of pneumatic devices are rock drills, pavement breakers, riveters, forging presses, paint sprayers, blast cleaners, and atomizers. An air compressor is one of the major types of pneumatic devices.
Q. What devices use pneumatics?
Pneumatic device, any of various tools and instruments that generate and utilize compressed air. Examples include rock drills, pavement breakers, riveters, forging presses, paint sprayers, blast cleaners, and atomizers.
Q. What products use pneumatics?
A few common examples of things we use in our daily life that contain pneumatic fittings are:
- Bicycle/ball pumps.
- Tire pressure gauges.
- Some nail guns.
- The handicapped-access buttons which operate automatic doors.
- Vacuum cleaners.
- Some car shocks.
Q. How do we use pneumatics in everyday life?
Pneumatic Fittings In Everyday Life
- Tire pressure gauges.
- Vacuum cleaners.
- Some nail guns.
- Bicycle/ball pumps.
- The device that slows your screen door down so it doesn’t slam shut when you let go of it.
- The handicapped-access button that opens door for you.
- Some car’s shocks.
Q. What are the advantages of pneumatics?
Pneumatics takes advantages of the low friction, compressible nature of air. A lot of air can be moved rapidly, and although compressibility needs to be factored in, it can provide an advantage with unmatched response and cycle times.
Q. What is the purpose of pneumatics?
As such, pneumatics are generally used when much smaller loads are involved. A pneumatic system generally uses an air compressor to reduce the volume of the air, thereby increasing the pressure of the gas. The pressurized gas travels through pneumatic hoses and is controlled by valves on the way to the actuator.
Q. What fluid is most commonly used in pneumatics?
compressed air
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems?
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Pneumatic
- • Easy channeled.
- • Temperature is flexible.
- • The transfer of power and the speed is very easy to set up.
- • Can be stored.
- • Easy utilized.
- •
- • Easy to leak.
- • Potential noise.
Q. What are two advantages of a hydraulic system?
Hydraulic System Advantages
- Hydraulic systems are easy to control and accurate.
- Hydraulic systems are simpler and easier to maintain because these systems use less moving parts.
- Only hydraulic systems can deliver constant torque or force regardless of speed changes.
- Easy to spot leakages of a hydraulic system.
Q. What are the disadvantages of a hydraulic system?
Disadvantages of hydraulic system:
- Poor resistance to working fluid pollution;
- Sensitive to temperature changes;
- Hidden danger of leakage;
- Difficult manufacturing and high cost;
- It is not suitable for long-distance transmission and requires hydraulic energy.
Q. What are the pros and cons of using a hydraulic system?
Advantages of hydraulic systems include power, accuracy, efficiency and ease of maintenance. But they disadvantages too: they can leak, which makes them messy, and the fluids inside them are often caustic to paint and some seals.
Q. What are the applications of fluid power?
Fluid Power Applications
| Electrohydraulics* | Electropneumatics* | Pneumatics Automation at Work* |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-stall control for hydrostatic drive | Multiple welding machine | Assembly |
| Concrete saw | Paint spray system | Broaching |
| Airframe tester | Pneumatic torquer for engine bolts | Clamping |
| Missile pump test | Well-digger brake | Drilling |
Q. Where are fluid power systems used?
While fluid power can be used in most any industry or application, it is commonly seen in markets that include packaging, off-highway, mining, offshore/marine, medical, material handling, construction, aerospace, automation, robotics, and entertainment. And fluid power is an important technology.
Q. What are the three types of fluids?
The Types of Fluids are:
- Ideal Fluid. An ideal fluid is incompressible and it is an imaginary fluid that doesn’t exist in reality.
- Ideal plastic Fluid.
- Real Fluid.
- Newtonian Fluid.
- Non-Newtonian Fluid.
- Incompressible Fluid.
- Compressible Fluid.
Q. What are the 2 types of fluid power?
There are two basic types of fluid power systems: hydraulic systems, which use liquids such as water and oil, and pneumatic systems, which utilize neutral gases such as air.