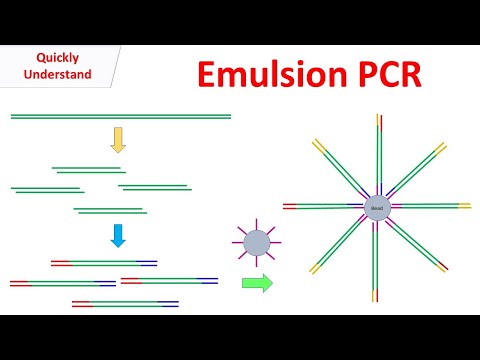
Q. How does emulsion PCR work?
Emulsion PCR (EmPCR) is a commonly employed method for template amplification in multiple NGS-based sequencing platforms. The basic principle of emPCR is dilution and compartmentalization of template molecules in water droplets in a water-in-oil emulsion.
Q. What is bridge PCR?
Bridging PCR (BPCR) is a combination of two processes, a recombination between two template sequences and an amplification of the recombinant template. Two parental sequences share a homologous region (a region in which the sequence is identical) and diverge in the nonhomologous flanking sequences.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does emulsion PCR work?
- Q. What is bridge PCR?
- Q. How was emulsion PCR used during genome sequencing?
- Q. What is emulsion PCR used for?
- Q. Does Illumina use emulsion PCR?
- Q. What is pyrosequencing used for?
- Q. Why is it called shotgun sequencing?
- Q. Is PCR used in NGS?
- Q. What is the pyrosequencing technique?
- Q. Which PCR is used in pyrosequencing?
- Q. Which is the best description of emulsion PCR?
- Q. How are microemulsions different from ordinary emulsions?
- Q. How are microemulsions used in the industrial world?
- Q. How is the polymerization rate of a microemulsion controlled?
Q. How was emulsion PCR used during genome sequencing?
This emulsion PCR (ePCR) method allowed spatial isolation of each template to a single bubble and enabled clonal amplification of the template on each bead. In 2005, two ground-breaking studies built on these discoveries and described high-throughput methods for rapidly and cheaply sequencing a whole bacterial genome.
Q. What is emulsion PCR used for?
Emulsion PCR (ePCR) is an important technique that permits amplification of DNA molecules in physically separated picoliter-volume water-in-oil droplets, and thus avoids formation of unproductive chimeras and other artifacts between similar DNA sequences.
Q. Does Illumina use emulsion PCR?
Reversible terminator sequencing (Illumina) Whilst many other techniques use emulsion PCR to amplify the DNA library fragments, reversible termination uses bridge PCR, improving the efficiency of this stage of the process.
Q. What is pyrosequencing used for?
Pyrosequencing is used to reveal the genetic code of a section of DNA. It is also able to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertion-deletions or other sequence variations, in addition to being able to quantify DNA methylation and allele frequency.
Q. Why is it called shotgun sequencing?
In genetics, shotgun sequencing is a method used for sequencing random DNA strands. It is named by analogy with the rapidly expanding, quasi-random shot grouping of a shotgun. Computer programs then use the overlapping ends of different reads to assemble them into a continuous sequence. …
Q. Is PCR used in NGS?
PCR techniques play an integral role in targeted NGS sequencing, allowing for the generation of multiple NGS libraries and the sequencing of multiple targeted regions simultaneously.
Q. What is the pyrosequencing technique?
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that detects light emitted during the sequential addition of nucleotides during the synthesis of a complementary strand of DNA.
Q. Which PCR is used in pyrosequencing?
DNA polymerase incorporates the correct, complementary dNTPs onto the template. This incorporation releases pyrophosphate (PPi). ATP sulfurylase converts PPi to ATP in the presence of adenosine 5´ phosphosulfate.
Q. Which is the best description of emulsion PCR?
DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3360-0_4 Abstract Emulsion PCR (EmPCR) is a commonly employed method for template amplification in multiple NGS-based sequencing platforms. The basic principle of emPCR is dilution and compartmentalization of template molecules in water droplets in a water-in-oil emulsion.
Q. How are microemulsions different from ordinary emulsions?
In contrast to ordinary emulsions, microemulsions form upon simple mixing of the components and do not require the high shear conditions generally used in the formation of ordinary emulsions. The three basic types of microemulsions are direct (oil dispersed in water, o/w), reversed (water dispersed in oil, w/o) and bicontinuous.
Q. How are microemulsions used in the industrial world?
Microemulsions also have industrial applications, one of them being the synthesis of polymers. Microemulsion polymerization is a complex heterogeneous process where transport of monomers, free radicals and other species (such as chain transfer agent, co-surfactant and inhibitors) between the aqueous and organic phases, takes place.
Q. How is the polymerization rate of a microemulsion controlled?
Polymerization rate is controlled by monomer partitioning between the phases, particle nucleation, and adsorption and desorption of radicals. Particle stability is affected by the amount and type of surfactant and pH of dispersing medium. It is also used in the process of creating nanoparticles.