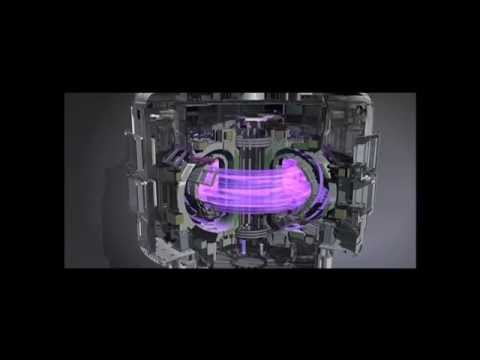
Q. How does magnetic field affect plasma?
The magnetic field affects the plasma transport to the chamber wall, changing the ionization balance and the plasma spatial distribution. In collisionless fusion plasma, a magnetic field may cause low frequency instabilities that affect the plasma transport and the plasma global confinement.
Q. Can magnetic fields be created?
A magnetic field can be created by running electricity through a wire. All magnetic fields are created by moving charged particles. Even the magnet on your fridge is magnetic because it contains electrons that are constantly moving around inside.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does magnetic field affect plasma?
- Q. Can magnetic fields be created?
- Q. What happens when plasma hits Plasma?
- Q. Does plasma follow magnetic field lines?
- Q. Where do you find plasma in your everyday life?
- Q. What does a magnetic field do to a charged particle in a plasma?
- Q. Do plasmas conduct electricity?
- Q. How do you make a plasma field?
- Q. Why do charged particles spiral along magnetic field lines?
- Q. When a charged particle moves in a straight line a magnetic field is?
- Q. Can a magnetic field accelerate a charged particle?
- Q. Why can’t a magnetic field change the speed of electrons?
- Q. How does magnetism affect our everyday life?
- Q. Does a moving charge produce magnetic field?
- Q. What is a magnetic field caused by?
Q. What happens when plasma hits Plasma?
Magnetic field lines connecting different plasma populations act as channels for the transport of plasmas, currents, electric fields, and waves between the two environments. When a flowing magnetized plasma strikes a solid object, an atmosphere, or a magnetosphere, strong interactions of various types can occur.
Q. Does plasma follow magnetic field lines?
The ions and electrons of a plasma interacting with the Earth’s magnetic field generally follow its magnetic field lines. Plasmas exhibit more complex second-order behaviors, studied as part of magnetohydrodynamics.
Q. Where do you find plasma in your everyday life?
More exotic sources of plasma include particles in nuclear fusion reactors and weapons, but everyday sources include the Sun, lightning, fire, and neon signs. Other examples of plasma include static electricity, plasma balls, St. Elmo’s fire, and the ionosphere.
Q. What does a magnetic field do to a charged particle in a plasma?
The answer is the interaction with the magnetic field. The force initially results in an acceleration parallel to itself, but the magnetic field deflects the resulting motion in the drift direction.
Q. Do plasmas conduct electricity?
Being made of charged particles, plasmas can do things gases cannot, like conduct electricity. Speaking of electrostatic interactions, because particles in a plasma – the electrons and ions – can interact via electricity and magnetism, they can do so at far greater distances than an ordinary gas.
Q. How do you make a plasma field?
A plasma may be produced in the laboratory by heating a gas to an extremely high temperature, which causes such vigorous collisions between its atoms and molecules that electrons are ripped free, yielding the requisite electrons and ions. A similar process occurs inside stars.
Q. Why do charged particles spiral along magnetic field lines?
The component of velocity parallel to the lines is unaffected, and so the charges spiral along the field lines. If field strength increases in the direction of motion, the field will exert a force to slow the charges (and even reverse their direction), forming a kind of magnetic mirror.
Q. When a charged particle moves in a straight line a magnetic field is?
The velocity component perpendicular to the magnetic field creates circular motion, whereas the component of the velocity parallel to the field moves the particle along a straight line. The pitch is the horizontal distance between two consecutive circles. The resulting motion is helical.
Q. Can a magnetic field accelerate a charged particle?
The reason is that the magnetic field doesn’t affect the speed is because the magnetic field applies a force perpendicular to the velocity. Hence, the force can’t do work on the particle. So it can not change the speed.
Q. Why can’t a magnetic field change the speed of electrons?
The magnetic force will not change the speed of a moving electron because the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity. A moving electron in a uniform magnetic field will undergo uniform circular motion.
Q. How does magnetism affect our everyday life?
Magnets in electric generators turn mechanical energy into electricity, while some motors use magnets to convert electricity back into mechanical work. Mines use magnetic sorting machines to separate useful metallic ores from crushed rock. In food processing, magnets remove small metal bits from grains and other food.
Q. Does a moving charge produce magnetic field?
A charged particle moving without acceleration produces an electric as well as a magnetic field. It produces an electric field because it’s a charge particle. But when it is at rest, it doesn’t produce a magnetic field.
Q. What is a magnetic field caused by?
Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric charges. Every substance is made up of tiny units called atoms. The magnetic field is the area around a magnet that has magnetic force. All magnets have north and south poles. Opposite poles are attracted to each other, while the same poles repel each other.