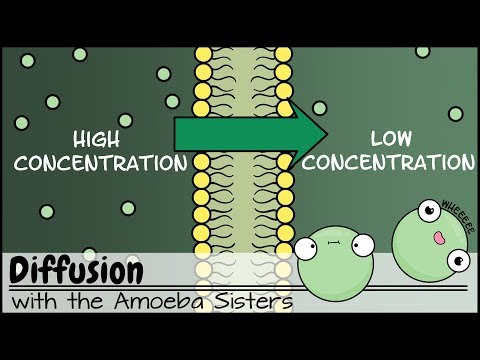
Q. How does diffusion relate to cells?
Molecules can move into or out of cells by the process of diffusion . Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from an area where they are at a higher concentration to areas where they are at a lower concentration. This is due to the random movement of the molecules.
Q. Is Diffusion a cellular process?
DIFFUSION THROUGH A CELL MEMBRANE. Introduction: Substances, such as water, ions, and molecules needed for cellular processes, can enter and leave cells by a passive process such as diffusion.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does diffusion relate to cells?
- Q. Is Diffusion a cellular process?
- Q. How does diffusion play in cellular respiration?
- Q. How does diffusion work in a cell membrane?
- Q. Which of the following does not affect the rate of diffusion?
- Q. What are the 3 variables in the numerator of Fick’s Law of Diffusion?
- Q. What is flux diffusion?
- Q. What is Fick’s second law used for?
- Q. What is Q in Fick’s law?
- Q. Why is Fick’s law important in biology?
- Q. What is the difference between Fick’s first and second law?
- Q. How do you calculate rate of diffusion?
- Q. What is the relationship between molecular size and the rate of diffusion?
- Q. Why is rate of diffusion important?
- Q. What would increase the rate of diffusion across a cell membrane?
Q. How does diffusion play in cellular respiration?
The body needs a way to get oxygen in and carbon dioxide out, which is through diffusion. The carbon dioxide concentration is much greater in your blood than the alveoli. So, by the rule of diffusion, the carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the alveoli, where it can be exhaled through the lungs.
Q. How does diffusion work in a cell membrane?
In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into (or out of) the cell by moving down it.
Q. Which of the following does not affect the rate of diffusion?
The amount of energy available for transport molecules does not affect the rate of diffusion. This is because diffusion is a passive process.
Q. What are the 3 variables in the numerator of Fick’s Law of Diffusion?
Fick’s Law essentially states that the rate of diffusion of a gas across a permeable membrane is determined by the chemical nature of the membrane itself, the surface area of the membrane, the partial pressure gradient of the gas across the membrane, and the thickness of the membrane.
Q. What is flux diffusion?
Fick’s first law J is the diffusion flux, of which the dimension is amount of substance per unit area per unit time. J measures the amount of substance that will flow through a unit area during a unit time interval. D is the diffusion coefficient or diffusivity. x is position, the dimension of which is length.
Q. What is Fick’s second law used for?
Fick’s 2nd law of diffusion Consider diffusion at the front and rear surfaces of an incremental planar volume. Fick’s 2nd law of diffusion describes the rate of accumulation (or depletion) of concentration within the volume as proportional to the local curvature of the concentration gradient.
Q. What is Q in Fick’s law?
Fick’s Law of diffusion describes the time course of the transfer of a solute between two compartments that are separated by a thin membrane, given by. (7.1) where. q = quantity of solute. A = membrane surface area.
Q. Why is Fick’s law important in biology?
The blood system in humans continually brings more oxygen to the cell and takes carbon dioxide away, maintaining a high concentration gradient. Fick’s law is used to measure the rate of diffusion.
Q. What is the difference between Fick’s first and second law?
The first law can only be applied to systems in which the conditions remain the same— in other words, if the flux coming into the system equals the flux going out. Fick’s second law is more applicable to physical science and other systems that are changing.
Q. How do you calculate rate of diffusion?
Key Equations
- rate of diffusion=amount of gas passing through an areaunit of time.
- rate of effusion of gas Arate of effusion of gas B=√mB√mA=√MB√MA.
Q. What is the relationship between molecular size and the rate of diffusion?
The relationship between molecular size and the rate of diffusion is an inverse relationship; more simply put, the smaller a molecule, the faster it diffuses.
Q. Why is rate of diffusion important?
Diffusion is important to cells because it allows them to gain the useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow, and lets them get rid of waste products.
Q. What would increase the rate of diffusion across a cell membrane?
As with any chemical reaction, increasing the temperature or pressure increases the kinetic energy of the particles, thus increasing the rate of diffusion. Concentration Gradient: The greater the concentration gradient (the difference in concentration either side of the membrane) the greater the rate of diffusion.