Q. How does gamma rays change the nucleus?
In gamma decay, depicted in Fig. 3-6, a nucleus changes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state through the emission of electromagnetic radiation (photons). The number of protons (and neutrons) in the nucleus does not change in this process, so the parent and daughter atoms are the same chemical element.
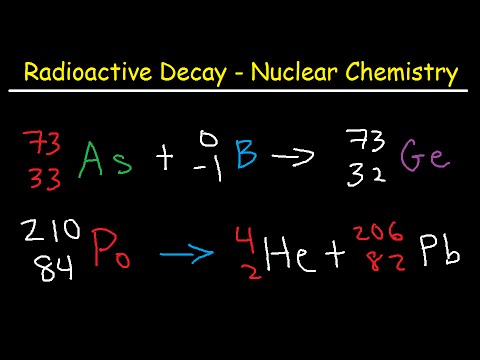
Q. How does the beta particle change the nucleus?
Beta decay occurs when, in a nucleus with too many protons or too many neutrons, one of the protons or neutrons is transformed into the other. However within a nucleus, the beta decay process can change a proton to a neutron. An isolated neutron is unstable and will decay with a half-life of 10.5 minutes.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does gamma rays change the nucleus?
- Q. How does the beta particle change the nucleus?
- Q. How does Alpha Beta and gamma particle affect the mass number of an atom?
- Q. How does Alpha change the nucleus?
- Q. What are the 5 types of radioactive decay?
- Q. What is the radioactive symbol?
- Q. Which type of radiation is the most harmful?
- Q. What is beta decay example?
- Q. What happens if carbon 10 goes under beta decay?
- Q. What can beta decay penetrate?
- Q. What material can stop beta radiation?
- Q. What can gamma be stopped by?
- Q. Why gamma ray is dangerous?
- Q. Does water stop gamma rays?
- Q. Can gamma rays melt metal?
- Q. Can gamma radiation be stopped?
- Q. Which is the least penetrating radiation?
- Q. Can radiation melt your skin?
- Q. Are there any mutated animals in Chernobyl?
- Q. Can radiation melt your face?
- Q. Was Fukushima worse than Chernobyl?
- Q. Is Fukushima safe today?
- Q. Is Hiroshima still radioactive?
Q. How does Alpha Beta and gamma particle affect the mass number of an atom?
Alpha radiation decreases the atomic number of the emitting element by 2 and the atomic mass number by 4. Beta radiation increases the atomic number of an element by 1 and does not affect the atomic mass number. Gamma radiation does not affect the atomic number or the atomic mass number.
Q. How does Alpha change the nucleus?
Alpha radiation occurs when the nucleus of an atom becomes unstable (the ratio of neutrons to protons is too low) and alpha particles are emitted to restore balance. The nuclei of these elements are rich in neutrons, which makes alpha particle emission possible.
Q. What are the 5 types of radioactive decay?
Radioactivity
- Types of Decay. There are many types of emmitted particles and radiation that radioisotopes produce when they decay.
- Alpha, Beta, Gamma Composition. Alpha particles carry a positive charge, beta particles carry a negative charge, and gamma rays are neutral.
- Alpha Decay.
- Beta Decay.
- Gamma Decay.
Q. What is the radioactive symbol?
In Unicode. U+2622 ☢ RADIOACTIVE SIGN (HTML ☢ ) The international radiation symbol (also known as the trefoil) first appeared in 1946, at the University of California, Berkeley Radiation Laboratory. At the time, it was rendered as magenta, and was set on a blue background.
Q. Which type of radiation is the most harmful?
Gamma rays
Q. What is beta decay example?
The decay of technetium-99, which has too many neutrons to be stable, is an example of beta decay. A neutron in the nucleus converts to a proton and a beta particle. The nucleus ejects the beta particle and some gamma radiation. The new atom retains the same mass number, but the number of protons increases to 44.
Q. What happens if carbon 10 goes under beta decay?
If a proton is converted into a neutron it is known as β+ decay, if a neutron is converted into a proton it is referred to as β- decay. The β+ decay of carbon-10. In this example, a proton of carbon is converted into a neutron and the emitted beta particle is a positron.
Q. What can beta decay penetrate?
Very energetic beta particles can penetrate up to one-half an inch through skin and into the body. They can be shielded with less than an inch of material, such as plastic. Shielding this very penetrating type of ionizing radiation requires thick, dense material such as several inches of lead or concrete.
Q. What material can stop beta radiation?
So unlike alpha, beta particles can penetrate a sheet of paper, but can easily be stopped by a thin sheet of either Perspex or aluminum. Crucially, though, in situations where beta radiation is not accompanied by gamma radiation, materials such as steel and lead are not suitable as shielding.
Q. What can gamma be stopped by?
Gamma rays have so much penetrating power that several inches of a dense material like lead, or even a few feet of concrete may be required to stop them.
Q. Why gamma ray is dangerous?
The extremely high energy of gamma rays allows them to penetrate just about anything. They can even pass through bones and teeth. This makes gamma rays very dangerous. They can destroy living cells, produce gene mutations, and cause cancer.
Q. Does water stop gamma rays?
Gamma rays can penetrate a moderate amount of water before being attenuated to the level of background radiation. They lose about half of their energy in penetrating 15 cm of water. Neutrons can penetrate several feet of water.
Q. Can gamma rays melt metal?
In general, mercury, being a liquid at room temperature, would not exhibit as noticeable effects from alpha radiation as would aluminum. Gamma radiation has little permanent effect on either metal.
Q. Can gamma radiation be stopped?
The energy that is released as the atoms become stable is known as radiation. There are three types of radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays. Beta particles can be blocked by a sheet of aluminum, but gamma rays require several inches of lead, concrete or steel to be stopped.
Q. Which is the least penetrating radiation?
There are three types of nuclear radiation: alpha, beta and gamma. Alpha is the least penetrating, while gamma is the most penetrating.
Q. Can radiation melt your skin?
People who have been exposed to high doses can also have skin damage ranging from itching to burns, blisters and ulcers. They may also have temporary hair loss. After the initial symptoms there may be a brief period of improvement.
Q. Are there any mutated animals in Chernobyl?
Despite looking normal, Chernobyl’s animals and plants are mutants. According to a 2001 study in Biological Conservation, Chernobyl-caused genetic mutations in plants and animals increased by a factor of 20.
Q. Can radiation melt your face?
Radiation is just energy being deposited in your body. However, a radiation dose high enough to melt your skin is going to cause unconsciousness well before that happens, and acute death as well.
Q. Was Fukushima worse than Chernobyl?
Chernobyl is widely acknowledged to be the worst nuclear accident in history, but a few scientists have argued that the accident at Fukushima was even more destructive. Both events were far worse than the partial meltdown of a nuclear reactor at Three Mile Island near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.
Q. Is Fukushima safe today?
The no-entry zone around the nuclear plant makes up less than 3% of the prefecture’s area, and even inside most of the no-entry zone, radiation levels have declined far below the levels that airplane passengers are exposed to at cruising altitude. Needless to say, Fukushima is perfectly safe for tourists to visit.
Q. Is Hiroshima still radioactive?
The radiation in Hiroshima and Nagasaki today is on a par with the extremely low levels of background radiation (natural radioactivity) present anywhere on Earth. It has no effect on human bodies.