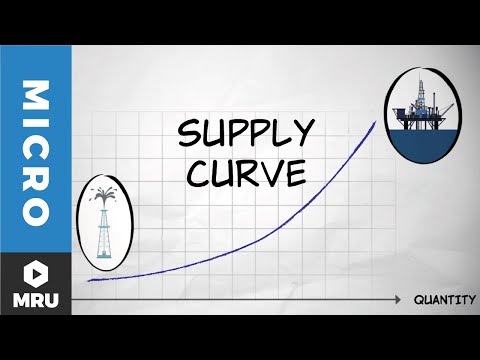
How a Supply Curve Works. The supply curve will move upward from left to right, which expresses the law of supply: As the price of a given commodity increases, the quantity supplied increases (all else being equal). In other words, supply will increase. Technology is a leading cause of supply curve shifts.
Q. What does a market supply curve show quizlet?
A market supply curve shows. the quantity supplied by producers at different prices. When a percentage change in price is perfectly matched by an equal percentage change in quantity supplied, elasticity is exactly one, and supply is.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does a market supply curve show quizlet?
- Q. What does a market supply schedule shows?
- Q. What is an example of supply affecting price?
- Q. What is an example of supply?
- Q. What is the difference between change in demand and quantity demanded?
- Q. What causes shift in supply curve?
- Q. How do you shift a supply curve?
- Q. What does a decrease in quantity demanded look like?
- Q. What happens to the supply curve when supply decreases?
- Q. What is the difference between a decrease in demand and a decrease in quantity demanded?
- Q. What happens if quantity demanded decreases?
- Q. How do you find quantity demanded?
- Q. How do you find quantity demanded when given price?
Q. What does a market supply schedule shows?
The supply schedule shows you how the supply changes when you increase or decrease the price. The market supply schedule is a table that lists the quantity supplied for a good or service that suppliers throughout the whole economy are willing and able to supply at all possible prices.
Q. What is an example of supply affecting price?
Supply and demand rise and fall until an equilibrium price is reached. For example, suppose a luxury car company sets the price of its new car model at $200,000. While the initial demand may be high, due to the company hyping and creating buzz for the car, most consumers are not willing to spend $200,000 for an auto.
Q. What is an example of supply?
The noun means an amount or stock of something that is available for use. That stock has been supplied. A mother, for example, may take a large supply of diapers (UK: nappies) with her when she goes on vacation with her baby. This means a large amount that is available for use.
Q. What is the difference between change in demand and quantity demanded?
A change in demand means that the entire demand curve shifts either left or right. A change in quantity demanded refers to a movement along the demand curve, which is caused only by a chance in price.
Q. What causes shift in supply curve?
Supply curve shift: Changes in production cost and related factors can cause an entire supply curve to shift right or left. This causes a higher or lower quantity to be supplied at a given price. The ceteris paribus assumption: Supply curves relate prices and quantities supplied assuming no other factors change.
Q. How do you shift a supply curve?
If costs fall, more can be produced, and the supply curve will shift to the right. Any change in an underlying determinant of supply, such as a change in the availability of factors, or changes in weather, taxes, and subsidies, will shift the supply curve to the left or right.
Q. What does a decrease in quantity demanded look like?
A decrease in quantity demanded represents movement along the demand curve with changes in price. Thus, the quantity demanded goes up as the price comes down. This is a movement along the demand curve.
Q. What happens to the supply curve when supply decreases?
Understanding Change in Supply An increase in the change in supply shifts the supply curve to the right, while a decrease in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left.
Q. What is the difference between a decrease in demand and a decrease in quantity demanded?
A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease. An increase in supply, all other things unchanged, will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity demanded will increase. A decrease in supply will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity demanded will decrease.
Q. What happens if quantity demanded decreases?
As we can see on the demand graph, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. Economists call this the Law of Demand. If the price goes up, the quantity demanded goes down (but demand itself stays the same). If the price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
Q. How do you find quantity demanded?
Price Elasticity on Quantity Demanded = [Pi x (Qj – Qi)] / [Qi x (Pj – Pi)]
- The Initial and final prices of goods and services are represented by Pi and Pj respectively.
- The Initial and final quantity demanded of goods and services are represented by Qi and Qj respectively.
Q. How do you find quantity demanded when given price?
You use the demand formula, Qd = x + yP, to find the demand line algebraically or on a graph. In this equation, Qd represents the number of demanded hats, x represents the quantity and P represents the price of hats in dollars.