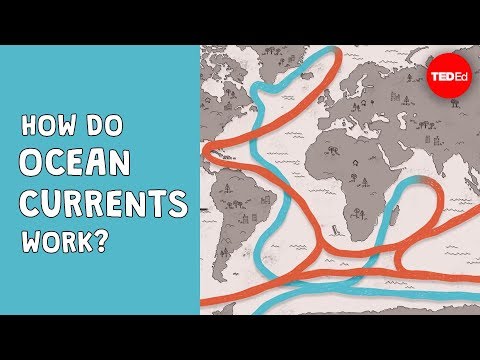
Q. How does ocean conveyor belt affect climate?
The ocean circulation conveyor belt helps balance climate. As part of the ocean conveyor belt, warm water from the tropical Atlantic moves poleward near the surface where it gives up some of its heat to the atmosphere. This process partially moderates the cold temperatures at higher latitudes.
Q. What would happen if the great ocean conveyor belt stopped?
If it continues to slow, that could have profound consequences for Earth’s inhabitants. Studies suggest it would mean much colder winters and hotter summers in Europe, changing rainfall patterns in the tropics, and warmer water building up along the U.S. coast that can fuel sea level rise and destructive storms.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does ocean conveyor belt affect climate?
- Q. What would happen if the great ocean conveyor belt stopped?
- Q. How does the ocean conveyor belt work?
- Q. How do ocean currents cause climate change?
- Q. What is the strongest current in the ocean?
- Q. What is the current in the ocean called?
- Q. What is the constant movement of ocean water?
- Q. What is the biggest gyre?
- Q. Where is the great Pacific garbage dump located?
- Q. Who is responsible for the Pacific garbage patch?
- Q. Why is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch a problem?
- Q. How many animals die in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch?
- Q. What countries dump their garbage in the ocean?
- Q. Does NYC still dump garbage in the ocean?
- Q. Why do we dump plastic in the ocean?
- Q. Which country pollutes the ocean the most?
- Q. What is the most polluted country in the world 2020?
- Q. Which country has the least plastic pollution?
- Q. Which country is plastic free?
Q. How does the ocean conveyor belt work?
A process known as thermohaline circulation, or the ocean conveyor belt, drives these deep, underwater currents. Thermohaline circulation moves a massive current of water around the globe, from northern oceans to southern oceans, and back again. Currents slowly turn over water in the entire ocean, from top to bottom.
Q. How do ocean currents cause climate change?
Ocean currents act as conveyer belts of warm and cold water, sending heat toward the polar regions and helping tropical areas cool off, thus influencing both weather and climate. When water molecules are heated, they exchange freely with the air in a process called evaporation.
Q. What is the strongest current in the ocean?
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
Q. What is the current in the ocean called?
Tides create a current in the oceans, which are strongest near the shore, and in bays and estuaries along the coast. These are called “tidal currents.” Tidal currents change in a very regular pattern and can be predicted for future dates.
Q. What is the constant movement of ocean water?
Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater driven by gravity, wind (Coriolis Effect), and water density. Ocean water moves in two directions: horizontally and vertically. Horizontal movements are referred to as currents, while vertical changes are called upwellings or downwellings.
Q. What is the biggest gyre?
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch
Q. Where is the great Pacific garbage dump located?
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch, also known as the Pacific trash vortex, spans waters from the West Coast of North America to Japan. The patch is actually comprised of the Western Garbage Patch, located near Japan, and the Eastern Garbage Patch, located between the U.S. states of Hawaii and California.
Q. Who is responsible for the Pacific garbage patch?
But specifically, scientists say, the bulk of the garbage patch trash comes from China and other Asian countries. This shouldn’t be a surprise: Overall, worldwide, most of the plastic trash in the ocean comes from Asia.
Q. Why is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch a problem?
Especially if most of the trash is contained in ‘garbage patch’ areas because of the way the debris naturally accumulates because of ocean currents. And that’s really the big problem — to prevent the debris from entering the ocean in the first place.
Q. How many animals die in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch?
100,000 marine animals die from getting entangled in plastic yearly – this is just the creatures we find! 1 in 3 marine mammal species get found entangled in litter, 12-14,000 tons of plastic are ingested by North Pacific fish yearly. Our marine pollution and debris are hazardous for creatures in the gyres.
Q. What countries dump their garbage in the ocean?
When the Environmental Protection Agency released its plan earlier this month for addressing marine litter, it named five Asian nations—China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam—as responsible for more than half of the plastic waste flowing into the oceans every year.
Q. Does NYC still dump garbage in the ocean?
New York City Mayor David N. Dinkins said the City is entering a new environmental era. “We will no longer dump sewage sludge–the byproduct of the sewage treatment process–in the ocean. Instead, we will put it to the use nature intended, land application for beneficial productivity.
Q. Why do we dump plastic in the ocean?
Rain or stormwater and wind can carry the plastic waste into the sea or into drains that lead to the sea. Illegal dumping of trash is a significant contributor.
Q. Which country pollutes the ocean the most?
The US is responsible for way more of the plastic polluting the world’s oceans than previously thought, a new study reveals. When it comes to the countries that contributed the most to coastal plastic pollution, the US could rank as high as third in the world, it estimates.
Q. What is the most polluted country in the world 2020?
Bangladesh
Q. Which country has the least plastic pollution?
Turkey generates about 5.6 billion tons of plastic waste per year. The average use of plastic bags in Turkey is 440 per person per year. As of January 1, 2019, the country banned single-use plastic bags and transitioned to reusable and paper bags in an effort to reduce plastic pollution.
Q. Which country is plastic free?
In 2018, during the 45th World Environment Day celebrations, India took the pledge to eliminate all single-use plastics – carry bags, straws, and water bottles among others from the country by 2022.