Adding small amounts of impurities allows control of the conductivity of the semiconductor: shallow donors, such as phosphorous in silicon, produce n-type conductivity (carried by electrons), and shallow acceptors, such as boron in silicon, produce p-type conductivity (carried by holes).
Q. What element is a semiconductor?
silicon
Table of Contents
- Q. What element is a semiconductor?
- Q. How can you increase the conductivity of metals?
- Q. Why impurities are added to semiconductors?
- Q. How do impurities affect electrical conductivity?
- Q. On which factor conductivity of semiconductor depends?
- Q. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change with temperature?
- Q. What is the conductivity of a semiconductor?
- Q. Why is conductivity of N type semiconductor?
- Q. What is N-type semiconductor?
- Q. How do you calculate conductivity of a semiconductor?
- Q. How does the energy gap in an intrinsic?
- Q. At what temperature will an intrinsic semiconductor behave like a perfect insulator?
- Q. What is the order of energy gap in intrinsic semiconductor?
- Q. What is the range of energy band gap of semiconductor?
- Q. Why is band gap important?
- Q. Which has highest band gap?
- Q. What is forbidden gap?
- Q. Why does band gap decrease with temperature?
- Q. What happens to a semiconductor at low temperatures?
- Q. Why does band gap increase as particle size decreases?
- Q. Why band gap of silicon is more than germanium?
Q. How can you increase the conductivity of metals?
There are many reasons for electroplating. It can enhance a component’s strength, solderability, and corrosion-resistance. Electroplating can also improve the electrical conductivity of a base material.৪ অক্টোবর, ২০১৮
Q. Why impurities are added to semiconductors?
Impurities are added into a semiconductor to actually increase the electric conductivity. The process of adding an impurity into the semiconductor to increase its ability to conduct electricity is known as doping and the impure semiconductor is known as a doped semiconductor.
Q. How do impurities affect electrical conductivity?
When impurities (like salts) dissolve in water, they form ions, and these ions make it possible for an electric current to pass through the solution.১ ডিসেম্বর, ২০২০
Q. On which factor conductivity of semiconductor depends?
Name two factors on which electrical conductivity of a pure semiconductor at a given temperature depends. Electrical conductivity of a pure semiconductor depends upon: (i) The width of the forbidden band….Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits.
| A | B | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change with temperature?
As the temperature increases, more electrons get the energy to jump from Conduction band to valence band, and thereby increases the conductivity of the semiconductor.
Q. What is the conductivity of a semiconductor?
Electrical Conduction in Semiconductors
| Material | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Conductivity (Ω-1-cm-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors | ||
| Carbon (Graphite) | 3-60 x 10-5 | 1.67 × 103 to 3.33 × 104 |
| Germanium | 1-500 x 10-3 | 2.0 to 1.00 × 103 |
| Silicon | 0.10- 60 | 1.67 × 10-2 to 10 |
Q. Why is conductivity of N type semiconductor?
n-type semiconductor contains an increased number of electrons in the conduction band. Therefore, Si doped with P has more number of electrons in the conduction band than those in the conduction band in pure Si. Thus, the conductivity of Si-doped with P is higher than that of pure Si.
Q. What is N-type semiconductor?
An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Silicon of Group IV has four valence electrons and phosphorus of Group V has five valence electrons. * This free electron is the carrier of an n-type semiconductor.
Q. How do you calculate conductivity of a semiconductor?
Answer: The conductivity is obtained by adding the product of the electronic charge, q, the carrier mobility, and the density of carriers of each carrier type, or: As n-type material contains almost no holes, the conductivity equals: s = q mn n = 1.6 x 10-19 x 1400 x 1016 = 2.24 1/Wcm.
Q. How does the energy gap in an intrinsic?
Solution : When an intrinsic semiconductor is doped with the impurity atoms of valence five like As, P or Sb, some addition energy levels are produced, situation in the energy gap slightly below the conduction band which are called donor energy levels. Due to it, energy gap in semiconductor decreases.৩ জুন, ২০২০
Q. At what temperature will an intrinsic semiconductor behave like a perfect insulator?
zero kelvin
Q. What is the order of energy gap in intrinsic semiconductor?
The energy gap in a semiconductor is of the order of 1eV.
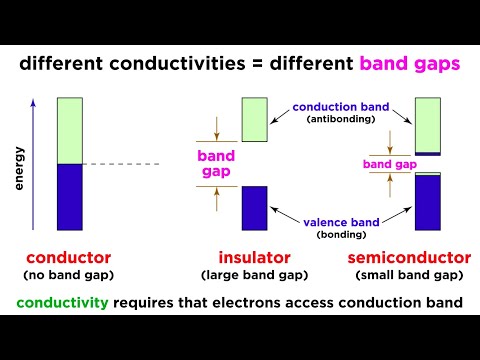
Q. What is the range of energy band gap of semiconductor?
Conventional semiconductors like silicon have a bandgap in the range of 1 – 1.5 electronvolt (eV), whereas wide-bandgap materials have bandgaps in the range of 2 – 4 eV. Generally, wide-bandgap semiconductors have electronic properties which fall in between those of conventional semiconductors and insulators.
Q. Why is band gap important?
As the electronegativity difference Δχ increases, so does the energy difference between bonding and antibonding orbitals. The band gap is a very important property of a semiconductor because it determines its color and conductivity.৩ ডিসেম্বর, ২০২০
Q. Which has highest band gap?
diamond
Q. What is forbidden gap?
The gap between valence band and conduction band is called as forbidden energy gap. As the name implies, this band is the forbidden one without energy. The forbidden energy gap if greater, means that the valence band electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus.
Q. Why does band gap decrease with temperature?
The band-gap energy of semiconductors tends to decrease with increasing temperature. When temperature increases, the amplitude of atomic vibrations increase, leading to larger interatomic spacing. Band gaps also depend on pressure.
Q. What happens to a semiconductor at low temperatures?
At lower temperatures, carriers move more slowly, so there is more time for them to interact with charged impurities. As a result, as the temperature decreases, impurity scattering increases, and the mobility decreases. This is just the opposite of the effect of lattice scattering.
Q. Why does band gap increase as particle size decreases?
Because of the confinement of the electrons and holes, the band gap energy increases between the valence band and the conduction band with decreasing the particle size.
Q. Why band gap of silicon is more than germanium?
Silicon has large band gap (1.12eV) than germanium (0.7eV). So, at same temperature, the thermal pair generation in silicon is less than germanium. Ge has higher electron and hole mobility and because of this Ge devices can function up to a higher frequency than Si devices.১৯ অক্টোবর, ২০১৯