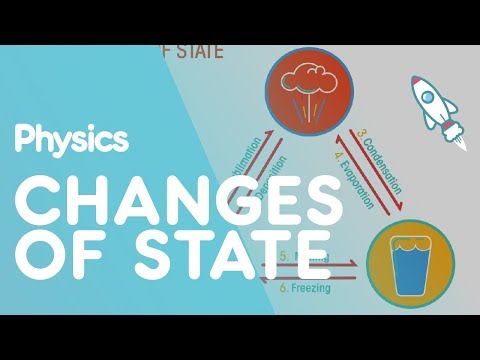
When temperature changes, matter can undergo a phase change, shifting from one form to another. Examples of phase changes are melting (changing from a solid to a liquid), freezing (changing from a liquid to a solid), evaporation (changing from a liquid to a gas), and condensation (changing from a gas to a liquid).
Q. What is the name of the phase change from solid to liquid?
melting
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the name of the phase change from solid to liquid?
- Q. What phase is ice cream?
- Q. What are phase changes called?
- Q. What happens during phase change?
- Q. Is energy required for each phase change?
- Q. What is the meaning of phase change?
- Q. What is the difference between a phase and a phase transition?
- Q. What is a transition phase in writing?
- Q. Is it possible that phase changes happens with changing temperature?
- Q. Why is there no change in temperature during a phase change?
- Q. How does the temperature and pressure affect changes in phase?
Q. What phase is ice cream?
Answer: Ice cream exists simultaneously as a solid (the ice crystals), a liquid (the milk and sugar solution), and a gas (the air bubbles), adding to its unique properties.
Q. What are phase changes called?
A phase change is a change in the states of matter. For example, a solid may become a liquid. This phase change is called melting. When a solid changes into a gas, it is called sublimation. When a gas changes into a liquid, it is called condensation.
Q. What happens during phase change?
A phase change is occuring; the liquid water is changing to gaseous water, or steam. When considering phase changes, the closer molecules are to one another, the stronger the intermolecular forces. Good! For any given substance, intermolecular forces will be greatest in the solid state and weakest in the gas state.
Q. Is energy required for each phase change?
All phase changes require a gain or a loss of heat energy. Changes in phase from solid to liquid (melting) and from liquid to gas (boiling) require energy. When solid ice melts and becomes a liquid, the particles of the substance move farther apart and heat energy is gained.
Q. What is the meaning of phase change?
A phase change is when matter changes to from one state (solid, liquid, gas, plasma) to another. (see figure 1). These changes occur when sufficient energy is supplied to the system (or a sufficient amount is lost), and also occur when the pressure on the system is changed.
Q. What is the difference between a phase and a phase transition?
a phase is a region with homogeneous (uniform) properties and a conversion between states is called a “phase transition” a phase is a chemically distinct state of matter and a phase transition is a chemical change.
Q. What is a transition phase in writing?
In writing, a transition is a word or phrase that connects one idea to another. This connection can occur within a paragraph or between paragraphs. Transitions are used to show how sen- tences or paragraphs are related to each other and how they relate to the overall theme of the paper.
Q. Is it possible that phase changes happens with changing temperature?
No temperature change occurs from heat transfer if ice melts and becomes liquid water (i.e., during a phase change). Similarly, energy is needed to vaporize a liquid, because molecules in a liquid interact with each other via attractive forces. There is no temperature change until a phase change is complete.
Q. Why is there no change in temperature during a phase change?
The term change of phase means the same thing as the term change of state. i.e. during phase change, the energy supplied is used only to separate the molecules ; no part of it is used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules. So its temperature will not rise, since kinetic energy of molecules remains the same.
Q. How does the temperature and pressure affect changes in phase?
When thermal energy is added to a substance, its temperature increases, which can change its state from solid to liquid (melting), liquid to gas (vaporization), or solid to gas (sublimation). When the pressure exerted on a substance increases, it can cause the substance to condense.