Q. How does air density affect pressure?
The air’s density depends on its temperature, its pressure and how much water vapor is in the air. In the free atmosphere, the air’s density decreases as the air is heated. Pressure has the opposite effect on air density. Increasing the pressure increases the density.
Q. What is the relationship between air density and air pressure?
The more gas particles there are within a given area, the greater the air density. Likewise, the greater the air density, the more gas particles there are per unit volume. Therefore, there are more air particles bombarding with a surface. Thus, the air pressure increases as the air density increases and visa versa.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does air density affect pressure?
- Q. What is the relationship between air density and air pressure?
- Q. How does heating air affect its density and pressure?
- Q. How does heat affect air pressure?
- Q. What is the relationship between air pressure and temperature?
- Q. How much does air expand with temperature?
- Q. Why does air get colder when it moves?
- Q. How does air get cooled?
- Q. Is fast air colder?
- Q. Does humidity make you feel colder?
- Q. Does higher humidity make it feel warmer?
- Q. How do you feel in humid weather?
- Q. Can you survive 100 humidity?
- Q. What happens when humidity reaches 0%?
- Q. Is 1% humidity possible?
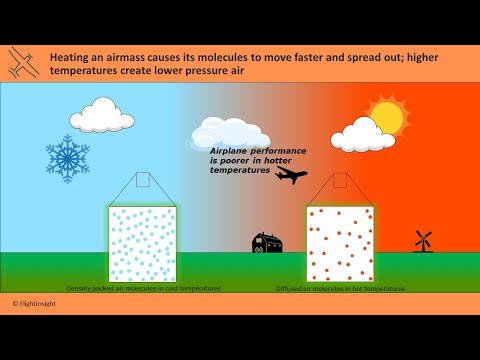
Q. How does heating air affect its density and pressure?
As temperature increases the air becomes less dense and its air pressure decreases. The less heated air will be cooler and denser.
Q. How does heat affect air pressure?
Warm air is less dense and has a lower pressure associated with it. As the sun heats the ground, the air near the ground warms. Remember, heat is less dense than cold air so the warm air will rise. This rising motion creates a natural vacuum lowering the air pressure at the Earth’s surface.
Q. What is the relationship between air pressure and temperature?
Air pressure is influenced by temperature because, as the air is warmed, the molecules start moving around more, so they bump into each other more often and create more pressure. But, air pressure also affects temperature – the more those molecules bump into each other, the more heat they generate.
Q. How much does air expand with temperature?
increasing one cubic inch for every degree A contraction of one cubic inch occurs for every degree below 32 degrees. 491 cubic inches ot air at 32 deg.
Q. Why does air get colder when it moves?
As the air surrounding our body is continuously replaced (i.e. air in flow) heat transfer is more effective i.e. more heat is sucked out of our bodies and we feel cooler. Moving air feels colder than still air because it causes evaporation of moisture from your skin, which in turn causes cooling.
Q. How does air get cooled?
The simplest cooling method of air is by contact with a colder surface – the Earth’s surface. Radiation cooling occurs when air near the ground is cooled by the Earth’s surface losing heat by radiation. Advection cooling occurs when a warmer body of air from another source passes across a colder surface.
Q. Is fast air colder?
The air molecules collide with our body’s molecules, and this collision allows the heat energy to be exchanged from our body to the air. The air then carries this away. The faster the air is, the faster this happens, so our bodies can’t readily recreate the “heat field” around us, and thus we feel cooler.
Q. Does humidity make you feel colder?
In cold weather, high humidity levels will make you feel colder. Clothing keeps your body warm by trapping a small layer of warm air around you. High humidity and cold weather will leave you feeling colder than if humidity levels were low.
Q. Does higher humidity make it feel warmer?
It refers to the fact that high humidity makes it feel hotter than the actual air temperature. So when the relative humidity of the air is high, meaning the air has a high moisture content, the sweat evaporation process slows down. The result? It feels hotter to you.
Q. How do you feel in humid weather?
Humidity is how much water vapor is in the air. When we perspire, our bodies normally rely on air to get rid of the sweat that accumulates on the skin. This allows the body to cool down. When the humidity in the air is high, the warm moisture stays on our skin longer, making us feel even hotter.
Q. Can you survive 100 humidity?
Surprisingly, yes, the condition is known as supersaturation. At any given temperature and air pressure, a specific maximum amount of water vapor in the air will produce a relative humidity (RH) of 100 percent. Supersaturated air literally contains more water vapor than is needed to cause saturation.
Q. What happens when humidity reaches 0%?
This means that at 0% relative humidity, the ambient vapor pressure is zero, and Delta-e is then equal to the saturation vapor pressure of water at body temperature (about 37 C or 99 F), which is about 6.5 kilopascals.
Q. Is 1% humidity possible?
The humidity gets pretty close to 0% (true 0% is pretty much impossible, the same way 100% purity is basically impossible). You can work all day in the dry room and not feel uncomfortable (it is maintained at a nice 70 degrees with excellent air circulation).